Question: part 2 #include #include #include struct node { int n; struct node *next; }; struct node *head = NULL; void print(){ struct node * current
part 2
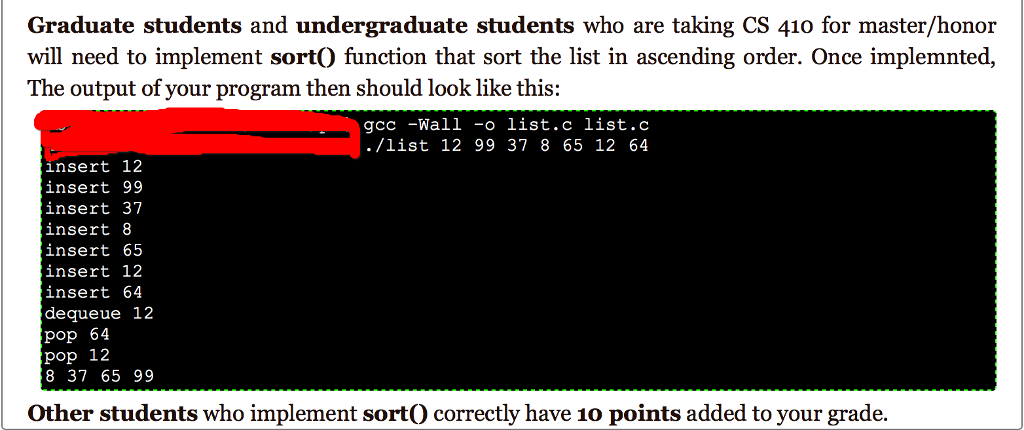
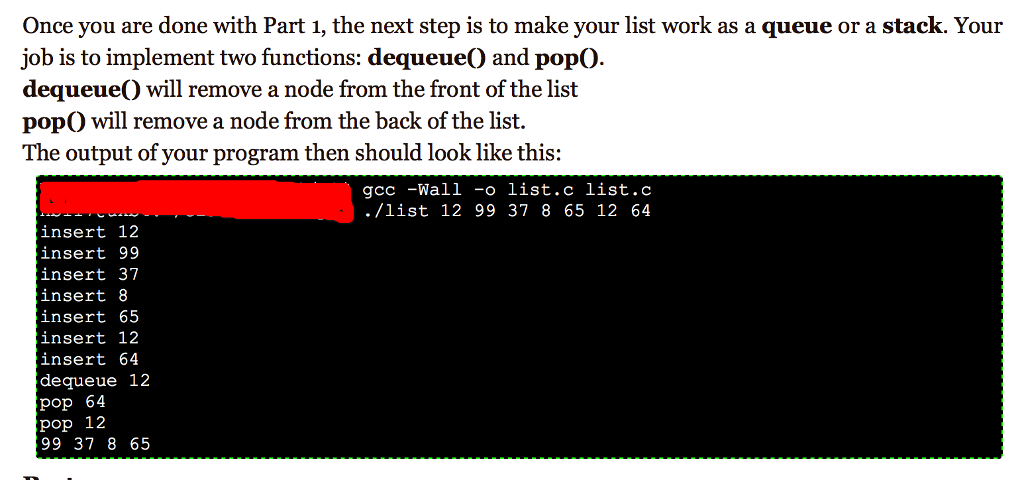
#include#include #include struct node { int n; struct node *next; }; struct node *head = NULL; void print(){ struct node * current = head; while(current!=NULL){ printf("%d ", current->n); current=current->next; } printf(" "); } void insert(int number){ } void dequeue(){ } void pop(){ } void sort(){ } int main(int argc, char * argv[]){ int i; for(i=1;i Once you are done with Part 1, the next step is to make your list work as a queue or a stack. Youir job is to implement two functions: dequeue) and popO dequeue) will remove a node from the front of the list popO will remove a node from the back of the list. The output of your program then should look like this: gcc-Wall -o list.c list.c ./list 12 99 37 8 65 12 64 insert 12 insert99 insert 37 insert 8 insert 65 insert 12 insert 64 dequeue 12 Pop 64 pop 12 99 37 8 65
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


