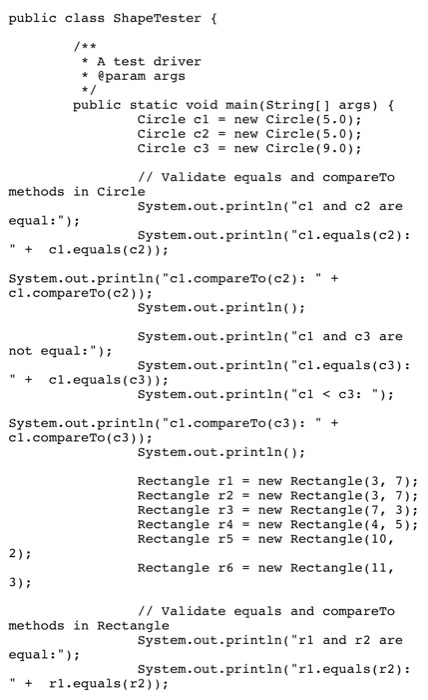
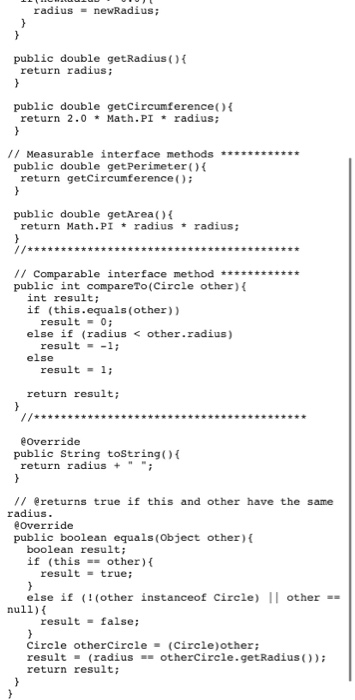
Question: Part 1 1. The class Name represents a person's first and last names A. Write the subclass ProperName from the superclass, Name, adding data fields
Part 1 1. The class Name represents a person's first and last names A. Write the subclass ProperName from the superclass, Name, adding data fields for middle initial and a title such as Ms., Dr. or Sir. B. Provide reasonable constructors, setter, and getter methods for the new C. Override the toString method so that it behaves correctly for the new class. 2. Test your class with the use ProperName file 3. Explain why inheritance is appropriate in the definition of Proper Name but is not a reasonable choice for the definition of the class Nickname, NickName.java 4. Attach your file ProperName.java via the Browse My Computer button and enter your response to #3 in the Comments text box for this lab assignment Part 2 1. The class Circle implements the comparable and Measurable interfaces. Modify the class so that it extends the abstract class Shape. 2. Implement the class Rectangle that extends Shape and implements both the comparable and Measurable interfaces. The dass will have two private data members, length and width Use the area of the rectangle as a basis for comparison when implementing the compare to and equal methods. The toString() method should return a String representation of the length and width of the object 3. Derive the class Square from Rectangle without adding any additional data members. Its parameterized constructor should accept a single value representing a side of the square: it must call the parameterized constructor in Rectangle. You must overriding the following methods: toString getShapeName() 4. Compile and execute the Shape Tester program to test your Circle, Rectangle, and Square classes. 5. To the Shape Tester program, add an array of 12 Shape objects, assign ALL of the Circle, Rectangle and Square objects previously created in the driver to o Write an enhanced for loop that displays the results of a call to the getShapeName() method and a call to the toString() method for each array element of the new array. Compile and execute the Shape Tester o Explain why a method without implementation in the Shape class will compile and execute properly. 6. Inside the block of the enhanced for loop, add a statement that will display a call to the getArea() method for each of the Shape objects in the array of Shapes Compile and execute the Shape Tester Explain the results of this modification to the code 7. To the ShapeTester program, o add an array of Measurable objects, assign ALL of the Rectangle and Square objects created in the driver to the array Write an enhanced for loop that displays the results of a call to the getArea() method for each array element. Compile and execute the Shape Tester Explain why this code will compile and execute properly 8. Submit your files Circle.java, Rectangle.java, Square.java and ShapeTester java along with your responses to the questions posed in Part 2 /** An interface for methods that return * the perimeter and area of an object. * / public interface Measurable /** Task: Gets the perimeter. * @return the perimeter */ public double getPerimeter(); /** Task: Gets the area. * @return the area */ public double getArea(); 17 An abstract class representing a geometric shape. // Classes that extend this class must implement getShapeName(). public abstract class Shape { private int numSides; public Shape() { numSides = 0; public Shape(int sides) { if (sides > 0) { numSides = sides; else{ numSides = 0; public int getNumSides() { return numSides; // @returns an appropriate name for this Shape class public abstract String getShapeName(); /** An interface for methods that return * the perimeter and area of an object. * / public interface Measurable /** Task: Gets the perimeter. * @return the perimeter */ public double getPerimeter(); /** Task: Gets the area. * @return the area */ public double getArea(); // An abstract class representing a geometric shape. // Classes that extend this class must implement getShapeName(). public abstract class Shape { private int numSides; public Shape() { numSides = 0; public Shape(int sides) { if (sides > 0) { numSides = sides; else{ numSides = 0; public int getNumSides() { return numSides; // @returns an appropriate name for this Shape class public abstract String getShapeName(); public class ShapeTester { * A test driver * @param args public static void main(String[] args) { Circle cl = new Circle(5.0); Circle c2 = new Circle(5.0); Circle c3 = new Circle(9.0); 1/ Validate equals and compare To methods in Circle System.out.println("cl and c2 are equal:"); System.out.println("cl.equals(c2): " + cl.equals(c2)); System.out.println("cl.compareTo(c2):" + cl.compareTo(c2)); System.out.println(); System.out.println("cl and c3 are not equal:"); System.out.println("cl.equals(c3): " + cl.equals(03)); System.out.println("cl , Measurable{ private double radius; public Circle() { radius = 1.0; public Circle( double newRadius) { setRadius (newRadius); public void setRadius (double newRadius) { if(newRadius > 0.0){ radius = newRadius; public double getRadius() { return radius; public double getCircumference() { return 2.0 * Math.PI * radius; // Measurable interface methods ******* public double getPerimeter() { return getCircumference(); public double getArea() { return Math.PI * radius * radius; //** // Comparable interface method *********** public int compareTo (Circle other) { int result; if (this.equals(other)) result = 0; else if (radius and Measurable interfaces. Modify the class so that it extends the abstract class Shape. 2. Implement the class Rectangle that extends Shape and implements both the comparable and Measurable interfaces. The dass will have two private data members, length and width Use the area of the rectangle as a basis for comparison when implementing the compare to and equal methods. The toString() method should return a String representation of the length and width of the object 3. Derive the class Square from Rectangle without adding any additional data members. Its parameterized constructor should accept a single value representing a side of the square: it must call the parameterized constructor in Rectangle. You must overriding the following methods: toString getShapeName() 4. Compile and execute the Shape Tester program to test your Circle, Rectangle, and Square classes. 5. To the Shape Tester program, add an array of 12 Shape objects, assign ALL of the Circle, Rectangle and Square objects previously created in the driver to o Write an enhanced for loop that displays the results of a call to the getShapeName() method and a call to the toString() method for each array element of the new array. Compile and execute the Shape Tester o Explain why a method without implementation in the Shape class will compile and execute properly. 6. Inside the block of the enhanced for loop, add a statement that will display a call to the getArea() method for each of the Shape objects in the array of Shapes Compile and execute the Shape Tester Explain the results of this modification to the code 7. To the ShapeTester program, o add an array of Measurable objects, assign ALL of the Rectangle and Square objects created in the driver to the array Write an enhanced for loop that displays the results of a call to the getArea() method for each array element. Compile and execute the Shape Tester Explain why this code will compile and execute properly 8. Submit your files Circle.java, Rectangle.java, Square.java and ShapeTester java along with your responses to the questions posed in Part 2 /** An interface for methods that return * the perimeter and area of an object. * / public interface Measurable /** Task: Gets the perimeter. * @return the perimeter */ public double getPerimeter(); /** Task: Gets the area. * @return the area */ public double getArea(); 17 An abstract class representing a geometric shape. // Classes that extend this class must implement getShapeName(). public abstract class Shape { private int numSides; public Shape() { numSides = 0; public Shape(int sides) { if (sides > 0) { numSides = sides; else{ numSides = 0; public int getNumSides() { return numSides; // @returns an appropriate name for this Shape class public abstract String getShapeName(); /** An interface for methods that return * the perimeter and area of an object. * / public interface Measurable /** Task: Gets the perimeter. * @return the perimeter */ public double getPerimeter(); /** Task: Gets the area. * @return the area */ public double getArea(); // An abstract class representing a geometric shape. // Classes that extend this class must implement getShapeName(). public abstract class Shape { private int numSides; public Shape() { numSides = 0; public Shape(int sides) { if (sides > 0) { numSides = sides; else{ numSides = 0; public int getNumSides() { return numSides; // @returns an appropriate name for this Shape class public abstract String getShapeName(); public class ShapeTester { * A test driver * @param args public static void main(String[] args) { Circle cl = new Circle(5.0); Circle c2 = new Circle(5.0); Circle c3 = new Circle(9.0); 1/ Validate equals and compare To methods in Circle System.out.println("cl and c2 are equal:"); System.out.println("cl.equals(c2): " + cl.equals(c2)); System.out.println("cl.compareTo(c2):" + cl.compareTo(c2)); System.out.println(); System.out.println("cl and c3 are not equal:"); System.out.println("cl.equals(c3): " + cl.equals(03)); System.out.println("cl , Measurable{ private double radius; public Circle() { radius = 1.0; public Circle( double newRadius) { setRadius (newRadius); public void setRadius (double newRadius) { if(newRadius > 0.0){ radius = newRadius; public double getRadius() { return radius; public double getCircumference() { return 2.0 * Math.PI * radius; // Measurable interface methods ******* public double getPerimeter() { return getCircumference(); public double getArea() { return Math.PI * radius * radius; //** // Comparable interface method *********** public int compareTo (Circle other) { int result; if (this.equals(other)) result = 0; else if (radius