Question: Part 1: Memory access and moving data Instruction Value after execution of instruction Li al, data A1 = Li a2, offset A2 = Sw al,
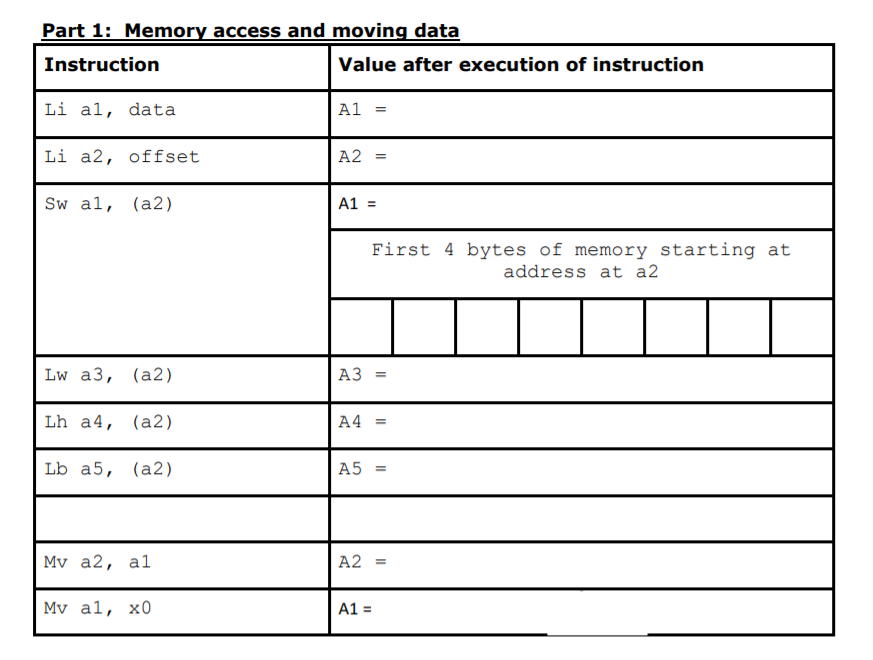
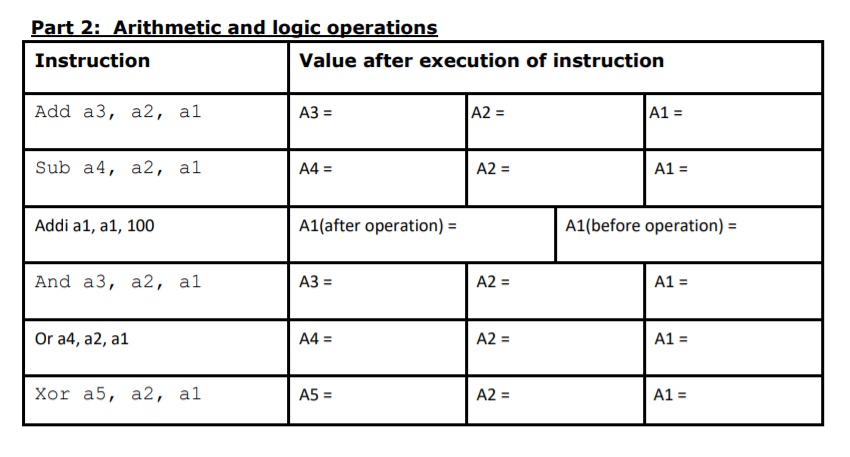
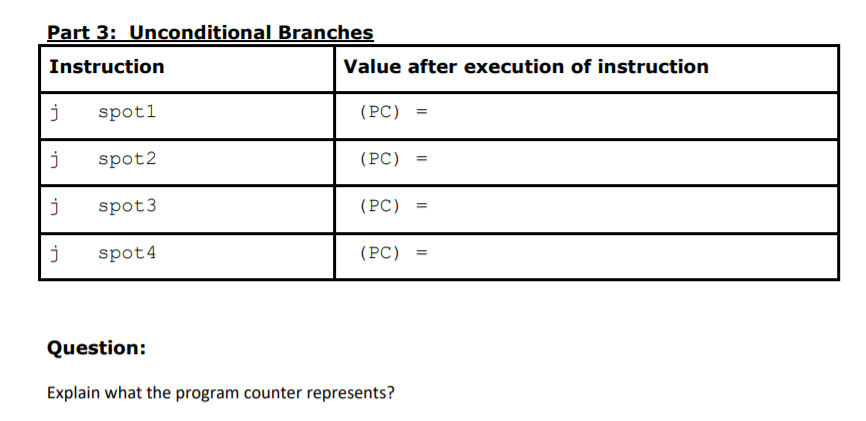
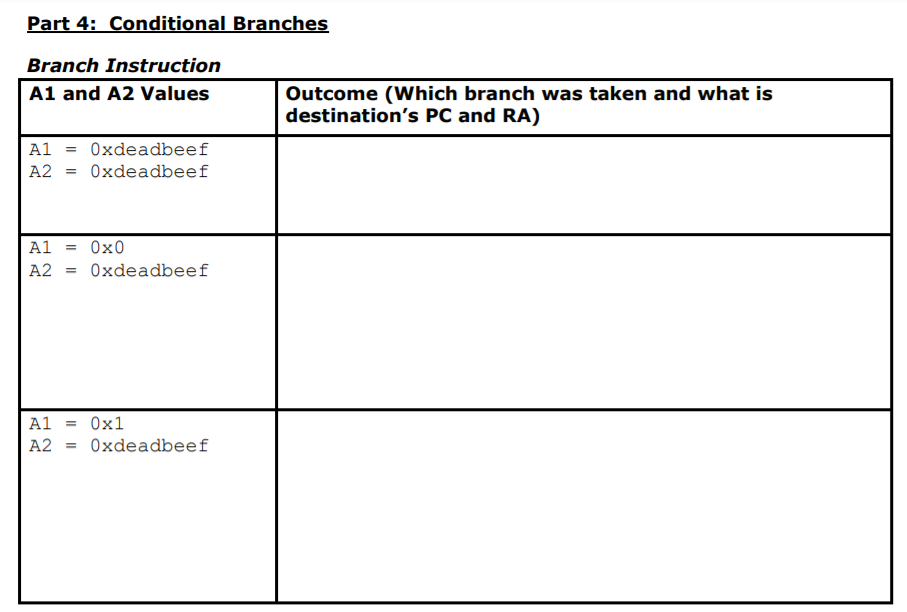
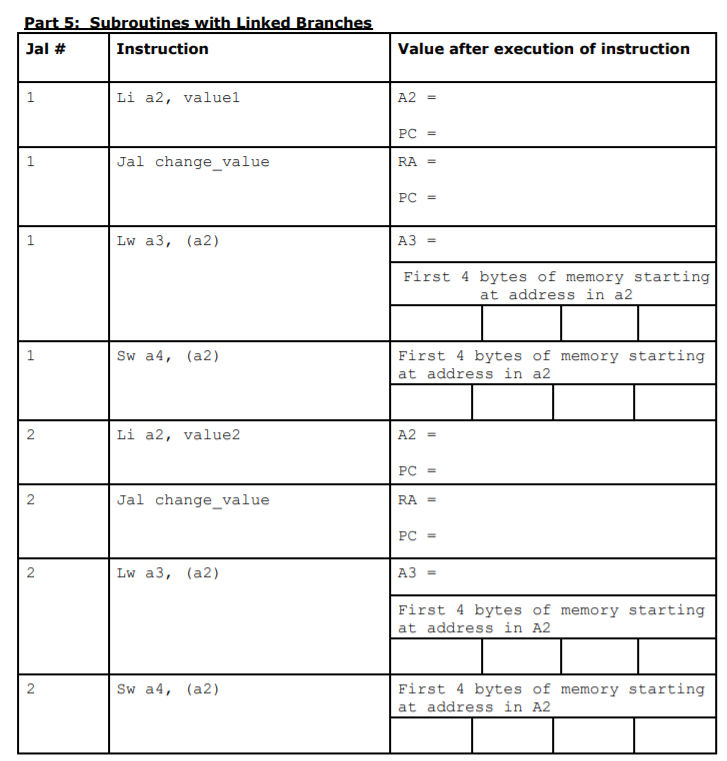
Part 1: Memory access and moving data Instruction Value after execution of instruction Li al, data A1 = Li a2, offset A2 = Sw al, (a2) A1 = First 4 bytes of memory starting at address at a 2 Lw a3, (a2) A3 = Lh a4, (a2) A4 = Lb a5, (a2) A5 Mva2, al A2 My al, x0 A1 = Part 2: Arithmetic and logic operations Instruction Value after execution of instruction Add a3, a2, al A3 = A2 = A1 = Sub a4, a2, al A4 = A2 = A1 = Addi a1, a1, 100 A1(after operation) = A1(before operation) = And a3, a2, al A3 = A2 = A1 = Or a4, a2, a1 A4 = A2 = A1 = Xor a5, a2, al A5 = A2 = A1 = Part 3: Unconditional Branches Instruction Value after execution of instruction j spoti (PC) = j spot2 (PC) = j spot3 (PC) j spot4 (PC) = Question: Explain what the program counter represents? Part 4: Conditional Branches Branch Instruction A1 and A2 Values Outcome (Which branch was taken and what is destination's PC and RA) A1 = Oxdeadbeef A2 = Oxdeadbeef A1 Ox0 Oxdeadbeef A2 = A1 = 0x1 A2 = Oxdeadbeef Part 5: Subroutines with Linked Branches Jal # Instruction Value after execution of instruction Li a2, value1 A2 = PC = Jal change_value RA = PC = 1 Lw a3, (a2) A3 First 4 bytes of memory starting at address in a2 Sw a4, (a2) First 4 bytes of memory starting at address in a2 N Li a2, value2 A2 = PC = 2 2 Jal change_value RA PC = N Lw a3, (a2) A3 = First 4 bytes of memory starting at address in A2 2 2 Sw a4, (a2) First 4 bytes of memory starting at address in A2 Part 1: Memory access and moving data Instruction Value after execution of instruction Li al, data A1 = Li a2, offset A2 = Sw al, (a2) A1 = First 4 bytes of memory starting at address at a 2 Lw a3, (a2) A3 = Lh a4, (a2) A4 = Lb a5, (a2) A5 Mva2, al A2 My al, x0 A1 = Part 2: Arithmetic and logic operations Instruction Value after execution of instruction Add a3, a2, al A3 = A2 = A1 = Sub a4, a2, al A4 = A2 = A1 = Addi a1, a1, 100 A1(after operation) = A1(before operation) = And a3, a2, al A3 = A2 = A1 = Or a4, a2, a1 A4 = A2 = A1 = Xor a5, a2, al A5 = A2 = A1 = Part 3: Unconditional Branches Instruction Value after execution of instruction j spoti (PC) = j spot2 (PC) = j spot3 (PC) j spot4 (PC) = Question: Explain what the program counter represents? Part 4: Conditional Branches Branch Instruction A1 and A2 Values Outcome (Which branch was taken and what is destination's PC and RA) A1 = Oxdeadbeef A2 = Oxdeadbeef A1 Ox0 Oxdeadbeef A2 = A1 = 0x1 A2 = Oxdeadbeef Part 5: Subroutines with Linked Branches Jal # Instruction Value after execution of instruction Li a2, value1 A2 = PC = Jal change_value RA = PC = 1 Lw a3, (a2) A3 First 4 bytes of memory starting at address in a2 Sw a4, (a2) First 4 bytes of memory starting at address in a2 N Li a2, value2 A2 = PC = 2 2 Jal change_value RA PC = N Lw a3, (a2) A3 = First 4 bytes of memory starting at address in A2 2 2 Sw a4, (a2) First 4 bytes of memory starting at address in A2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


