Question: Part 1 : Part - 3 (Abstract Class and Interface) Consider the Class that you designed in Part-1 of this project and do the following:

Part 1 :
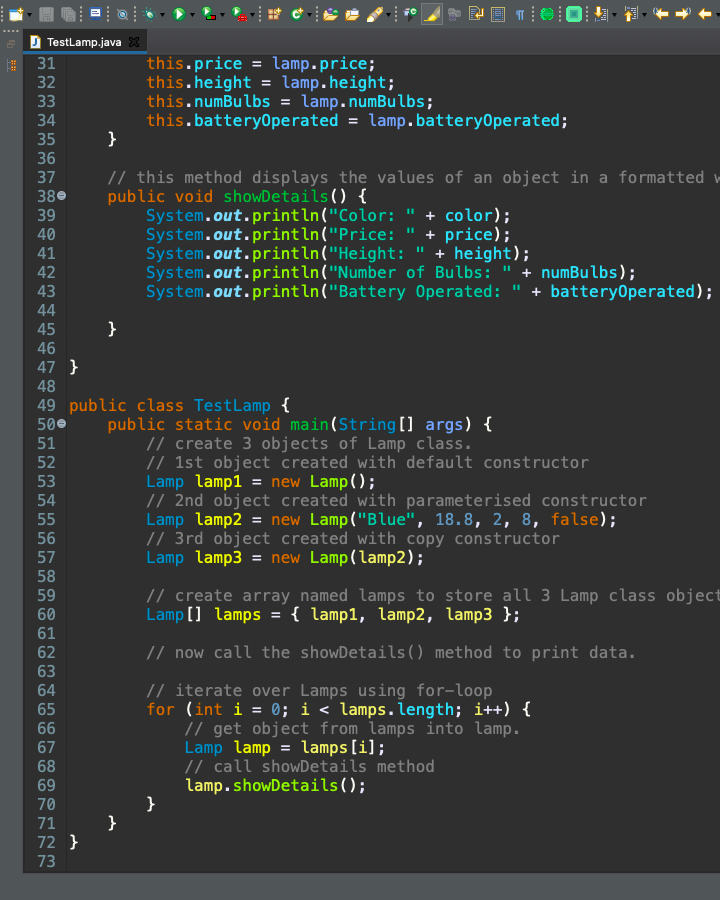
Part - 3 (Abstract Class and Interface) Consider the Class that you designed in Part-1 of this project and do the following: 1. Implement the Comparable and Cloneable interface for your class. 2. The Test class should create 10 instances (objects) of your class. 3. Store these instances in Array and ArrayList. 4. Show the demo of sorting these objects stored in Array and ArrayList. Include the below in your project report: The code of implementing Comparable and Cloneable Interfaces. Sereenshot of relevant (Comparable and Cloneable) outputs. 0 t. TestLamp.java 1 class Lamp { 2 // member variables Sp 3 private String color; 4 private double price; 5 private double height; Sp 6 private int numBulbs; 7 private boolean batteryOperated; 8 9 // default constructor, sets all member variables to some default values. 100 public Lamp() { 11 this.color = "Red"; 12 this.price = 20.5; 13 this.height = 1.5; 14 this.numBulbs = 18; 15 this.batteryOperated = true; 16 17 } 18 19 // parameterised constructor to set values of member variables. 200 public Lamp(String color, double price, double height, int numBulbs, boolean batteryOperated) { 21 this.color = color; 22 this.price = price; 23 this.height = height; 24 this.numBulbs = numBulbs; 25 this.batteryOperated = batteryOperated; 26 } 27 28 // copy constructor 290 public Lamp(Lamp lamp) { 30 this.color = lamp.color; 31 this.price = lamp.price; 32 this.height = lamp. height; 33 this.numBulbs = lamp.numBulbs; 34 this.batteryOperated = lamp.batteryOperated; 35 } 36 37 // this method displays the values of an object in a formatted way. 380 public void showDetails() { 39 System.out.println("Color: " + color); 40 System.out.println("Price: " + price); 41 System.out.println("Height: " + height); 42 System.out.println("Number of Bulbs: " + numBulbs); 43 System.out.println("Battery Operated: + batteryOperated); Writable Smart Insert 11:28: 275 44 TestLamp.java X 31 this.price = lamp.price; 32 this.height = lamp.height; 33 this.numBulbs = lamp.numBulbs; 34 this.batteryOperated = lamp.batteryOperated; 35 } 36 37 // this method displays the values of an object in a formatted v 38 public void showDetails() { 39 System.out.println("Color: " + color); 40 System.out.println("Price: + price); 41 System.out.println("Height: + height); 42 System.out.println("Number of Bulbs: " + numBulbs); 43 System.out.println("Battery Operated: + batteryOperated); 45 } 46 47 } 48 49 public class TestLamp { 500 public static void main(String[] args) { 51 Il create 3 objects of Lamp class. 52 // 1st object created with default constructor 53 Lamp lamp1 = new Lamp(); 54 // 2nd object created with parameterised constructor 55 Lamp lamp2 = new Lamp("Blue", 18.8, 2, 8, false); 56 // 3rd object created with copy constructor 57 Lamp lamp3 = new Lamp (lamp2); 58 59 Il create array named lamps to store all 3 Lamp class object 60 Lamp [] lamps = { lampi, lamp2, lamp3 }; 61 62 // now call the showDetails() method to print data. 63 64 // iterate over Lamps using for-loop 65 for (int i = 0; i
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


