Question: Option pricing using Black-Scholes The EUR/NOK exchange rate is 11, the one-year EUR interest rate is 0.0%, and the one-year NOK interest rate is 1.0%.
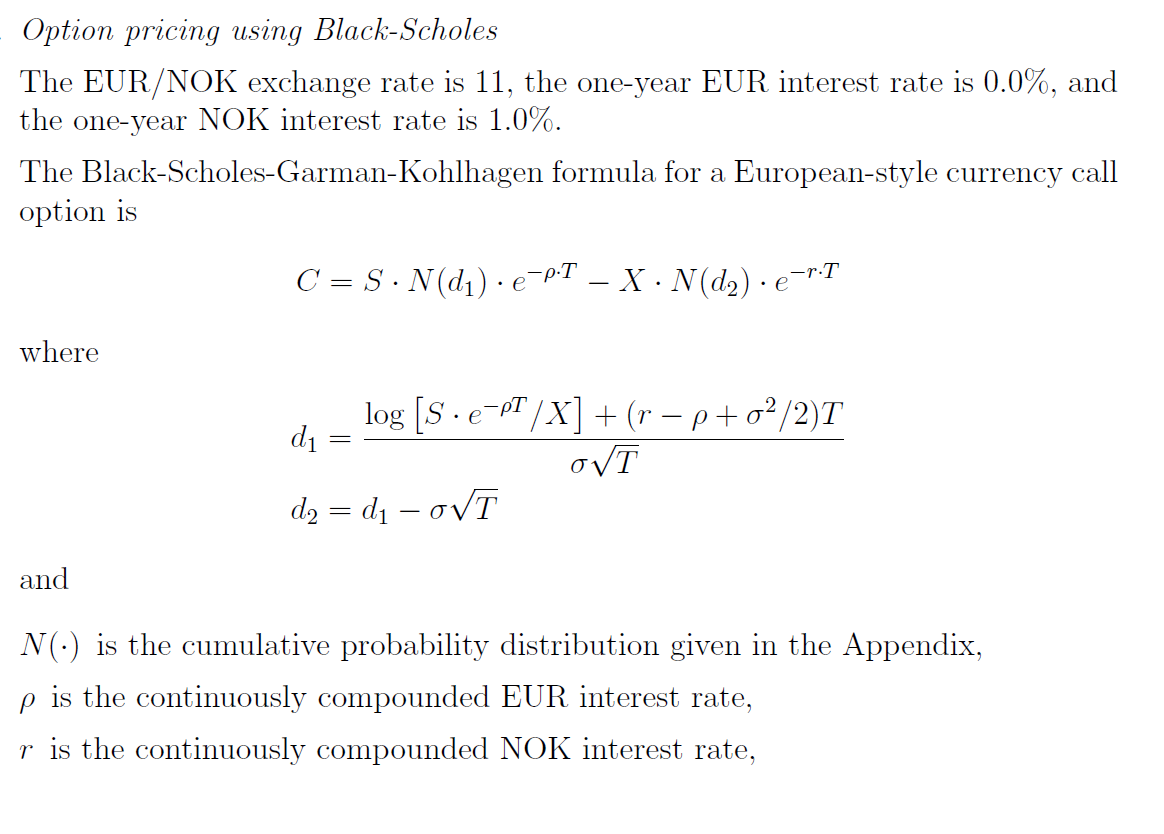


Option pricing using Black-Scholes The EUR/NOK exchange rate is 11, the one-year EUR interest rate is 0.0%, and the one-year NOK interest rate is 1.0%. The Black-Scholes-Garman-Kohlhagen formula for a European-style currency call option is C = S. N(d). e-PT X N(d2) e-r:T where log (s.e-T/X] + (r-p+o2/2)T d1 d2 = d - OVT and NO) is the cumulative probability distribution given in the Appendix, p is the continuously compounded EUR interest rate, r is the continuously compounded NOK interest rate, T is time to maturity of the option, S is the current spot exchange rate in terms of NOK / EUR, X is the strike price, o is the volatility. (a) You consider hedging a EUR 1M payment that was due one year from now. Please draw a diagram where you show (i) the unhedged position, (ii) a forward / synthetic forward hedge, and (iii) an options hedge. Please be careful such that the figure is qualitatively correct. (b) Step by step, show that for a one-year at-the-money call option where p = 0, the formulas for d and d2 can be written r 0 0 d1 + and d2 0 (c) Attached please find a spreadsheet and an Rdata file (question3b.xlsx and question3b.Rdata, respectively), containing quarterly NOK/EUR ex- change rates from first quarter 1999 to first quarter 2020.1 Depending on your choice of software, use one of them to compute the annualized standard deviation of exchange-rate changes. Remember: in general, if there are T data points per year then the conversion formula is annualized = Omeasured : VT (d) Compute the price of an at-the-money call option using your estimated stan- dard deviation based on quarterly data. (e) During the last two months we have experienced particularly large move- ments in exchange rates. Attached please find a spreadsheet and an Rdata file (question3d.xlsx and question3d. Rdata, respectively), containing daily NOK/EUR exchange rates from the beginning of March to the end of April this year. Depending on your choice of software, use one of them to com- pute the annualized standard deviation of exchange-rate changes. You can assume that there are 260 trading days in one year. (f) Assuming that the options traders now use an implied volatility close to the annualized daily volatility the last two months, compute the price of an at-the-money call option using your estimated standard deviation based on recent daily data. What implications do the changes in volatility have for the cost of hedging? Please provide brief intuition. Option pricing using Black-Scholes The EUR/NOK exchange rate is 11, the one-year EUR interest rate is 0.0%, and the one-year NOK interest rate is 1.0%. The Black-Scholes-Garman-Kohlhagen formula for a European-style currency call option is C = S. N(d). e-PT X N(d2) e-r:T where log (s.e-T/X] + (r-p+o2/2)T d1 d2 = d - OVT and NO) is the cumulative probability distribution given in the Appendix, p is the continuously compounded EUR interest rate, r is the continuously compounded NOK interest rate, T is time to maturity of the option, S is the current spot exchange rate in terms of NOK / EUR, X is the strike price, o is the volatility. (a) You consider hedging a EUR 1M payment that was due one year from now. Please draw a diagram where you show (i) the unhedged position, (ii) a forward / synthetic forward hedge, and (iii) an options hedge. Please be careful such that the figure is qualitatively correct. (b) Step by step, show that for a one-year at-the-money call option where p = 0, the formulas for d and d2 can be written r 0 0 d1 + and d2 0 (c) Attached please find a spreadsheet and an Rdata file (question3b.xlsx and question3b.Rdata, respectively), containing quarterly NOK/EUR ex- change rates from first quarter 1999 to first quarter 2020.1 Depending on your choice of software, use one of them to compute the annualized standard deviation of exchange-rate changes. Remember: in general, if there are T data points per year then the conversion formula is annualized = Omeasured : VT (d) Compute the price of an at-the-money call option using your estimated stan- dard deviation based on quarterly data. (e) During the last two months we have experienced particularly large move- ments in exchange rates. Attached please find a spreadsheet and an Rdata file (question3d.xlsx and question3d. Rdata, respectively), containing daily NOK/EUR exchange rates from the beginning of March to the end of April this year. Depending on your choice of software, use one of them to com- pute the annualized standard deviation of exchange-rate changes. You can assume that there are 260 trading days in one year. (f) Assuming that the options traders now use an implied volatility close to the annualized daily volatility the last two months, compute the price of an at-the-money call option using your estimated standard deviation based on recent daily data. What implications do the changes in volatility have for the cost of hedging? Please provide brief intuition
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


