Question: Part B. Using the traditional? method, which bases decisions solely on a? product's contribution to profits and? overhead, what is the optimal product mix and


Part B.
Using the traditional? method, which bases decisions solely on a? product's contribution to profits and? overhead, what is the optimal product mix and what is the overall? profitability?
Part C.
Using the bottleneck method, which bases decisions solely on a? product's contribution to profits and? overhead, what is the optimal product mix and what is the overall? profitability?
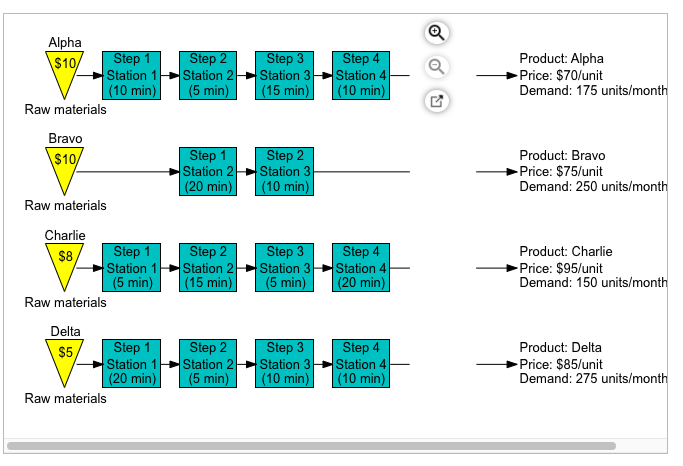
Cooper River Glass Works (CRGW) produces four different models of desk lamps as shown on the flowchart. The operations manager knows that total monthly demand exceeds the capacity available for production. Thus, she is interested in determining the product mix which will maximize profits. Each model's price, routing, processing times, and material cost is provided in the flowchart. Demand next month is estimated to be 175 units of model Alpha, 250 units of model Bravo, 150 units of model Charlie, and 275 units of model Delta. CRGW operates only one 8 hours shift per day and is scheduled to work 20 days next month (no overtime). Further, each station requires a 10% capacity cushion. Click the icon to view the Cooper River Glass Works Flowchart. Step 1 Alpha $10/ Station 1 (10 min) Raw materials Step 2 Station 2 (5 min) Step 3 Station 3 (15 min) Step 4 Station 4 (10 min) Product: Alpha Price: $70/unit Demand: 175 units/month Bravo $10/ Step 1 Station 2 (20 min) Step 2 Station 3 (10 min) Product: Bravo Price: $75/unit Demand: 250 units/month Raw materials Step 2 Station 2 (15 min) Step 3 Station 3 (5 min) Step 4 Station 4 (20 min) Product: Charlie Price: $95/unit Demand: 150 units/month Charlie $8 Step 1 Station 1 (5 min) Raw materials Delta $5 Step 1 Station 1 (20 min) Raw materials Step 2 Station 2 (5 min) Step 3 Station 3 (10 min) Step 4 Station 4 (10 min) Product: Delta Price: $85/unit Demand: 275 units/month Cooper River Glass Works (CRGW) produces four different models of desk lamps as shown on the flowchart. The operations manager knows that total monthly demand exceeds the capacity available for production. Thus, she is interested in determining the product mix which will maximize profits. Each model's price, routing, processing times, and material cost is provided in the flowchart. Demand next month is estimated to be 175 units of model Alpha, 250 units of model Bravo, 150 units of model Charlie, and 275 units of model Delta. CRGW operates only one 8 hours shift per day and is scheduled to work 20 days next month (no overtime). Further, each station requires a 10% capacity cushion. Click the icon to view the Cooper River Glass Works Flowchart. a. Which station is the bottleneck? The bottleneck is with a total load of minutes for the next month. (Enter your response as a whole number.)Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


