Question: Part Two Net Present Value Method Net present value (NPV) e used to evaluate the financial viability of potential projects. It determines the present value
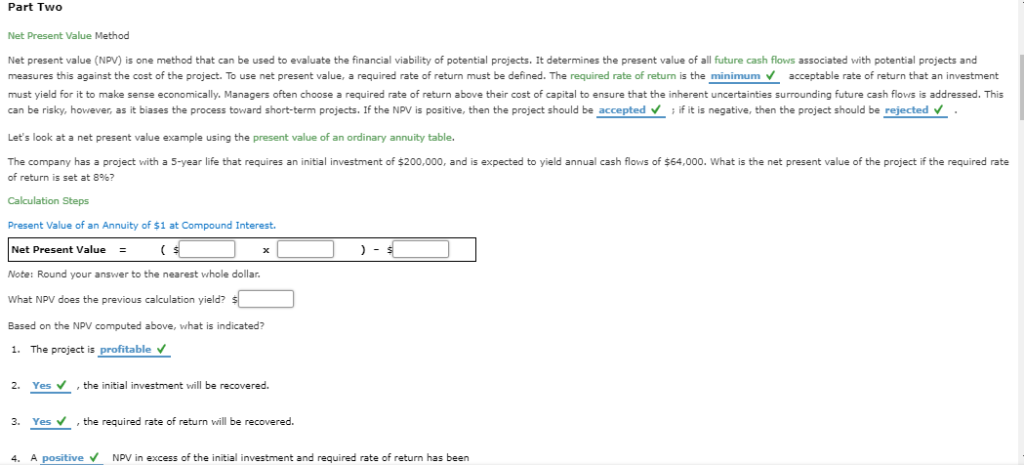
Part Two Net Present Value Method Net present value (NPV) e used to evaluate the financial viability of potential projects. It determines the present value of all future cash flows associated with potential projects and one method that can measures this against the cost of the project. To use net present value, a required rate of return must be defined. The required rate return is the minimum acceptable rate of return that an investment must yield for it to make sense economically. Managers often choose a required rate of return above their cost of capital to ensure that the inherent uncertainties surrounding future cash flows is addressed. This can be risky, however, as it biases the process toward short-term projects. If the NPV positive, then the project should be accepted if it is negative, then the project should be rejected Let's look at a net present value example using the present value of an ordinary annu ity table. The company has a project with a 5-year life that requires an initial investment of $200,000, and is expected to yield annual cash flows of $64,000. What is the net present value of the project if the required rate of return is set at 8%? Calculation Steps Present Value of an Annuity of $1 at Compound Interest. Net Present Value ) - Note: Round vour answer to the nearest whole dollar. What NPV does the previous calculation yield? s Based on the NPV computed above, what indicated? 1. The project is profitable ,the initial investment will be recovered. 2. Yes Yes the required rate of return will be recovered. 3 positive NPV in excess of the initial investment and required rate Freturn has been 4
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


