Question: Our task is to implement a solution using the solve() method in the code below for the temporal difference agent. Assume that the discount factor
Our task is to implement a solution using the solve() method in the code below for the temporal difference agent.
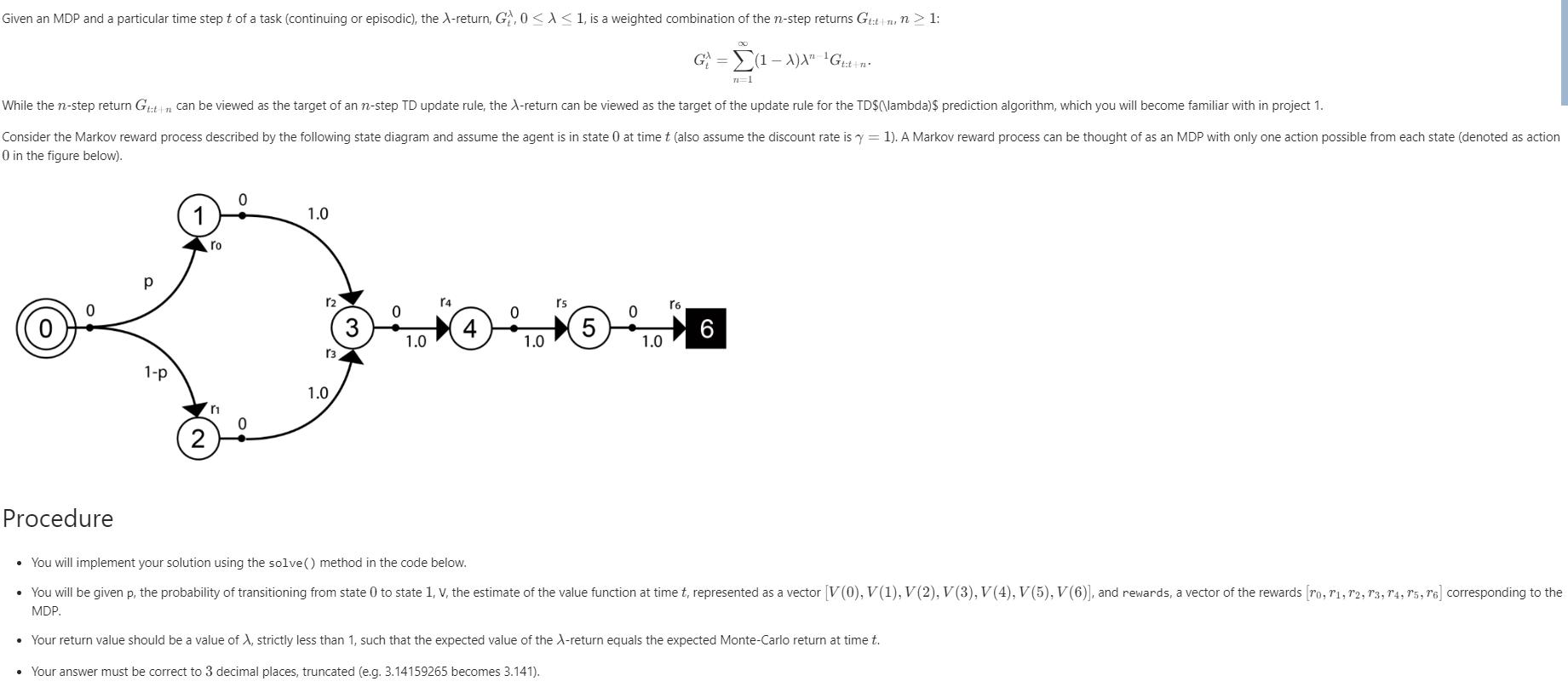
Assume that the discount factor is 1.
For the parameters of the function solve() we are given p , the probability of transitioning from state 0 to state 1. Another parameter in the function solve() is V which is the estimate of the value function at time , represented as a vector [V0, V1, V2, V3, V4, V5, V6]. The last parameter in the function solve() is rewards which is a vector of the rewards [r0, r1, r2, r3, r4, r5, r6] corresponding to the MDP.
The return value should be a value of lambda less than 1.
The value of the lambda-return equals the expected Monte-Carlo return at time t.
The answer must be rounded to 3 decimal places.
Here is the template code we were given. Note that we are not allowed to use other libraries.
import numpy as np
class TDAgent(object):
def __init__(self):
pass
def solve(self, p, V, rewards):
"""Implement the agent"""
pass
return True
We were also given a set of unit tests to verify our solution.
import unittest
class TestTDNotebook(unittest.TestCase):
def test_case_1(self):
agent = TDAgent()
np.testing.assert_almost_equal(
agent.solve(
p=0.81,
V=[0.0, 4.0, 25.7, 0.0, 20.1, 12.2, 0.0],
rewards=[7.9, -5.1, 2.5, -7.2, 9.0, 0.0, 1.6]
),
0.622,
decimal=3
)
def test_case_2(self):
agent = TDAgent()
np.testing.assert_almost_equal(
agent.solve(
p=0.22,
V=[12.3, -5.2, 0.0, 25.4, 10.6, 9.2, 0.0],
rewards=[-2.4, 0.8, 4.0, 2.5, 8.6, -6.4, 6.1]
),
0.519,
decimal=3
)
def test_case_3(self):
agent = TDAgent()
np.testing.assert_almost_equal(
agent.solve(
p=0.64,
V=[-6.5, 4.9, 7.8, -2.3, 25.5, -10.2, 0.0],
rewards=[-2.4, 9.6, -7.8, 0.1, 3.4, -2.1, 7.9]
),
0.207,
decimal=3
)
unittest.main(argv=[''], verbosity=2, exit=False)
Here is my approach so far.
import numpy as np
class TDAgent(object):
def __init__(self):
pass
def solve(self, p, V, rewards):
"""
Implement the agent to calculate the value of lambda
"""
# Initialize variables
lambda_values = np.arange(0, 1.01, 0.01) # possible values for lambda
min_difference = float('inf')
best_lambda = 0
# Calculate the Monte-Carlo return for the start state
monte_carlo_return = p * (rewards[0] + rewards[2] + rewards[4] + rewards[5] + rewards[6]) +
(1-p) * (rewards[1] + rewards[3] + rewards[4] + rewards[5] + rewards[6])
# Loop through all possible lambda values to find the one that minimizes the difference with Monte-Carlo return
for lambda_val in lambda_values:
G_lambda = 0 # Initialize Gt(λ)
# Calculate Gt(λ) using the formula, assuming discount factor is 1
for t in range(6):
Gt = np.sum(rewards[t:])
G_lambda += (1 - lambda_val) * (lambda_val ** t) * Gt
# Calculate the difference between Gt(λ) and Monte-Carlo return
difference = abs(G_lambda - monte_carlo_return)
# Update min_difference and best_lambda
if difference min_difference = difference
best_lambda = lambda_val
return round(best_lambda, 3)
The issue is that my approach fails all of the unit tests. I don't understand what I am doing wrong and how to resolve it.
Here is what I understand so far. You may correct me if I am wrong:
Essentially we just need to account for the stochasticity of transitioning from state 0 to state 1/state 2. The rest of the transitions between the states are deterministic. Therefore we just calcule the monte-carlo return and then iterate through the possible lambda vales to converge to a lamda value with the least difference.
Given an MDP and a particular time step t of a task (continuing or episodic), the X-return, G, 0 1, is a weighted combination of the n-step returns Gt:n, n > 1: G = (1-X)X" Gt+n+ While the n-step return Gut can be viewed as the target of an n-step TD update rule, the X-return can be viewed as the target of the update rule for the TD$(\lambda)$ prediction algorithm, which you will become familiar with in project 1. Consider the Markov reward process described by the following state diagram and assume the agent is in state 0 at time t (also assume the discount rate is y=1). A Markov reward process can be thought of as an MDP with only one action possible from each state (denoted as action 0 in the figure below). Procedure 1-p ro 0 1.0 12 13 1.0 3 0 1.0 4 0 1.0 r5 5 0 1.0 n=1 16 You will implement your solution using the solve() method in the code below. You will be given p, the probability of transitioning from state 0 to state 1, V, the estimate of the value function at time t, represented as a vector [V (0), V(1), V(2), V(3), V(4), V(5), V(6)], and rewards, a vector of the rewards [ro, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16] corresponding to the MDP. Your return value should be a value of X, strictly less than 1, such that the expected value of the X-return equals the expected Monte-Carlo return at time t. Your answer must be correct to 3 decimal places, truncated (e.g. 3.14159265 becomes 3.141).
Step by Step Solution
3.32 Rating (152 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The main mistake that you made in your original code is that you were calculating the MonteCarlo return incorrectly You were assuming that the agent always transitions to state 1 from state 0 which is ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


