Question: only a and b pt 2 for reference newsvendor model 3. The warehouse store in Problem #2 has a lot of market power. It has


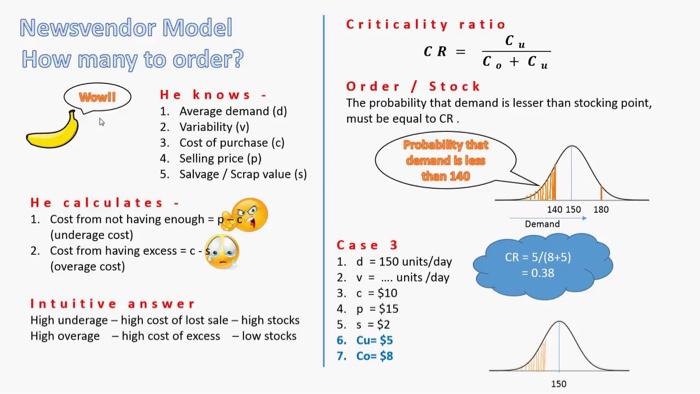
3. The warehouse store in Problem #2 has a lot of market power. It has convinced its supplier to build a warehouse nearby and to provide vendor-managed-inventory (VMI) services - including delivery-- for free, with inventory being delivered on consignment. Under a vendor-managed inventory system, the warehouse store no longer sends orders to the supplier. Instead the supplier is responsible for managing the inventory according to some rules that are mutually agreed upon by the buyer and supplier. Under a consignment system, the buyer does not pay the supplier for the goods until the buyer has sold the product. Thus, the supplier owns the inventory and incurs the financial cost of holding it until it is sold. It costs approximately $50 for the supplier to make a delivery, and $6.00 for the supplier to manufacture a package of paper towels. The supplier uses an annual inventory holding cost rate of 80%. The supplier plans to (electronically) check the inventory status at the warehouse store at the end of each day, and expects to be able to make a delivery by the end of the following day. The warehouse store has asked for a 98% probability of no stockout during the order cycle, but the supplier also recognizes that each shortage will result in a lost sale, and it will therefore lose its profit if a shortage occurs. For simplicity, you may assume that a year has 50 weeks, and each week has 7 working days. (That is, deliveries can be made on any day of the week.) (a) How often should the supplier send a truck to the warehouse store? (b) Use the Newsvendor model to estimate the economically optimal probability of no stockout during the order cycle. 2. A well-known warehouse store has a contract with a manufacturer for its store-brand" 12- roll package of paper towels. The warehouse store pays $8 per package and seyls a package for $10. Daily demand at a typical store in a quiet suburban area averages about 360 packages and has a standard deviation of 60. The store is open 350 days per year. The manufacturer is in another state and charges $750 per truck for each delivery. Each truck can hold up to 5000 packages and takes 2 days from the time an order is placed until the goods are available on the shelf of the warehouse store. According to the terms of the contract with the manufacturer, the order quantity is restricted to be a multiple of 100. The store uses an annual holding cost rate of 80% for paper and plastic goods. Newsvendor Model How many to order? C Wowll He knows 1. Average demand (d) 2. Variability (v) 3. Cost of purchase (c) 4. Selling price (p) 5. Salvage / Scrap value (s) He calculates 1. Cost from not having enough =p (underage cost) 2. Cost from having excess = c-s. (overage cost) Criticality ratio CR = C. + C Order / Stock The probability that demand is lesser than stocking point, must be equal to CR Probability that demand Islans than 140 180 140 150 Demand CR = 5/(8+5) = 0.38 Intuitive answer High underage - high cost of lost sale - high stocks High overage - high cost of excess - low stocks Case 3 1. d = 150 units/day 2. V = .... units /day 3. c = $10 4. p = $15 5. s = $2 6. Cu= $5 7. Co= $8 150
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


