Question: Overview of This Assignment 4 Files: 2 C source files 1 header file . 1 makefile You must upload the files to a CS Linux
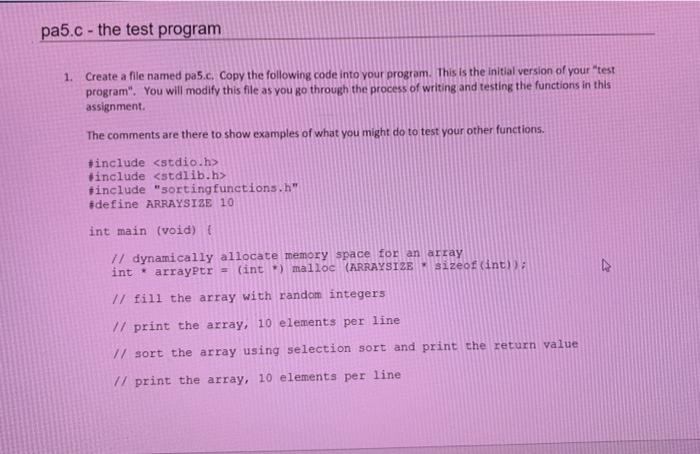
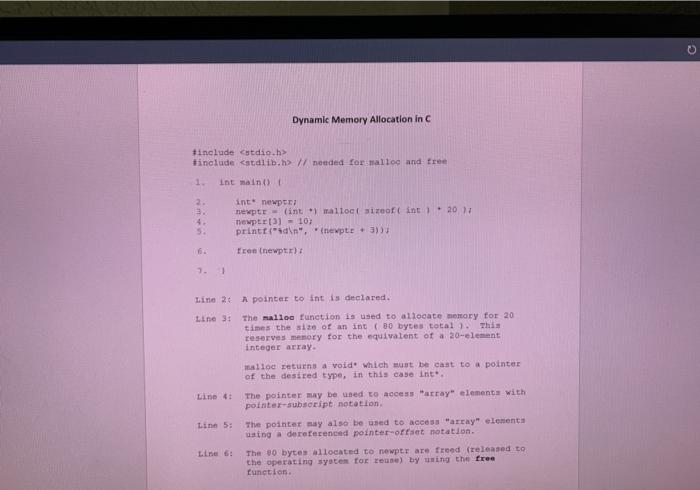
Overview of This Assignment 4 Files: 2 C source files 1 header file . 1 makefile You must upload the files to a CS Linux host, make, then run the executable on Linux. Once you have finished and tested the programs, you will upload them to the PA 5 assignment in Canvas. C Programming Skills That You Are Practicing in This Assignment 1. Become proficient at writing and using makefiles. 2. Become proficient in working with pointers in C. 3. Master the process of swapping. 4. Develop an understanding of the selection sort and insertion sort algorithms. makefile - do this first! . . Include an "all" target that builds an executable named pa5 (no extension). Write separate targets for pas, pas.o, and sortingfunctions.o. Include a "clean" target that removes all object files (all files ending with .o). . pa5.c - the test program 1. Create a file named pa5.c. Copy the following code into your program. This is the initial version of your "test program". You will modify this file as you go through the process of writing and testing the functions in this assignment. The comments are there to show examples of what you might do to test your other functions. #include #include #include sorting functions.h" #define ARRAYSIZE 10 int main (void) { // dynamically allocate memory space for an array int . arrayPtr = (int *) malloc (ARRAYSIZE sizeof(int)); // fill the array with random integers 1/ print the array, 10 elements per line // sort the array using selection sort and print the return value pa5.c - the test program 1. Create a file named pa5.c. Copy the following code into your program. This is the initial version of your "test program". You will modify this file as you go through the process of writing and testing the functions in this assignment. The comments are there to show examples of what you might do to test your other functions. include finclude finclude "sorting functions.h" #define ARRAYSIZE 10 int main (void) { 1/ dynamically allocate memory space for an array int arrayPtr = (int) malloc (ARRAYSIZE sizeof(int)); // fill the array with random integers // print the array, 10 elements per line // sort the array using selection sort and print the return value // print the array, 10 elements per line // fill the array again with random integers 17 print the array 1/ sort with insertion sort and print the return value // print the array 2. Create a file called sortingfunctions.h Write a preprocessor wrapper (following convention for constant name) and then insert the following prototypes. int selectionsort (int * const array, int size); int insertionSort (int . const array, int size); void swap (int numi, int . num2 ): void fillArray( int const data, int size, int min, int max); void neat Print (int . const data, int size, int numPerline, int fieldsize ); . 3. Create a file called sortingfunctions.c Write the implementation of the five functions. int selectionsort (int * const data, int size ); sorts the array using the selection sort algorithm Caution: there ar are a lot of programs out there on the web that claim to be selection sort written in c. The class syllabus prohibits copying code from web sites. A grade of zero will be assigned for this assignment if the TA or instructor sees evidence that you have copied code. . You You cannot use the bracket notation to access array elements. have to use pointer/offset notation. The return value is a count of the number of comparisons that are made. Specifically, you should count the number of times that the program executes an 16 statement that compares the values of two array elements. int insertionsort (int const data, int size): . sorts the array using the insertion sort algorithm Caution: there are a lot of programs out there on the web that claim to be insertion sort written in c. The class syllabus prohibits copying code from web sites. A grade of zero will be assigned for this assignment if the Ta or instructor sees evidence that you have copied code. . You cannot use the bracket [ ] notation to access array elements. You have to use pointer/offset notation. The return value is a count of the number of comparisons that are made. Specifically, you should count the number of times that the program executes an it statement that compares the values of two array elements. . void swap ( int numi, int . num2): Exchanges the contents of the two memory locations. . void fillArray ( int const data, int size, int min, int max): Fills the array elements with integers from min to max (inclusive). You cannot use the bracket [ ] notation to access array elements. You have to use pointer/offset notation. . void neatprint (int . const data, int size, int numPerLine, int fieldsize): Prints the array elements in nice, neat columns using the parameters numPerline and fieldsize to control the layout. You cannot use the bracket notation to access array elements. You have to use pointer/offset notation. 4. Compilo, test, and debug your program as needed. 5. Submit 4 files. Do not zip or tar the files pa5c sortingfunctions sortingfunctions c makefile (You will need to copy this to a file named makefile c so you can submit it.) Dynamic Memory Allocation in C #include include // needed for malloc and free 1 int main() 2. 2. int newpt: newptr - int *allot sizeoft int 20 ) newptr) = 10) printtiidin", "newpte + 3) fren (newptr); 5. 7. Line 23 A pointer to int is declared. Line 31 The mallos function is used to allocate memory for 20 times the size of an int(30 bytes total). This reserves memory for the equivalent of a 20-element integer array. lloc returns a void' which must be cast to pointer of the desired type, in this case int. The pointer may be used to access array" elements with pointer-subscript notation The pointer may also be used to access harcay" elements using a dereferenced pointer-offset notation. The 30 bytes allocated to newptr are freed released to the operating system for reus) by using the free function. Line 5: Line 6