Question: one question it got two parts though please do them both. The equilibrium constant, K, is calculated using molar concentrations. For gaseous reactions another form
one question it got two parts though please do them both.
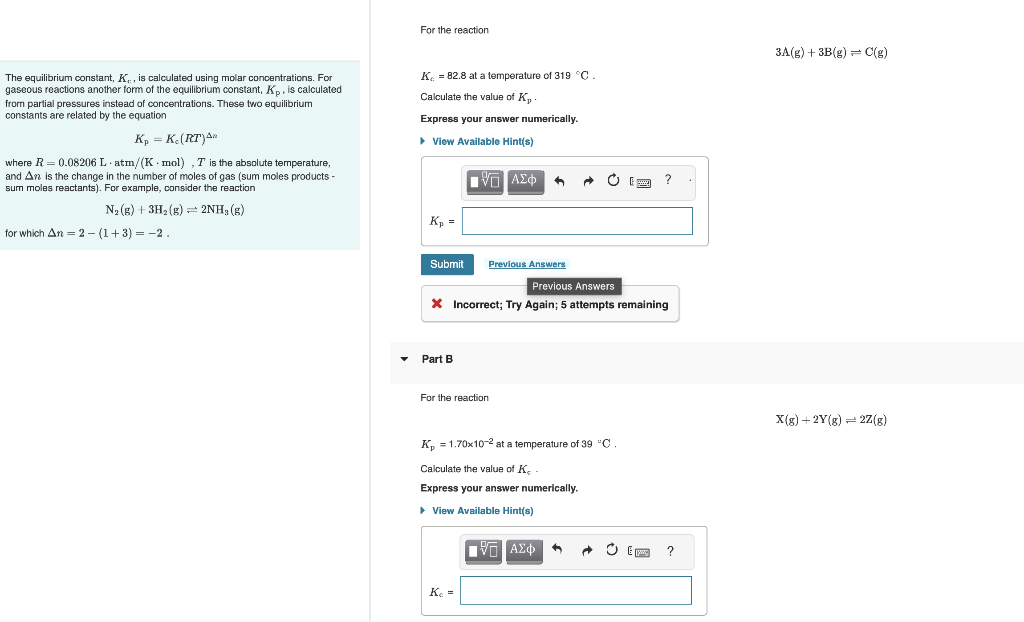
The equilibrium constant, K, is calculated using molar concentrations. For gaseous reactions another form of the equilibrium constant, Kp, is calculated K6=82.8 at a temperature of 319C. from partial pressures instead of concentrations. These two equilibrium Calculate the value of Kp. constants are related by the equation Express your answer numerically. Kp=Kc(RT)x where R=0.08206Latm/(Kmol),T is the absolute temperature, and n is the change in the number of moles of gas (sum moles products sum moles reactants). For example, consider the reaction N2(g)+3H2(g)2NH3(g) for which n=2(1+3)=2. Part B For the reaction X(g)+2Y(g)2Z(g) Kp=1.70102 at a temperature of 39C. Calculate the value of K. Express your answer numerically
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


