Question: % Parameters T = 4 ; % Defines the Period of T w 0 = 2 * pi / T; % Calculates the fundamental angular
Parameters T ; Defines the Period of T w pi T; Calculates the fundamental angular frequency t ::; Creates a time vector ranging from to with a step size of Coefficients a; Sets the DC component, representing the average value of the signal over one period an @npin sinpin; Formula for an calculated in task A bn @npin cospincospinpin; Formula for bn calculated in task A Ideal signal definition xideal t & t t & t ; Defines an ideal signal with amplitude from to and amplitude from to Fourier series approximations for N and N xfourier a onessizet; Start with DC component for N xfourier a onessizet; Start with DC component for N Define piecewise function fpiecewise @tt & t t & t ; Defines a piecewise function with values for t and for t Functions to compute Fourier coefficients computecoefficients @n deal Tintegral@t fpiecewiset cosn w t integral@t fpiecewiset cosn w t Tintegral@t fpiecewiset sinn w t integral@t fpiecewiset sinn w t; Inputs the Fourier coefficients for the piecewise function over the interval Calculate Fourier series for N harmonics for n :an bn computecoefficientsn; Inputs the Fourier coefficients for the nth harmonic xfourier xfourier an cosn w t bn sinn w t; Adds the nth harmonic to the Fourier series approximation end Calculate Fourier series for N harmonics for n :an bn computecoefficientsn; Inputs the Fourier coefficients for the nth harmonic xfourier xfourier an cosn w t bn sinn w t; Adds the nth harmonic to the Fourier series approximation end Plotting figureColor 'white'; Creates a figure with a white background Plot the ideal signal plott xideal, k 'LineWidth', 'DisplayName', 'Ideal xt; Plots the original ideal signal xt hold on; Holds the current plot for further additions Plot Fourier series approximations plott xfourierr 'LineWidth', 'DisplayName', 'Fourier Approx N; Plots the Fourier series approximation with harmonics plott xfourierb 'LineWidth', 'DisplayName', 'Fourier Approx N; Plots the Fourier series approximation with harmonics Add labels, legend, title, and grid xlabelTime t; Labels the xaxis as "Time t ylabelxt; Labels the yaxis as xt titleIdeal Signal and Fourier Series Approximations'; Adds a title displaying the Ideal Signal and Fourier Series Approximations legendLocation 'best'; Automatically place the legend grid on; Turns on the grid for better visualization axis; Sets the axis limits for the plot: x from to and y from to Add vertical and horizontal reference lines plotk 'LineWidth', ; Vertical line at t plotk 'LineWidth', ; Horizontal line at x hold off; Release the plot for further change
Edit the code to plot magnitude and phase spectrum for xt The code has to work Task Signal Processing
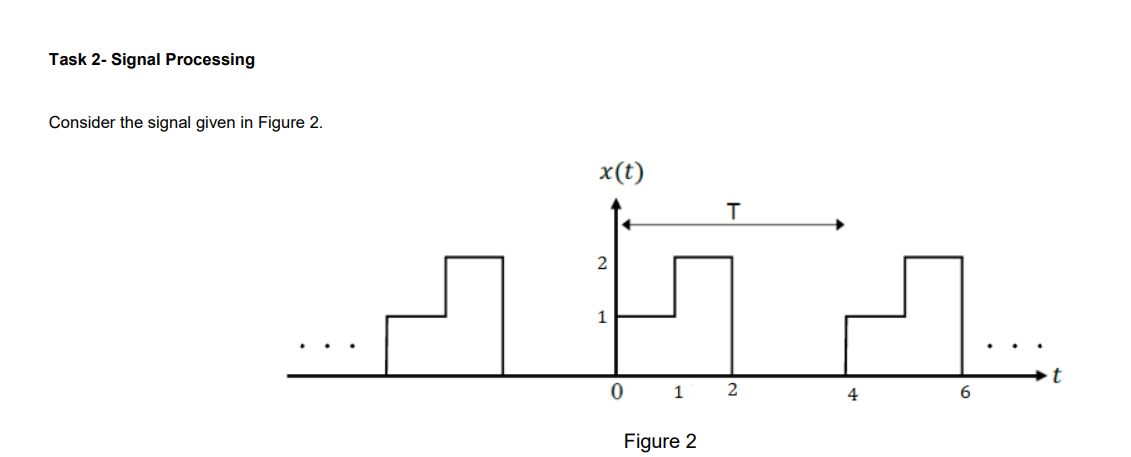
Consider the signal given in Figure
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


