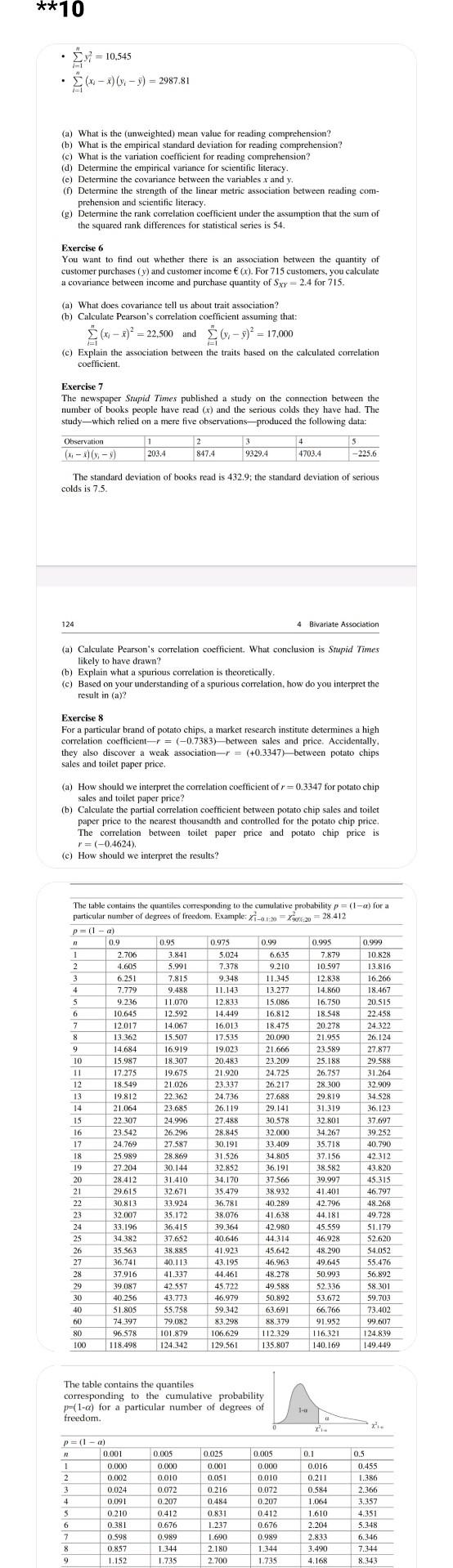
Question: Old MathJax webview .. **10 = 10,545 . (x1 - x)(-5) = 2987.81 x x (a) What is the (unweighted) mean value for reading comprehension?
Old MathJax webview
..
**10 = 10,545 . (x1 - x)(-5) = 2987.81 x x (a) What is the (unweighted) mean value for reading comprehension? (b) What is the empirical standard deviation for reading comprehension? (c) What is the variation coefficient for reading comprehension? (d) Determine the empirical variance for scientific literacy (c) Determine the covariance between the variables x and y () Determine the strength of the linear metric association between reading com- prehension and scientific literacy. (g) Determine the rank correlation coefficient under the assumption that the sum of the squared rank differences for statistical series is 54 Exercise 6 You want to find out whether there is an association between the quantity of customer purchases (y) and customer income (x). For 715 customers, you calculate a covariance between income and purchase quantity of Sxy=2.4 for 715. (a) What does covariance tell us about trait association? (b) Calculate Pearson's correlation coefficient assuming that: 6. ) * = 22,500 and 6-3) = 17,000 (c) Explain the association between the traits based on the calculated correlation coefficient. Exercise 7 The newspaper Stupid Times published a study on the connection between the number of books people have read (x) and the serious colds they have had. The studywhich relied on a mere five observations-produced the following data: Observation 1 2 13 5 (1.) 203.4 847.4 9329.4 4703.4 - 2256 4 The standard deviation of books read is 432.9; the standard deviation of serious colds is 7.5 124 4 Bivariate Association (a) Calculate Pearson's correlation coefficient. What conclusion is Stupid Times likely to have drawn? (b) Explain what a spurious correlation is theoretically (c) Based on your understanding of a spurious correlation, how do you interpret the result in (a)? Exercise 8 For a particular brand of potato chips, a market research institute determines a high correlation coefficient = (-0.7383) between sales and price. Accidentally, they also discover a weak association-r = (+0.3347)between potato chips sales and toilet paper price. (a) How should we interpret the correlation coefficient of r=0.3347 for potato chip sales and toilet paper price? (b) Calculate the partial correlation coefficient between potato chip sales and toilet paper price to the nearest thousandth and controlled for the potato chip price, The correlation between toilet paper price and potato chip price is r =(-0.4624). (c) How should we interpret the results? The table contains the quantiles corresponding to the cumulative probability p= (1-a) for a particular number of degrees of freedom. Example: xi-01:30 Xan 20 = 28.412 p= (1 - 0) n 0.9 0.95 0.975 0.99 0.995 0.999 1 2.706 3.841 5.024 6.635 7.879 10.828 2 4.605 5.991 7.378 9.210 10.597 13.816 3 6.251 7.815 9.348 11.345 12.838 16.266 4 7.779 9.488 11.143 13.277 14.860 18.467 5 9.236 11.070 12.833 15.086 16.750 20. SIS 6 10.645 12.592 14.449 16.812 18.548 22.458 7 12.017 14.067 16.013 18.475 20.278 24.322 8 13.362 15.507 17.535 20.090 21.955 26.124 9 14.684 16.919 19.023 21.666 23.589 27.877 10 15.987 18.307 20,483 23.209 25.188 29 588 11 17.275 19.675 21.920 24.725 26.757 31.264 12 18.549 21.026 23.337 26.217 28.300 32.909 13 19.812 22.362 24.736 27.688 29.819 34.528 14 21.064 23.68% 26.119 29.141 31.319 36.123 15 22.307 24.996 27.488 30.578 32.801 37.697 16 23.542 26.296 28.845 32.000 34.267 39.252 17 24.769 27.587 30.191 33.409 35.718 40.790 18 25.989 28.869 31.526 34.80 37.156 42313 19 27.204 30.144 32.852 36.191 38.582 43.820 20 28.412 31.410 34.170 37.566 39.997 45.315 21 29.615 32.671 35.479 38.932 41.401 46.797 22 30.813 33.924 36.781 40.289 42.796 48.268 23 32.007 35.172 38.076 41.638 44.181 49.728 24 33.196 36,419 39.364 42.980 45.559 51.179 25 34.382 37.652 40.616 44.314 46.928 52.620 26 35.563 38.885 41.923 45.642 48.290 54.052 27 36.741 40.113 43.195 46.963 49.645 55.476 28 37.916 41.337 44.461 48,278 50.993 56.892 29 39 087 42 557 45.722 49.588 52.336 58 301 30 40.256 43.773 46.979 50.892 53.672 59.703 40 51.805 55.758 59.342 63.691 66.766 73.402 60 74.397 79,082 83.298 88.379 91.952 99.607 80 96.578 101.879 106,629 112.329 116.321 124.839 100 118.498 124.342 129.561 135.807 140.169 149.449 The table contains the quantiles corresponding to the cumulative probability p=(1-a) for a particular number of degrees of freedom. 0 0.005 0.00 0.010 0.072 P=(1-0) n 0.001 1 0.000 2 0.002 3 0.024 4 0,091 5 0.210 6 0.381 7 0.598 8 0.857 9 1.152 0.207 0.412 0.676 0.989 1.344 1.735 0.025 0.001 0.051 0.216 0.484 0.831 1.237 1.690 2.180 2.700 0.005 0.000 0.010 0.072 0.207 0.412 0.676 0.989 1.344 1.735 0.1 0.016 0.211 0.584 1.064 1.610 2.204 2.833 3.490 4.168 0.5 0.455 1.386 2.366 3.357 4.351 5.348 6.346 7.344 8.343Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


