Question: On a winter day, a psychrometer has a dry-bulb reading of 35F and a wet-bulb reading of 31F. (Use the data in this table

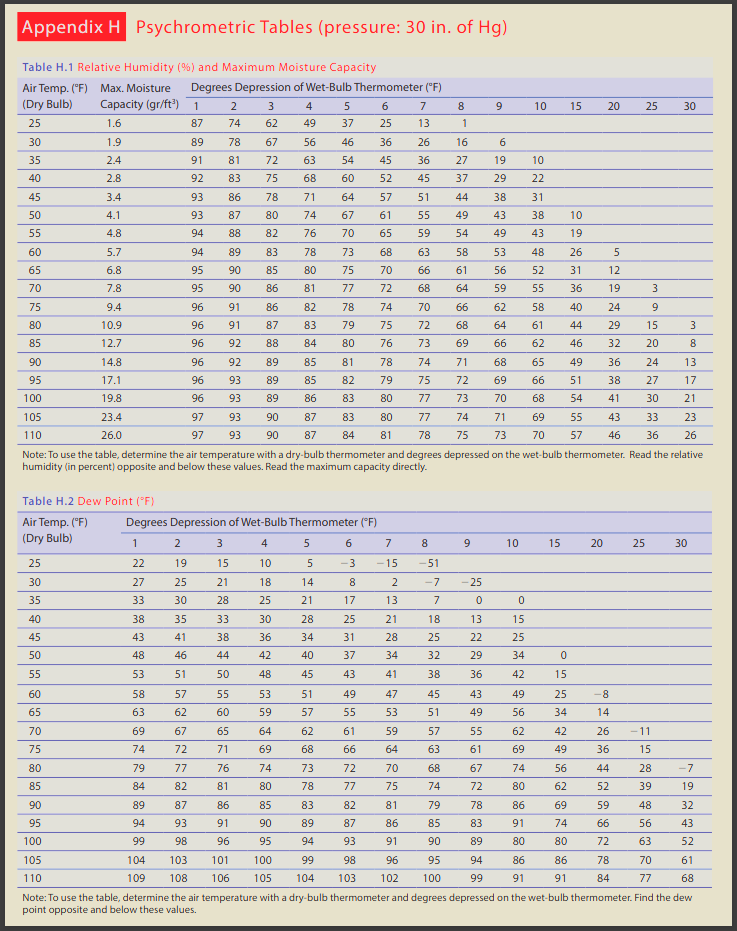
On a winter day, a psychrometer has a dry-bulb reading of 35F and a wet-bulb reading of 31F. (Use the data in this table as necessary.) (a) What is the actual moisture content of the air? (Enter your answer in gr/ft.) gr/ft (b) Would the water in the wick of the wet bulb freeze? Explain. Yes, coolness is due to water evaporating (latent heat removed from the bulb). Air temperature is below freezing, and water is replaced from the reservoir. No, coolness is due to water evaporating (latent heat removed from the bulb). Air temperature is above freezing, and water is replaced from the reservoir. Appendix H Psychrometric Tables (pressure: 30 in. of Hg) Table H.1 Relative Humidity (%) and Maximum Moisture Capacity Capacity (gr/ft) 1 Air Temp. (F) Max. Moisture Degrees Depression of Wet-Bulb Thermometer (F) (Dry Bulb) 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 15 20 25 30 25 1.6 87 74 62 49 37 25 13 1 30 1.9 89 78 35 2.4 91 81 62 67 56 46 36 26 16 72 63 54 45 36 27 19 69 10 40 2.8 92 83 75 68 60 52 45 37 29 22 45 3.4 93 86 78 71 64 57 51 44 38 31 50 4.1 93 87 80 74 67 61 55 49 43 38 10 55 4.8 94 88 82 76 70 65 59 54 49 43 19 60 5.7 94 89 83 78 73 68 63 58 53 48 26 5 65 6.8 95 90 85 80 75 70 66 61 56 52 31 12 70 7.8 95 90 86 81 77 72 68 64 59 55 36 19 3 75 9.4 96 91 86 82 78 74 70 66 62 58 40 24 9 80 10.9 96 91 87 83 79 75 72 68 64 61 44 29 15 3 85 12.7 96 92 88 84 80 76 73 69 66 62 46 32 20 8 90 14.8 96 92 89 85 81 78 74 71 68 65 49 36 24 13 95 17.1 96 93 89 85 82 79 75 72 69 66 51 38 27 17 100 19.8 96 93 89 86 83 80 77 73 70 68 54 41 30 21 105 23.4 97 93 90 87 83 80 77 74 71 69 55 43 33 23 110 97 93 90 87 84 81 78 75 73 70 57 46 36 26 26.0 Note: To use the table, determine the air temperature with a dry-bulb thermometer and degrees depressed on the wet-bulb thermometer. Read the relative humidity (in percent) opposite and below these values. Read the maximum capacity directly. Table H.2 Dew Point (F) Air Temp. (F) Degrees Depression of Wet-Bulb Thermometer (F) (Dry Bulb) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 6 10 15 20 25 30 25 22 19 15 10 5 -3 -15 -51 30 27 25 21 18 14 8 2 -7 -25 35 33 30 28 25 21 17 13 7 0 0 40 38 35 33 30 28 25 21 18 13 15 45 43 41 38 36 34 31 28 25 50 48 46 44 42 40 37 34 32 52 22 25 29 34 0 55 53 51 50 48 45 43 41 38 36 42 15 60 58 57 55 53 51 49 47 45 43 49 25 -8 65 63 62 60 59 57 55 53 51 49 56 34 14 70 69 75 74 80 79 627 65 64 62 61 59 57 55 62 42 26 -11 71 69 68 66 64 63 61 69 49 36 15 77 76 74 73 72 70 68 67 74 56 44 28 -7 85 84 82 81 80 78 77 75 74 72 80 62 52 39 19 90 89 87 86 85 83 82 81 79 78 86 69 59 48 32 95 94 93 91 90 89 87 86 85 83 91 74 66 56 43 100 99 98 96 95 94 93 91 90 89 80 80 72 63 52 105 104 103 101 100 99 98 96 95 94 86 86 78 70 61 110 109 108 106 105 104 103 102 100 99 91 91 84 77 68 Note: To use the table, determine the air temperature with a dry-bulb thermometer and degrees depressed on the wet-bulb thermometer. Find the dew point opposite and below these values.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


