Question: P7.2.5** Consider the actuator, process and sensor models for the DO process (Figure P7.2.5) presented in Example 3.9: Actuator: F (Fair ) spec air Process:
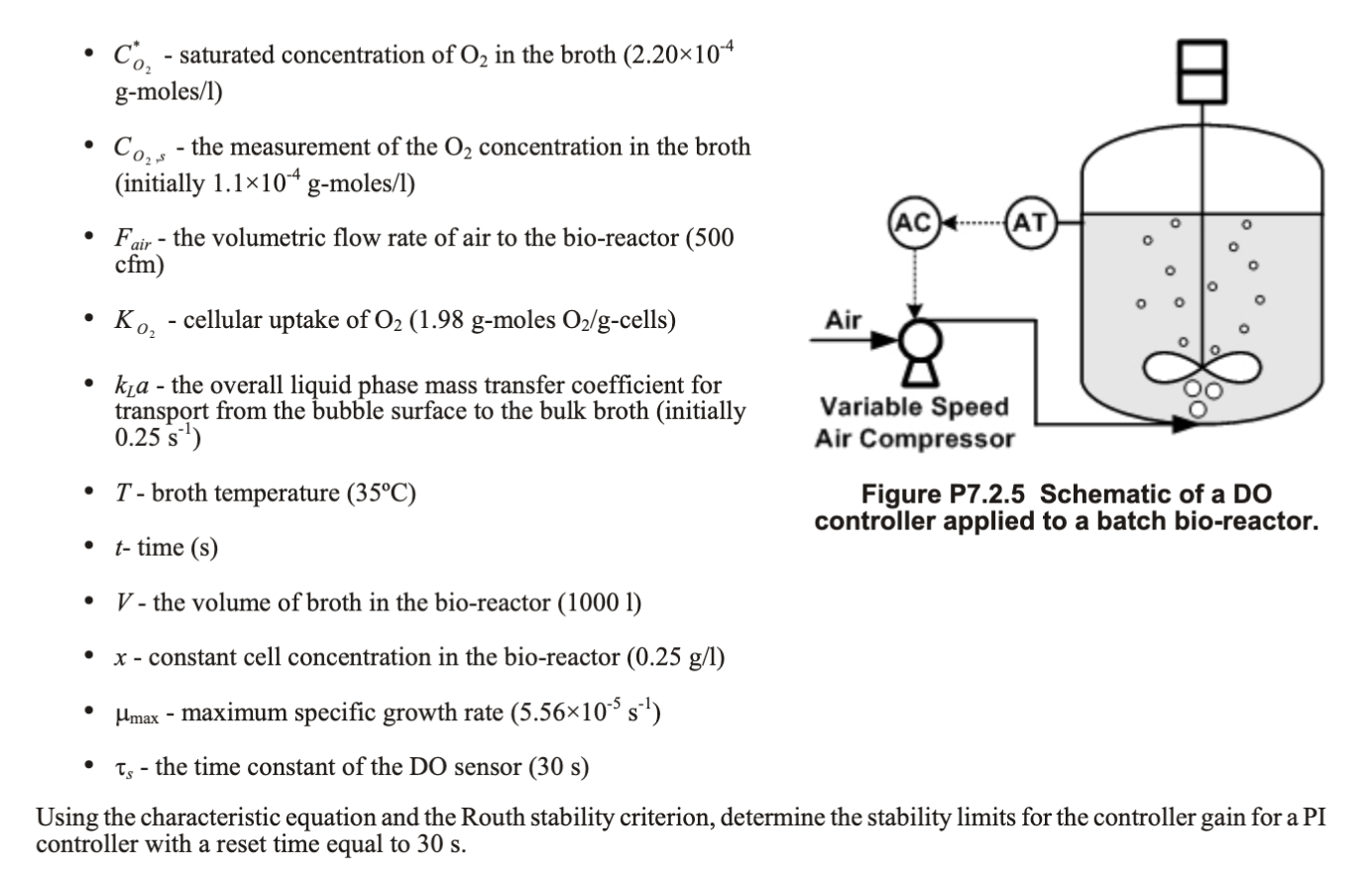
P7.2.5** Consider the actuator, process and sensor models for the DO process (Figure P7.2.5) presented in Example 3.9: Actuator: F (Fair ) spec air Process: k_a= 1 = 0.25+0.001(Fair 500) dCo =k, a(Co-Co)-K, mx* CO; , oM x dt dCo, 1 Sensor: = -(Co, -Co,-) dt Ts Co, - concentration of O2 in the reaction broth (initially 1.1x104 g-moles/1) - saturated concentration of O2 in the broth (2.20x10-4 g-moles/1) Co Cozy - the measurement of the O2 concentration in the broth (initially 1.1x104 g-moles/1) (AC) AT o F Fair - the volumetric flow rate of air to the bio-reactor (500 cfm) o o . K., - cellular uptake of O2 (1.98 g-moles O2/g-cells) Air O - ka - the overall liquid phase mass transfer coefficient for transport from the bubble surface to the bulk broth (initially 0.25 s) Variable Speed Air Compressor . T - broth temperature (35C) Figure P7.2.5 Schematic of a DO controller applied to a batch bio-reactor. t-time (s) V - the volume of broth in the bio-reactor (1000 1) x - constant cell concentration in the bio-reactor (0.25 g/l) Hmax - maximum specific growth rate (5.5610 s) Ts - the time constant of the DO sensor (30 s) Using the characteristic equation and the Routh stability criterion, determine the stability limits for the controller gain for a PI controller with a reset time equal to 30 s
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


