Question: #include #include #include struct node { int n; struct node *next; }; struct list { struct node *head; int count; }; void print(struct list *thislist){
#include
struct node { int n; struct node *next; };
struct list { struct node *head; int count; };
void print(struct list *thislist){ struct node * current = thislist->head; while(current!=NULL){ printf("%d ", current->n); current=current->next; } printf(" "); }
void insert(struct list *thislist, int number){ //create a new node struct node *tmp = malloc(sizeof(struct node)); tmp->n = number; tmp->next = NULL;
printf("insert %d ", number);
struct node *current = thislist->head;
//if the list is empty //head points to the new node (the only node) if(current == NULL){ thislist->head = tmp; thislist->count = 1; return; }
//find the last node while(current->next!=NULL){ current = current->next; } thislist->count = thislist->count + 1;
//the last node -> next points to the new node current->next = tmp;
return;
}
int size(struct list *thislist){ int count = 0; struct node *current = thislist->head; while(current != NULL){ count++; current = current->next; } return count; }
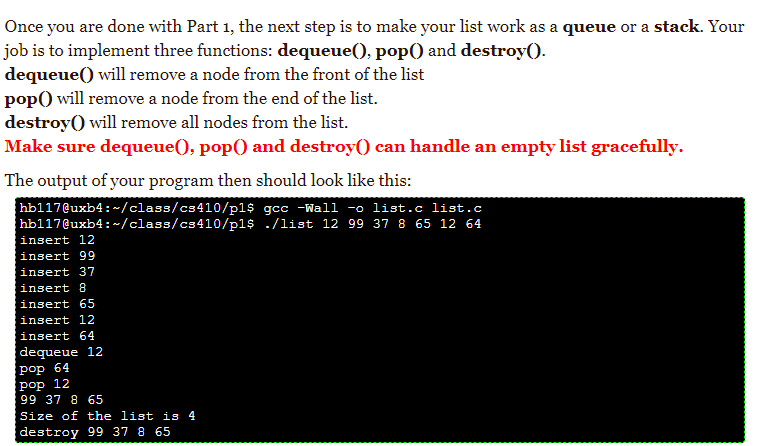
void dequeue(struct list *thislist){
}
void pop(struct list *thislist){
}
void destroy (struct list *thislist){
}
void sort(struct list *thislist){
}
int main(int argc, char * argv[]){
struct list * mylist = malloc(sizeof(struct list));
mylist->head = NULL;
//DO NOT make any modifications bellow this line int i; for(i=1;i } dequeue(mylist); pop(mylist); pop(mylist); sort(mylist); print(mylist); printf("Size of the list is %d ",size(mylist)); destroy(mylist); free(mylist); return 0; }
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


