Question: Options for Question 4 are increase , decrease , or remain the same . Question 1 12.0 points possible (graded, results hidden) Juan Howard is
 Options for Question 4 are increase, decrease, or remain the same.
Options for Question 4 are increase, decrease, or remain the same.
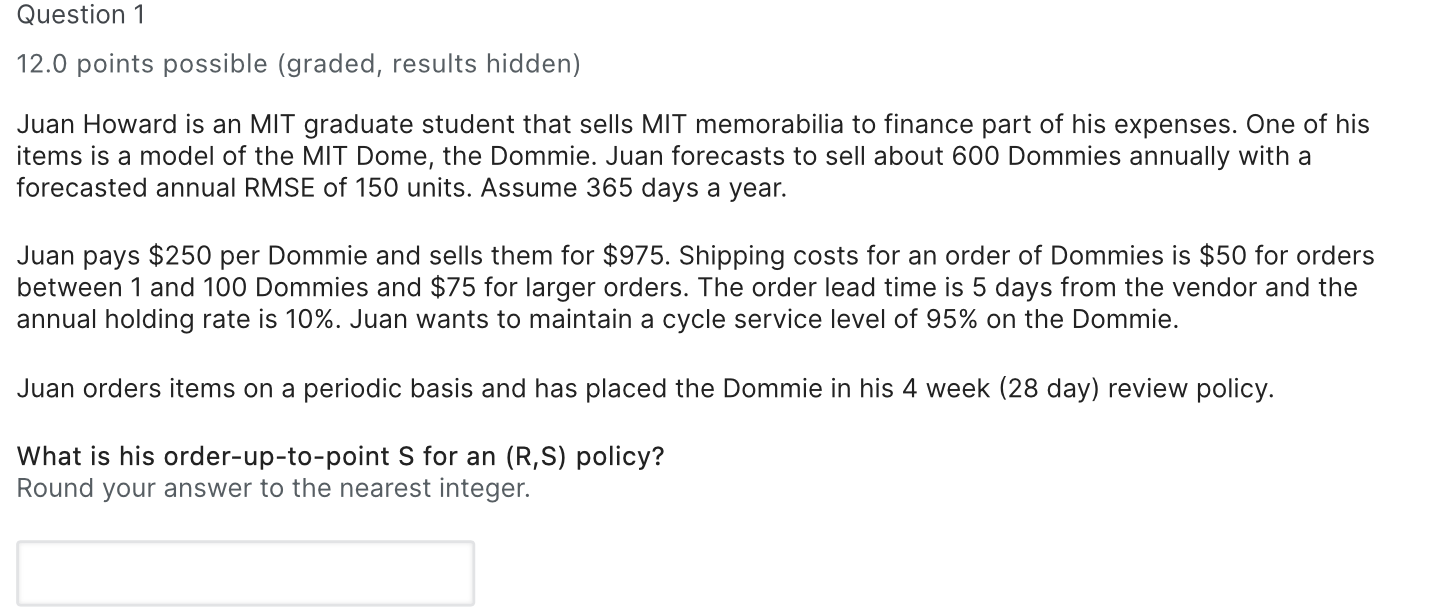
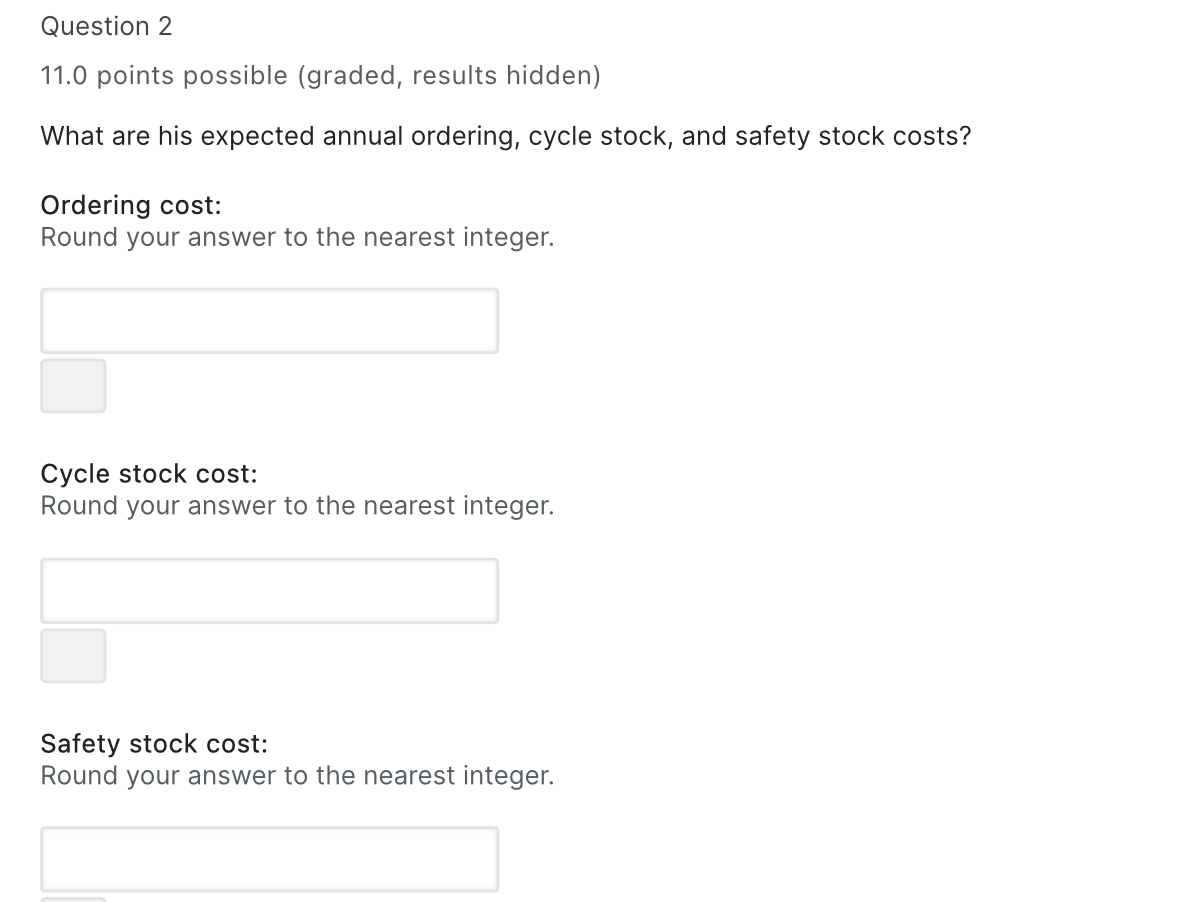
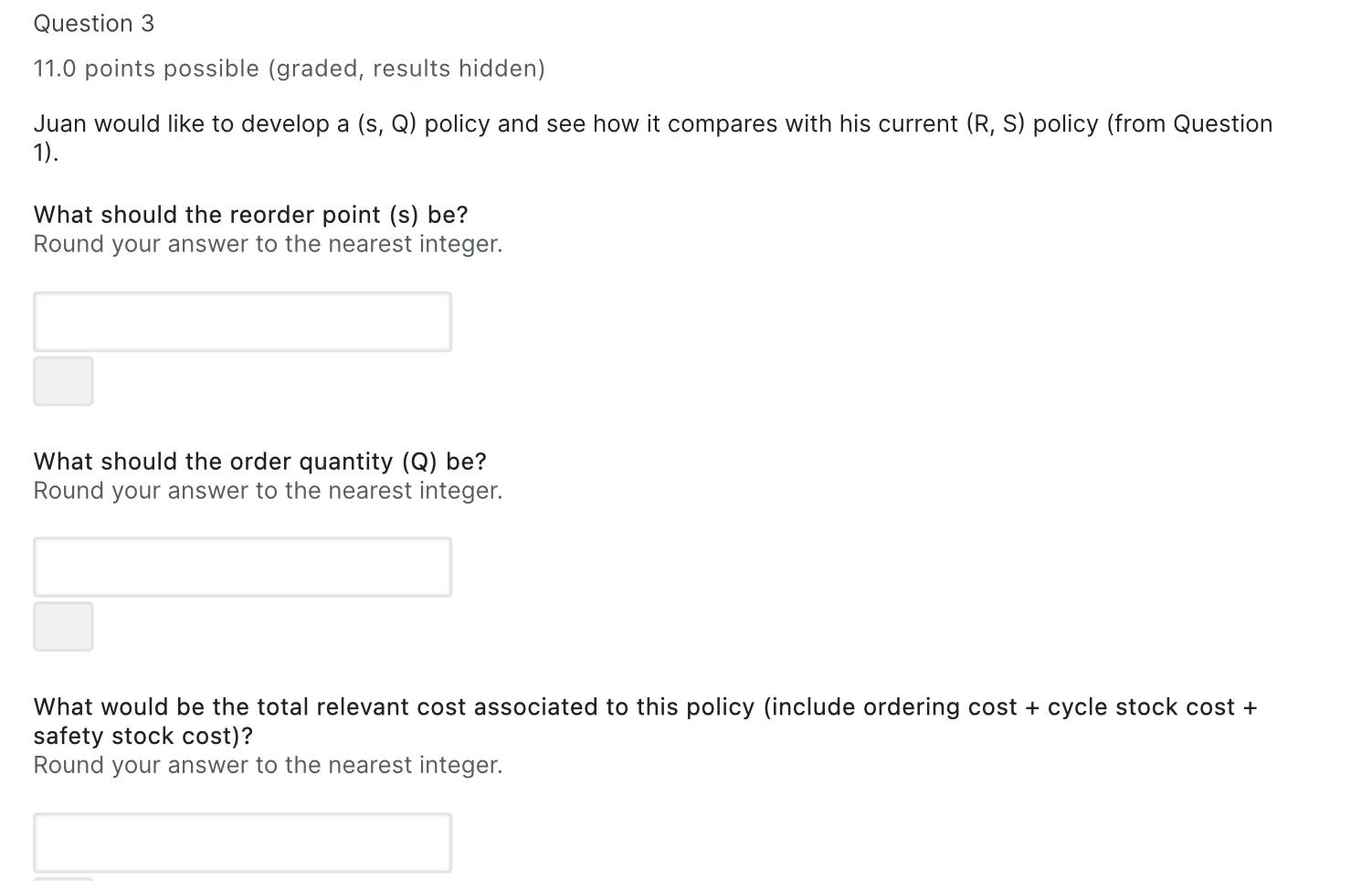
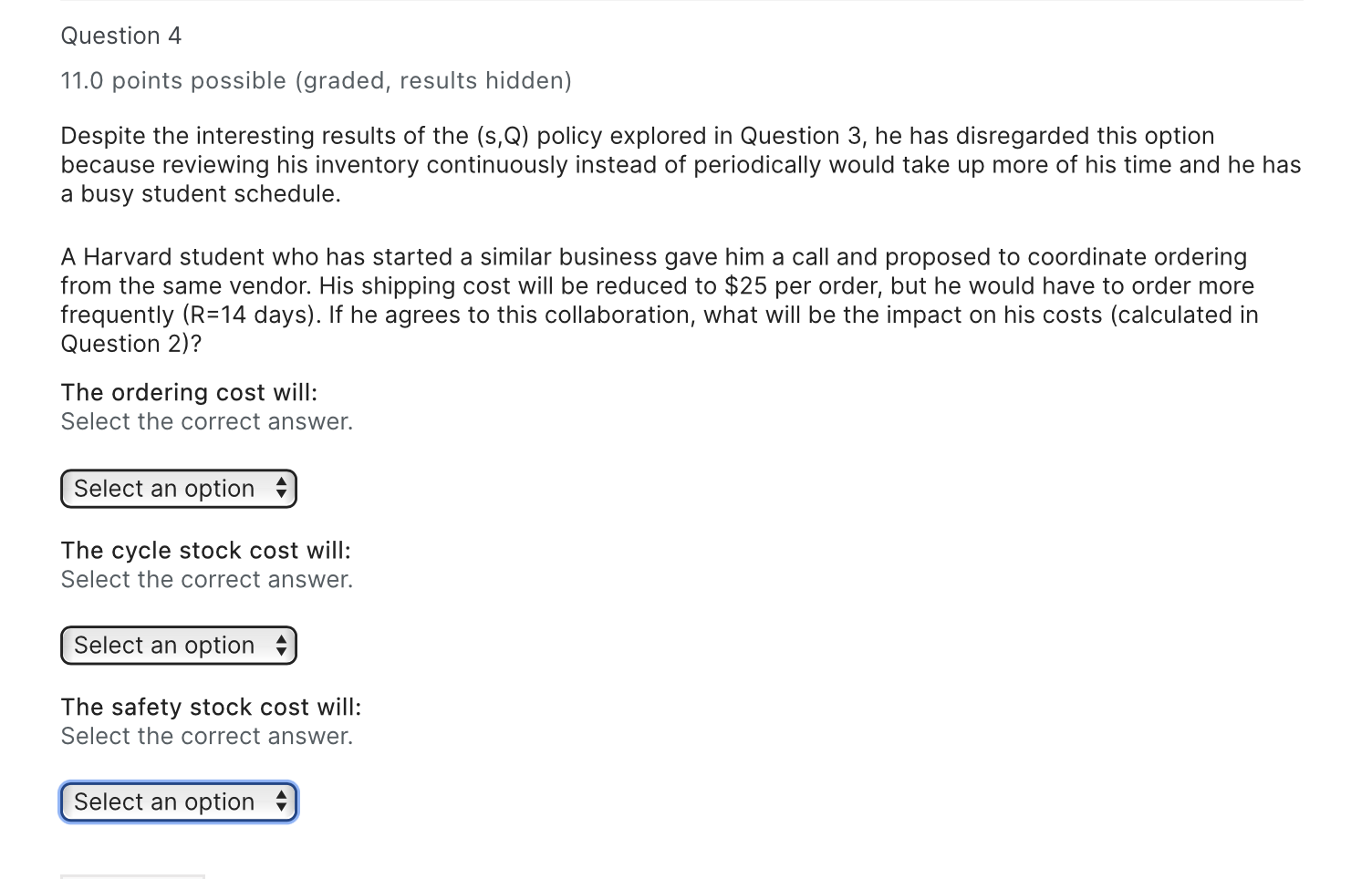
Question 1 12.0 points possible (graded, results hidden) Juan Howard is an MIT graduate student that sells MIT memorabilia to finance part of his expenses. One of his items is a model of the MIT Dome, the Dommie. Juan forecasts to sell about 600 Dommies annually with a forecasted annual RMSE of 150 units. Assume 365 days a year. Juan pays $250 per Dommie and sells them for $975. Shipping costs for an order of Dommies is $50 for orders between 1 and 100 Dommies and $75 for larger orders. The order lead time is 5 days from the vendor and the annual holding rate is 10%. Juan wants to maintain a cycle service level of 95% on the Dommie. Juan orders items on a periodic basis and has placed the Dommie in his 4 week (28 day) review policy. What is his order-up-to-point S for an (R,S) policy? Round your answer to the nearest integer. Question 2 11.0 points possible (graded, results hidden) What are his expected annual ordering, cycle stock, and safety stock costs? Ordering cost: Round your answer to the nearest integer. Cycle stock cost: Round your answer to the nearest integer. Safety stock cost: Round your answer to the nearest integer. Question 3 11.0 points possible (graded, results hidden) Juan would like to develop a (s, Q) policy and see how it compares with his current (R, S) policy (from Question 1). What should the reorder point (s) be? Round your answer to the nearest integer. What should the order quantity (Q) be? Round your answer to the nearest integer. What would be the total relevant cost associated to this policy (include ordering cost + cycle stock cost + safety stock cost)? Round your answer to the nearest integer. Question 4 11.0 points possible (graded, results hidden) Despite the interesting results of the (s,Q) policy explored in Question 3, he has disregarded this option because reviewing his inventory continuously instead of periodically would take up more of his time and he has a busy student schedule. A Harvard student who has started a similar business gave him a call and proposed to coordinate ordering from the same vendor. His shipping cost will be reduced to $25 per order, but he would have to order more frequently (R=14 days). If he agrees to this collaboration, what will be the impact on his costs (calculated in Question 2)? The ordering cost will: Select the correct answer. Select an option The cycle stock cost will: Select the correct answer. Select an option The safety stock cost will: Select the correct answer. Select an option Question 1 12.0 points possible (graded, results hidden) Juan Howard is an MIT graduate student that sells MIT memorabilia to finance part of his expenses. One of his items is a model of the MIT Dome, the Dommie. Juan forecasts to sell about 600 Dommies annually with a forecasted annual RMSE of 150 units. Assume 365 days a year. Juan pays $250 per Dommie and sells them for $975. Shipping costs for an order of Dommies is $50 for orders between 1 and 100 Dommies and $75 for larger orders. The order lead time is 5 days from the vendor and the annual holding rate is 10%. Juan wants to maintain a cycle service level of 95% on the Dommie. Juan orders items on a periodic basis and has placed the Dommie in his 4 week (28 day) review policy. What is his order-up-to-point S for an (R,S) policy? Round your answer to the nearest integer. Question 2 11.0 points possible (graded, results hidden) What are his expected annual ordering, cycle stock, and safety stock costs? Ordering cost: Round your answer to the nearest integer. Cycle stock cost: Round your answer to the nearest integer. Safety stock cost: Round your answer to the nearest integer. Question 3 11.0 points possible (graded, results hidden) Juan would like to develop a (s, Q) policy and see how it compares with his current (R, S) policy (from Question 1). What should the reorder point (s) be? Round your answer to the nearest integer. What should the order quantity (Q) be? Round your answer to the nearest integer. What would be the total relevant cost associated to this policy (include ordering cost + cycle stock cost + safety stock cost)? Round your answer to the nearest integer. Question 4 11.0 points possible (graded, results hidden) Despite the interesting results of the (s,Q) policy explored in Question 3, he has disregarded this option because reviewing his inventory continuously instead of periodically would take up more of his time and he has a busy student schedule. A Harvard student who has started a similar business gave him a call and proposed to coordinate ordering from the same vendor. His shipping cost will be reduced to $25 per order, but he would have to order more frequently (R=14 days). If he agrees to this collaboration, what will be the impact on his costs (calculated in Question 2)? The ordering cost will: Select the correct answer. Select an option The cycle stock cost will: Select the correct answer. Select an option The safety stock cost will: Select the correct answer. Select an option



 Options for Question 4 are increase, decrease, or remain the same.
Options for Question 4 are increase, decrease, or remain the same. 



