Question: Perform each hexadecimal operation. A 3 B 1 6 ( d ) A 3 B 1 6 ( e ) 9 1 B 1 6
Perform each hexadecimal operation. ABd ABe B
a
b
d
e B
a How many different logic outputs are required to represent an bit binary number
using parallel representation?
b How many are required using serial representation?
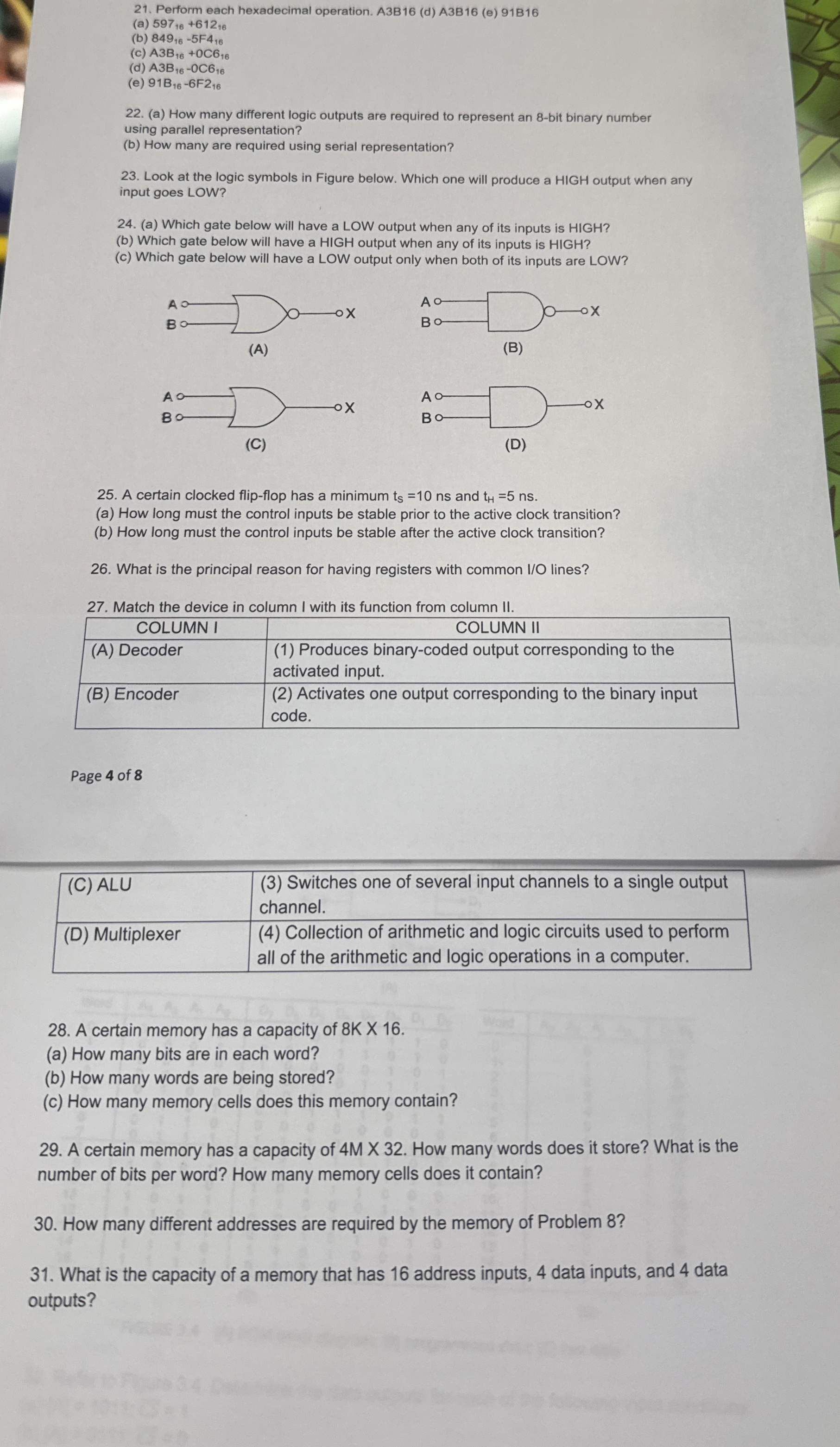
Look at the logic symbols in Figure below. Which one will produce a HIGH output when any
input goes LOW?
a Which gate below will have a LOW output when any of its inputs is HIGH?
b Which gate below will have a HIGH output when any of its inputs is HIGH?
c Which gate below will have a LOW output only when both of its inputs are LOW?
A certain clocked flipflop has a minimum and
a How long must the control inputs be stable prior to the active clock transition?
b How long must the control inputs be stable after the active clock transition?
What is the principal reason for having registers with common IO lines?
Match the device in column I with its function from column II
Page of
A certain memory has a capacity of
a How many bits are in each word?
b How many words are being stored?
c How many memory cells does this memory contain?
A certain memory has a capacity of How many words does it store? What is the
number of bits per word? How many memory cells does it contain?
How many different addresses are required by the memory of Problem
What is the capacity of a memory that has address inputs, data inputs, and data
outputs?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


