Question: P11-49A Comprehensive standards and variances problem (Learning Objectives 2, 3, 4, 5, & 6) Patterson Awning manufactures awnings and uses a standard cost system. The

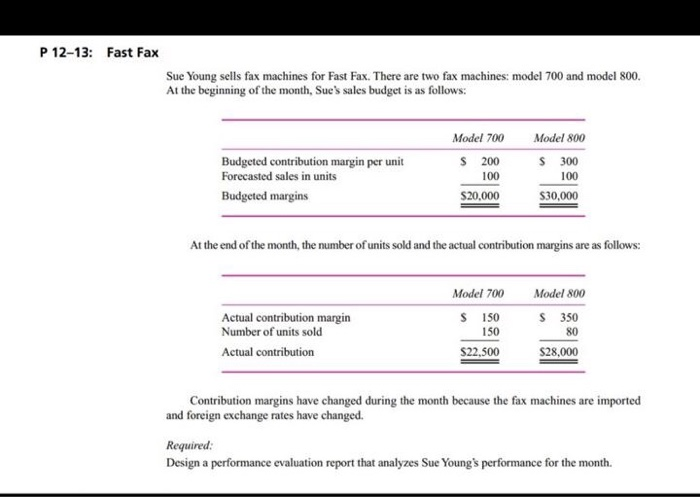
P11-49A Comprehensive standards and variances problem (Learning Objectives 2, 3, 4, 5, & 6) Patterson Awning manufactures awnings and uses a standard cost system. The company allocates overhead based on the number of direct labor hours. The following are the company's cost and standards data: Standards: Direct materials 22.0 yards per awning at $13.00 per yard Direct labor 5.0 hours per awning at $15.00 per hour Variable MOH standard rate $8.00 per direct labor hour Predetermined fixed MOH standard rate $6.00 per direct labor hour Total budgeted fixed MOH cost $63,500 Actual cost and operating data from the most recent month are as follows: Purchased 51,260 yards at a total cost of $661,254 Used 47,500 yards in producing 2,200 awnings Actual direct labor cost of $168,175 for a total of 10,850 hours Actual variable MOH $93,310 Actual fixed MOH 567,500 All manufacturing overhead is allocated on the basis of direct labor hours. Requirements 1. Calculate the standard cost of one awning. 2. Calculate the following variances: a. The direct material variances. b. The direct labor variances. c. The variable manufacturing overhead variances. d. The fixed manufacturing overhead variances. 3. Explain what each of the variances you calculated means and give at least one pos- sible explanation for each of those variances. Are any of the variances likely to be interrelated? P 12-13: Fast Fax Sue Young sells fax machines for Fast Fax. There are two fax machines: model 700 and model 800. At the beginning of the month, Sue's sales budget is as follows: Model 700 $ 200 Budgeted contribution margin per unit Forecasted sales in units Budgeted margins Model 800 $ 300 100 $30,000 100 $20,000 At the end of the month, the number of units sold and the actual contribution margins are as follows: Actual contribution margin Number of units sold Actual contribution Model 700 $ 150 150 $22,500 Model 800 $ 350 80 $28,000 Contribution margins have changed during the month because the fax machines are imported and foreign exchange rates have changed. Required: Design a performance evaluation report that analyzes Sue Young's performance for the month. P11-49A Comprehensive standards and variances problem (Learning Objectives 2, 3, 4, 5, & 6) Patterson Awning manufactures awnings and uses a standard cost system. The company allocates overhead based on the number of direct labor hours. The following are the company's cost and standards data: Standards: Direct materials 22.0 yards per awning at $13.00 per yard Direct labor 5.0 hours per awning at $15.00 per hour Variable MOH standard rate $8.00 per direct labor hour Predetermined fixed MOH standard rate $6.00 per direct labor hour Total budgeted fixed MOH cost $63,500 Actual cost and operating data from the most recent month are as follows: Purchased 51,260 yards at a total cost of $661,254 Used 47,500 yards in producing 2,200 awnings Actual direct labor cost of $168,175 for a total of 10,850 hours Actual variable MOH $93,310 Actual fixed MOH 567,500 All manufacturing overhead is allocated on the basis of direct labor hours. Requirements 1. Calculate the standard cost of one awning. 2. Calculate the following variances: a. The direct material variances. b. The direct labor variances. c. The variable manufacturing overhead variances. d. The fixed manufacturing overhead variances. 3. Explain what each of the variances you calculated means and give at least one pos- sible explanation for each of those variances. Are any of the variances likely to be interrelated? P 12-13: Fast Fax Sue Young sells fax machines for Fast Fax. There are two fax machines: model 700 and model 800. At the beginning of the month, Sue's sales budget is as follows: Model 700 $ 200 Budgeted contribution margin per unit Forecasted sales in units Budgeted margins Model 800 $ 300 100 $30,000 100 $20,000 At the end of the month, the number of units sold and the actual contribution margins are as follows: Actual contribution margin Number of units sold Actual contribution Model 700 $ 150 150 $22,500 Model 800 $ 350 80 $28,000 Contribution margins have changed during the month because the fax machines are imported and foreign exchange rates have changed. Required: Design a performance evaluation report that analyzes Sue Young's performance for the month
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


