Question: Partial deriv Q Consider the function f(2, y) = =2+ 2xy+ 2y3 Answer the questions below in the space provided (8 subquestions). Vf(1, 1) The
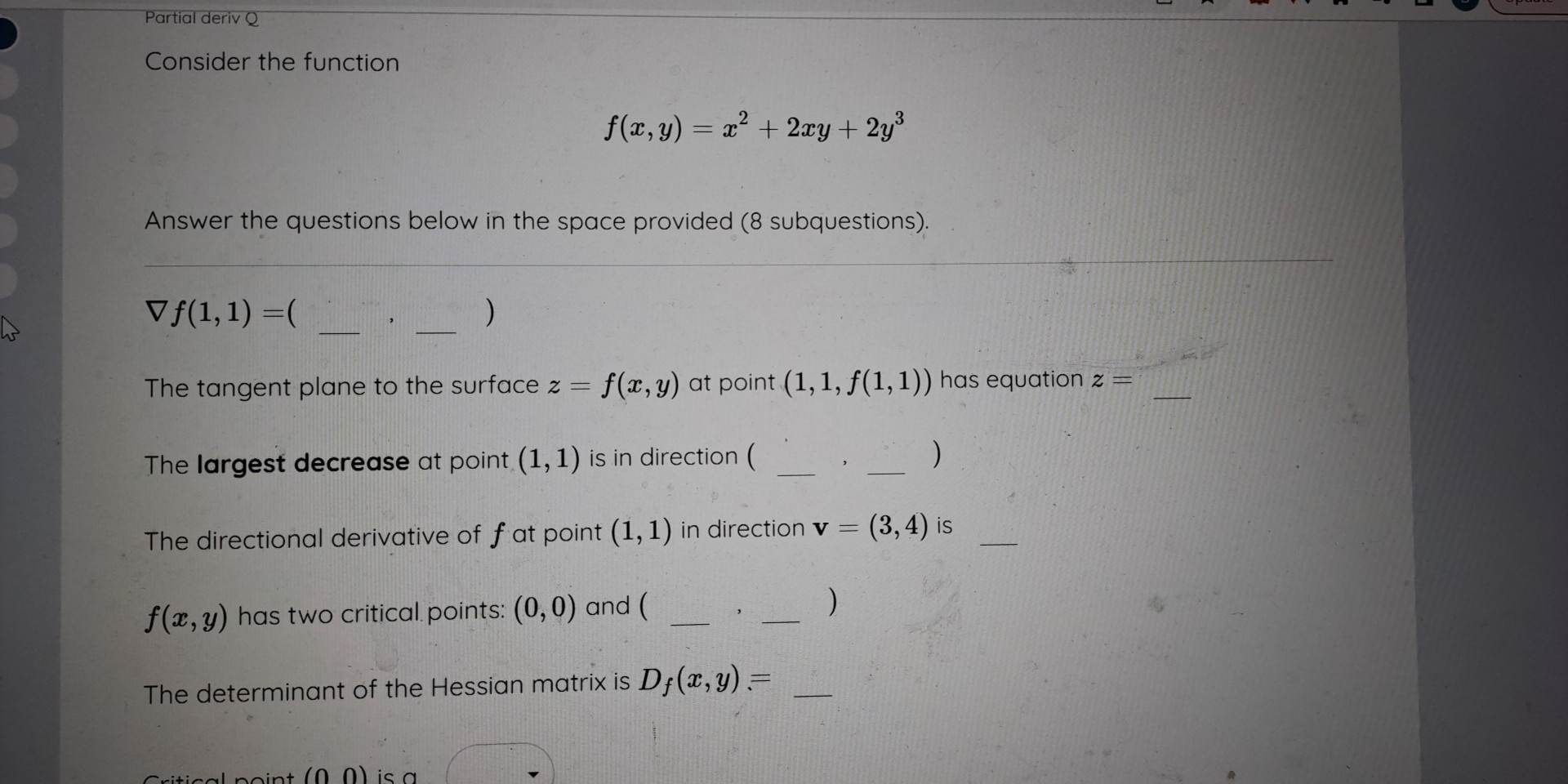
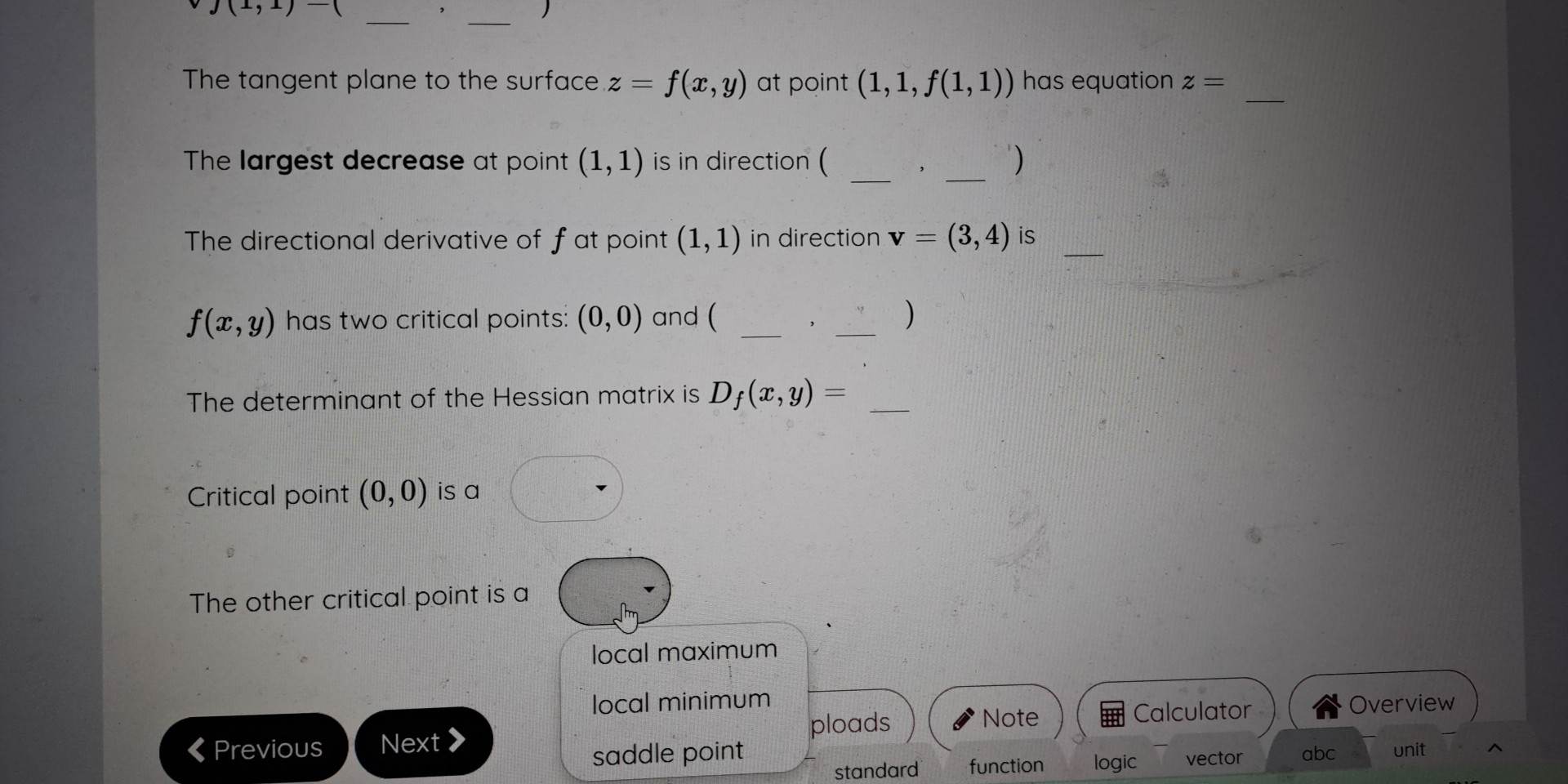
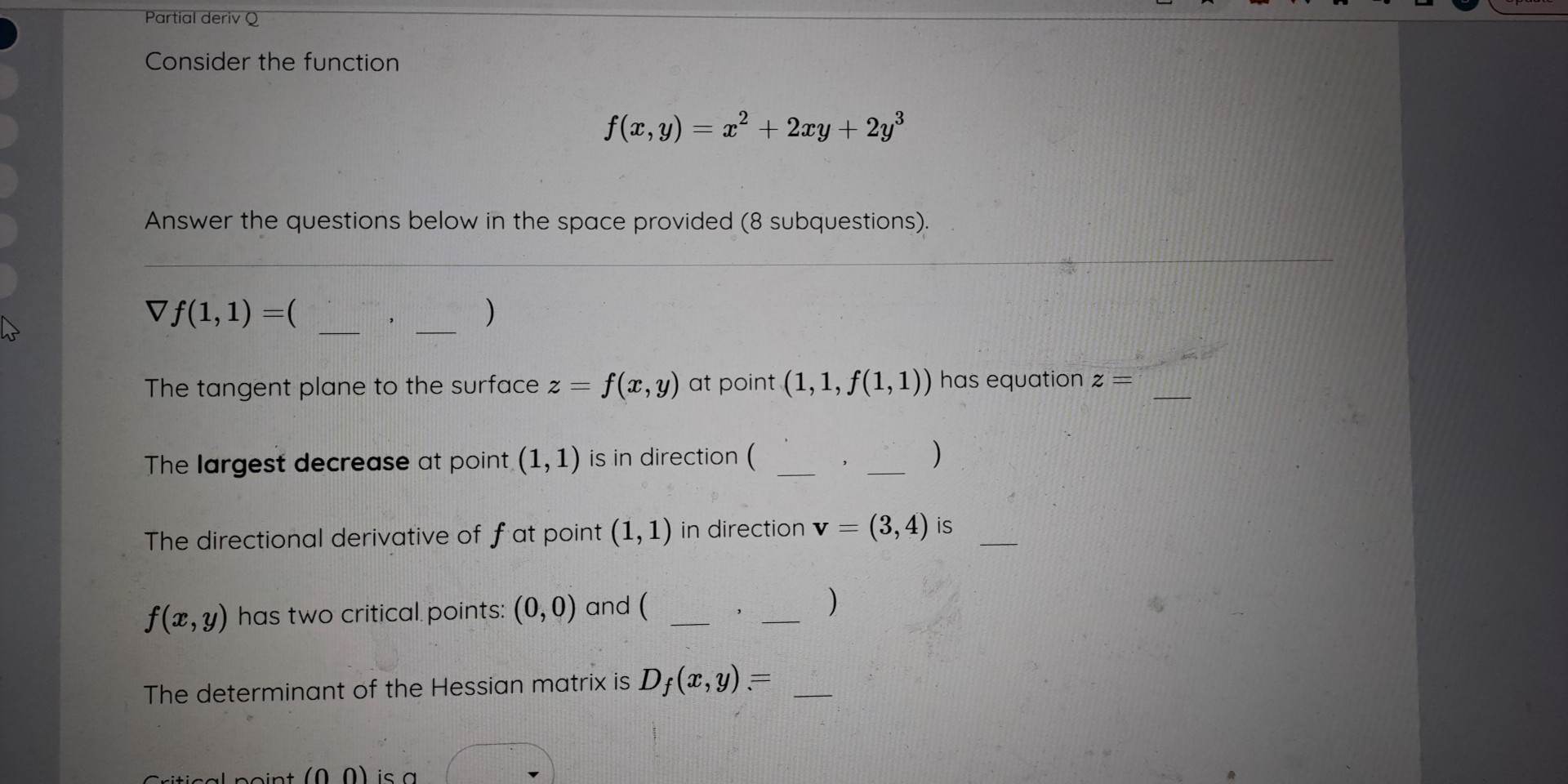

Partial deriv Q Consider the function f(2, y) = =2+ 2xy+ 2y3 Answer the questions below in the space provided (8 subquestions). Vf(1, 1) The tangent plane to the surface z = f(x, y) at point (1, 1, f(1, 1) ) has equation z = The largest decrease at point (1, 1) is in direction ( The directional derivative of f at point (1, 1) in direction v = (3, 4) is f(x, y) has two critical points: (0, 0) and ( The determinant of the Hessian matrix is D; (x, y) =The tangent plane to the surface z = f(x, y) at point (1, 1, f(1, 1) ) has equation z = The largest decrease at point (1, 1) is in direction ( The directional derivative of f at point (1, 1) in direction v = (3, 4) is f(x, y) has two critical points: (0, 0) and ( The determinant of the Hessian matrix is D; (x, y) = Critical point (0, 0) is a The other critical point is a local maximum local minimum ploads Note Calculator Overview saddle point standard function logic vector abc unit
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


