Question: part B please B D E 2 3 3 4 earliest completion time of the extended project with two workers? Give reasons for your answer


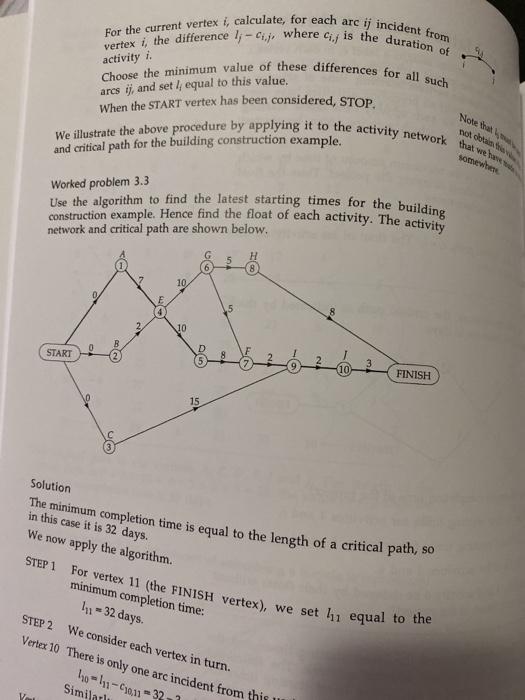




B D E 2 3 3 4 earliest completion time of the extended project with two workers? Give reasons for your answer including a possible schedule (found Question 2 (a) A project consists of five activities, A-E. The durations (in days) of the activities, and the precedence relations, are given in the following table. Activity Duration Preceding activities AC BE ) Using the activity network algorithm in Networks 2, construct an activity network for this project. (li) List any redundant arcs in your activity network. (You should ignore them when applying the subsequent algorithms.) (iii) Using the critical path construction algorithm in Networks 2, compile a table showing the earliest starting time for each activity. Hence find a critical path in the activity network, and state the length of this path. (iv) Using the algorithm for calculating latest starting times given in Networks 2 compile a table showing the latest starting time for each activity. Your answers should make clear how each algorithm is being applied, the order in which the vertices are considered, and what is happening at each stage. (b) The project in part (a) is extended by the addition of two more activities: P with duration 4 days, and Q with duration 3 days. The precedence relations involving these activities are: P must follow B; Q must follow P and E; D must follow P and Q. All of the precedence relations in part (a) remain in force. (1) Draw the new activity network showing all the arcs. (1) Find a critical path in the new network, and hence show that the earliest completion time for the extended project is 16 days. You can do this either by inspection, with an explanation of your reasoning, or by applying the critical path construction algorithm. (iii) If the duration of activity P is reduced to 1 day, what is the by inspection). (a) What is the minimum completion time of the project? (b) Calculate the earliest starting times for activities 4 and 6. (c) Calculate the latest starting times for activities 6 and 4. (d) Calculate the floats for activities 4 and 6. (e) Can both activity 4 and activity 6 be delayed by their floats without the completion of the In the above problem, we calculated the latest starting times and the Floats for two activities in a simple activity network. The following algorithm is a systematic method of calculating latest starting times for all the vertices. As in the solution to the above problem, we begin at the FINISH vertex and work back, vertex by vertex, until all the vertices have been considered. Algorithm for calculating latest starting times This algorithm is applied to an activity network (with n activities) for which we have calculated the minimum completion time. It is used to calculate the value of the latest starting time 1, for each vertex i, for in +1,1,...,1,0 STEP 1 For vertex n +1 (the FINISH vertex), set lus+1 equal to the minimum completion time. STEP 2 Carry out the following procedure for each vertex i, starting with i = n and continuing with i=1-1, i = -2, and so on, until all the vertices including vertex 0 (the START vertex) have been considered. For vertex 11 (the FINISH vertex), we set 111 equal to the Vertex i the difference I - C., where c, is the duratiohom activity i For the current vertex i, calculate, for each arc ij incident from Choose the minimum value of these differences for all such We illustrate the above procedure by applying it to the activity network that we are construction example. Hence find the float of each activity. The activity Use the algorithm to find the latest starting times for the building arcs ij, and set I equal to this value. When the START vertex has been considered, STOP, and critical path for the building construction example. Note than wobban. somewhere Worked problem 3.3 network and critical path are shown below. 5 H 8 6 10 10 D START LO ON FINISH 10 15 Solution The minimum completion time is equal to the length of a critical path, so in this case it is 32 days. We now apply the algorithm. STEP 1 minimum completion time: 132 days. STEP 2 We consider each vertex in turn. Vertex 10 There is only one arc incident from this 10-11-090,1 = 32 Similarly We give a formal statement of the algorithm, and then illustrate its use We assume that the network involves n activities. We regard the START vertex as the oth vertex and the FINISH vertex as the (11 + 1)th The duration of activity i represented by the arc ij is denoted by Cije The algorithm assigns labels Pj and e; to each vertex , for j = 0, 1, ..., . We adopt the following . Conventions vertex. 1 in + 1. When the algorithm has been completed: e; is the length of the longest path from the START vertex to vertex j; p, is the number of the preceding vertex on this longest path. W ca re ea Critical path construction algorithm 585 Part A: labelling procedure STEP 1 Assign to the START vertex (vertex 0) the labels po = 0 and eo = 0. STEP 2 Carry out the following procedure for each vertex j, starting with j = 1 and continuing with j = 2, j = 3, and so on, until all the vertices (including the FINISH vertex, corresponding to j = 1 + I) have been labelled. 26 Vela Welabel the START vertex with Po= 0 and = 0 For the current vertex j. calculate, for each arc de to Choose the maximum value of these sums for all ach aresi, and Set P. equal to the value of i for which this sum is largest in the case of a tie, choose any of the appropriate values STEP 3 Start with the FINISH vertex 1 + 1, and mark the arc joining this STEP 4 Consider the vertex j from which the last marked arc is incident. Mark the arc joining this vertex to the preceding vertex Py vertex ], the sume + sete, equal to this value Part B: tracing back procedure to the Pn+ Repeat until the START vertex is reached. STOP, The marked arcs form a critical path. The sum of the weights on the ares of the critical path is the minimum completion time, and is given by the value of 1 We illustrate the above procedure by an example. Worked problem 3.2 Find a critical path in the following activity network for the building construction example, using the critical path construction algorithm. 10 E 10 START 2 2 FINISH 15 activity network for building construction Solution Part A:labelling procedure STEP 1 STEP 2 We consider cash P=0 Vertext are numbered in such a way that each activity is assigned a number ding vertices. The activities greater than the number assigned to any activity which must precede it. Part B of the algorithm is a procedure for drawing the activity network, STEP 2 Delete all numbered vertices, their corresponding shadow If not all the vertices have been numbered, return to Step 1. Werson for De TO STEP Y R Activity network construction algorithm Part A: procedure for numbering the vertices START Represent each activity by a vertex. For each vertex, create a shadow vertex, so that for each activity there are two corresponding vertices - the original vertex and the shadow vertex. Construct a bipartite graph in which one set of vertices consists of the original vertices, and the other set consists of the shadow STARS F vertices. The active We illust network original vertices A. shadow vertices OA OB Worked Construc the abo- repeated Co activity No ON A prep If an activity Y must follow an activity X, draw an edge joining the original vertex representing Y to the shadow vertex representing X Bmal Clay Dinst X OX YO Eeres F pla Gere STEP 1 Number consecutively all the original vertices (chosen in any order) which have no edges incident with them. Record the numbering, together with the iteration number. Hins 1 fit vertices, and all edges incident with these vertices. pa If all the vertices have been numbered, go to Part B. Step 3. 18 Dinstall services and fittings Part B: procedure for drawing the activity network STEP 3 Draw a START vertex, and the vertices numbered in the Draw an arc from the START vertex to each vertex which was STEP 4 Draw the vertices which were numbered in the next iteration To each such vertex Y, draw an arc from each previously numbered vertex X if there is an edge joining the original vertex Y to the shadow vertex X in the original bipartite graph Construct an activity network for the building construction example, using the above algorithm. The activities and precedence relations are iteration numbered in the first Assign a weight of zero to each arc. activity X. constructed in Part A Assign a weight to each arc XY equal to the duration of the Repeat until all vertices have been included in the activity network STEP 5 Draw a FINISH vertex. From each terminal vertex Z (that is, each vertex whose out- degree is zero), draw an arc to the FINISH vertex. Assign a weight to each such are equal to the duration of the corresponding activity Z. STOP. The activity network has now been constructed. We illustrate the above procedure by using it to construct an activity network for the building construction example. Worked problem 3.1 repeated below. activity duration (in days) preceding activities A prepare foundations B make and position doorframe Clay drains, floor base and screed 7 2 E 15 erest
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


