Question: Part A: Assuming all conditions for conducting a hypothesis test are met, what are the no and alternative hypothesis? Part B: identify the test statistic
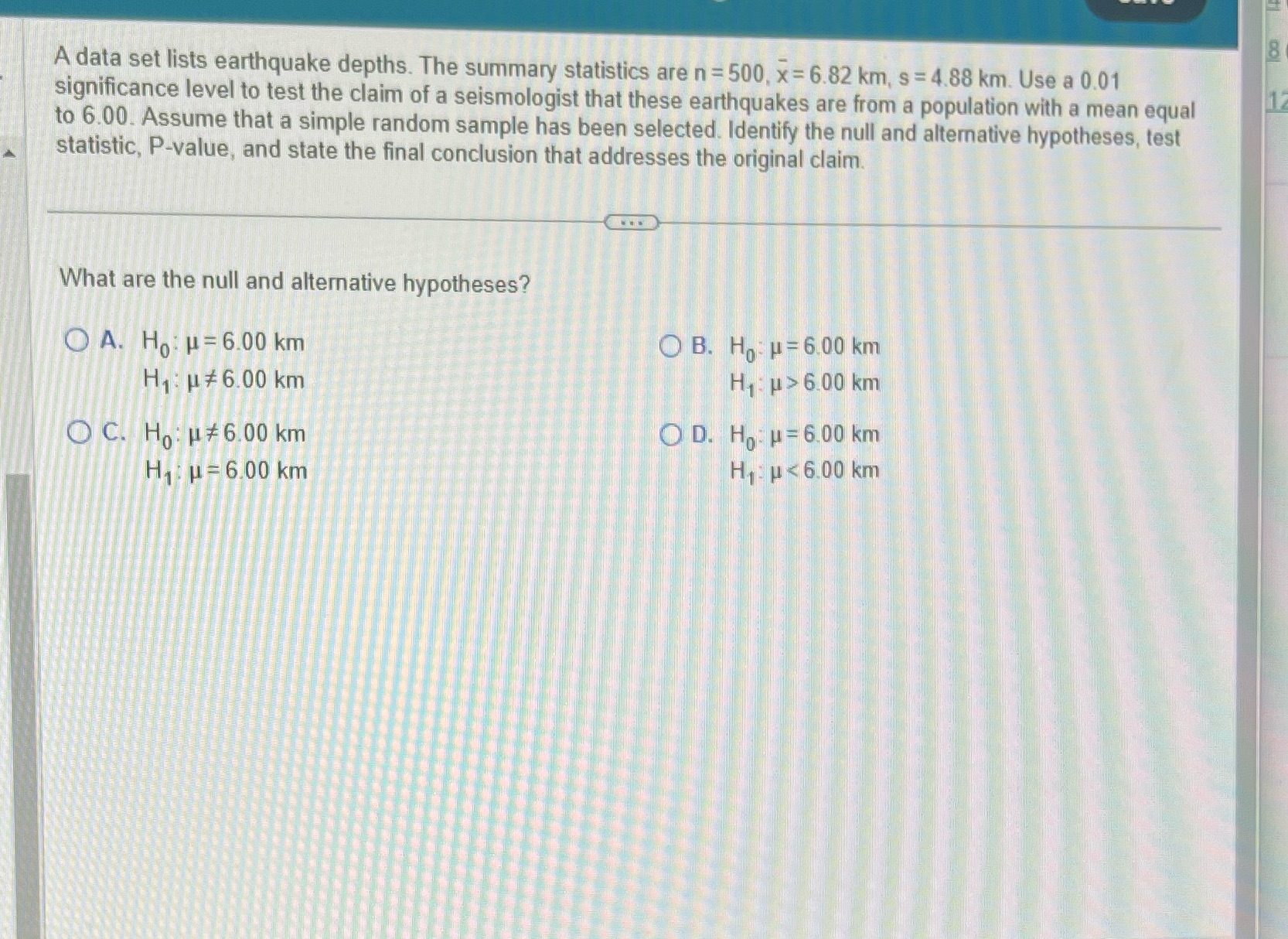
Part A: Assuming all conditions for conducting a hypothesis test are met, what are the no and alternative hypothesis? Part B: identify the test statistic Part C: Identify the P value Part D: State the final conclusion that addresses the original claim. There is (sufficient/ not sufficient) Evidence to conclude that the mean prediction error is equal to zero (is/ is not) correct. There is In the mean production.
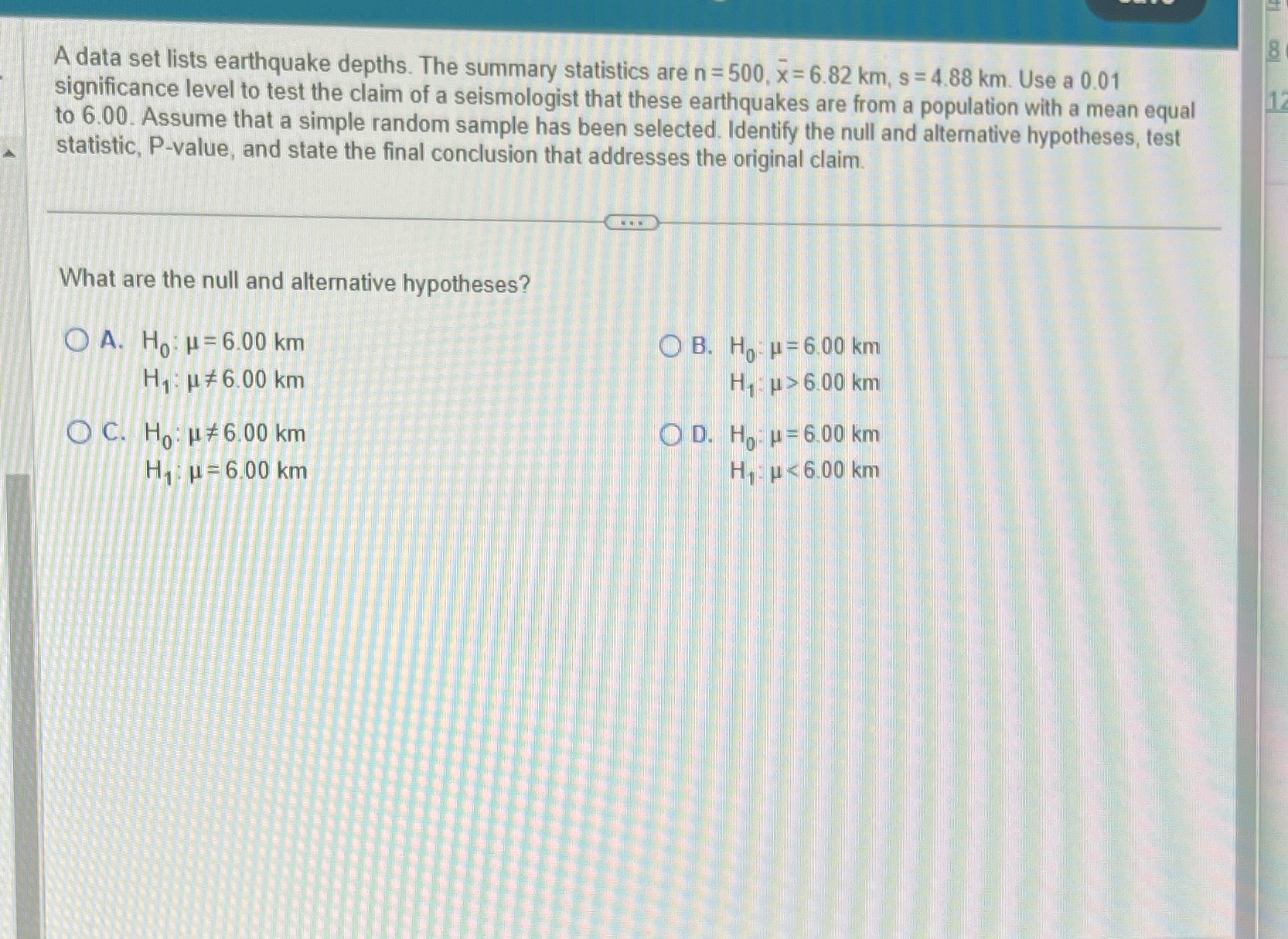
8 A data set lists earthquake depths. The summary statistics are n = 500, x= 6.82 km, s = 4.88 km. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim of a seismologist that these earthquakes are from a population with a mean equal to 6.00. Assume that a simple random sample has been selected. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses, test statistic, P-value, and state the final conclusion that addresses the original claim. What are the null and alternative hypotheses? O A. Ho: H = 6.00 km O B. Ho H=6.00 km H1: u # 6.00 km H1: J > 6 00 km OC. Ho: HI# 6.00 km OD. H . = 6.00 km Hu=6.00 km HE u
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


