Question: Pg 216: 6.3: Write a postorder traversal function for general trees, similar to the preorder traversal function named preorder given in Section 6.1.2. R E

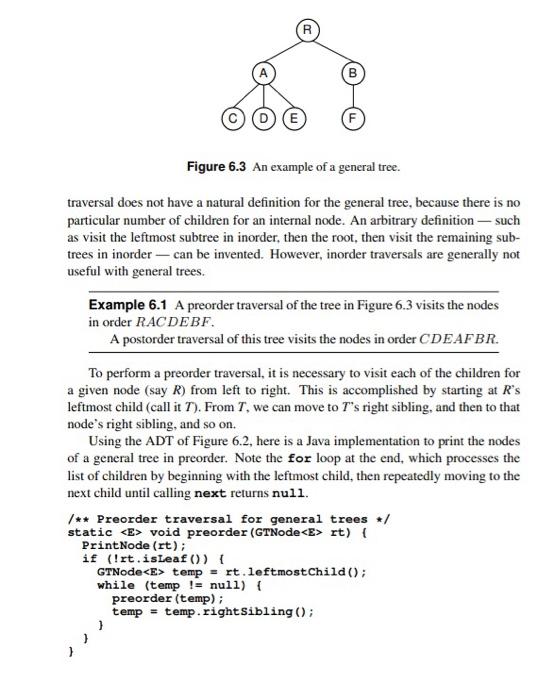
Pg 216: 6.3: Write a postorder traversal function for general trees, similar to the preorder traversal function named preorder given in Section 6.1.2. R E Figure 6.3 An example of a general tree. traversal does not have a natural definition for the general tree, because there is no particular number of children for an internal node. An arbitrary definition - such as visit the leftmost subtree in inorder, then the root, then visit the remaining sub- trees in inorder - can be invented. However, inorder traversals are generally not useful with general trees. Example 6.1 A preorder traversal of the tree in Figure 6.3 visits the nodes in order RAC DEBF A postorder traversal of this tree visits the nodes in order CDEAFBR. To perform a preorder traversal, it is necessary to visit each of the children for a given node (say R) from left to right. This is accomplished by starting at R's leftmost child (call it T). From T, we can move to T's right sibling, and then to that node's right sibling, and so on. Using the ADT of Figure 6.2, here is a Java implementation to print the nodes of a general tree in preorder. Note the for loop at the end, which processes the list of children by beginning with the leftmost child, then repeatedly moving to the next child until calling next returns null /** Preorder traversal for general trees */ static
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


