Question: Part A A solution initially contains A, B, and in the following concentrations: [A] = 0.300 M, [B] = 0.950 M, and [C] = 0.700
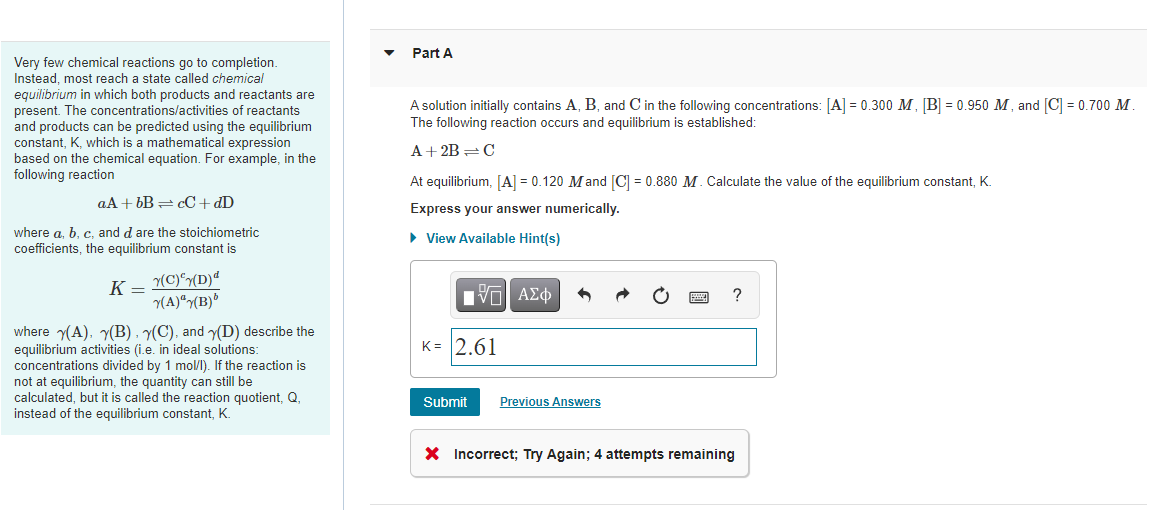
Part A A solution initially contains A, B, and in the following concentrations: [A] = 0.300 M, [B] = 0.950 M, and [C] = 0.700 M. The following reaction occurs and equilibrium is established: Very few chemical reactions go to completion Instead, most reach a state called chemical equilibrium in which both products and reactants are present. The concentrations/activities of reactants and products can be predicted using the equilibrium constant, K, which is a mathematical expression based on the chemical equation. For example, in the following reaction aA + bB =cC+ dD A + 2B=C At equilibrium, [A] = 0.120 Mand [C] = 0.880 M. Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant, K. Express your answer numerically. View Available Hint(s) where a, b, c, and d are the stoichiometric coefficients, the equilibrium constant is K (C)(D) 7(A)(B) ? K= 2.61 where (A), 7(B) (C), and (D) describe the equilibrium activities (i.e. in ideal solutions: concentrations divided by 1 mol/l). If the reaction is not at equilibrium, the quantity can still be calculated, but it is called the reaction quotient, Q, instead of the equilibrium constant, K. Submit Previous Answers X Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remaining
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


