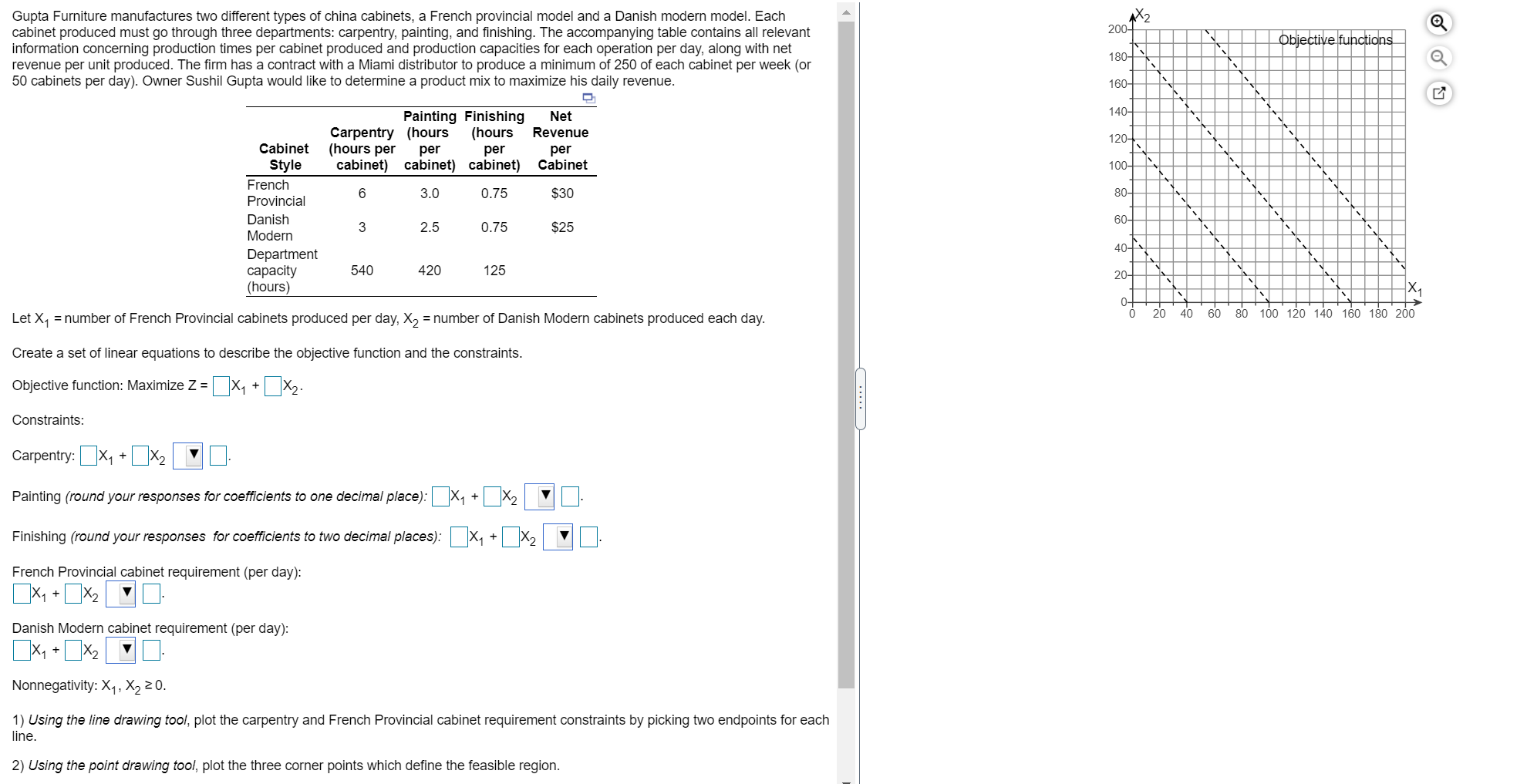
Question: PLEASE ANSWER ALL PARTS PART A PART B X2 200- Obiective functions Gupta Furniture manufactures two different types of china cabinets, a French provincial model
PLEASE ANSWER ALL PARTS
PART A

PART B

X2 200- Obiective functions Gupta Furniture manufactures two different types of china cabinets, a French provincial model and a Danish modern model. Each cabinet produced must go through three departments: carpentry, painting, and finishing. The accompanying table contains all relevant information concerning production times per cabinet produced and production capacities for each operation per day, along with net revenue per unit produced. The firm has a contract with a Miami distributor to produce a minimum of 250 of each cabinet per week (or 50 cabinets per day). Owner Sushil Gupta would like to determine a product mix to maximize his daily revenue. 180- 160- 140- Painting Finishing Carpentry (hours (hours (hours per per per cabinet) cabinet) cabinet) Net Revenue per Cabinet 120- 100- 6 3.0 0.75 $30 80- Cabinet Style French Provincial Danish Modern Department capacity (hours) 60- 3 2.5 0.75 $25 - 40-1 540 420 125 20- X1 0- 0 1-7 st 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 Let X1 = number of French Provincial cabinets produced per day, X2 = number of Danish Modern cabinets produced each day. Create a set of linear equations to describe the objective function and the constraints. Objective function: Maximize Z = x1 + x2 + ..... Constraints: Carpentry: Oxy + x2 + Painting (round your responses for coefficients to one decimal place): [X1 Finishing (round your responses for coefficients to two decimal places): (x2 + x2 French Provincial cabinet requirement (per day): x1 + x2 Danish Modern cabinet requirement (per day): x1 + x2 Nonnegativity: X1, X220. 1) Using the line drawing tool, plot the carpentry and French Provincial cabinet requirement constraints by picking two endpoints for each line. 2) Using the point drawing tool, plot the three corner points which define the feasible region. Do not plot the nonnegativity constraints. The optimal solution is X1 = and X2 = [ (enter your responses as whole numbers). Maximum revenue is $ per day (round your response to the nearest whole dollar). X2 o 400- Andy's Bicycle Company (ABC) has the hottest product on the upscale toy market - boy's and girl's bikes in bright fashion colors, with oversize hubs and axles; shell design safety tires; strong padded frames; chrome-plated chains, brackets and valves; and nonslip handlebars. Due to the seller's market for high-quality toys for the newest baby boomers, ABC can sell all the bicycles it manufactures at the following prices: boy's bikes, $220; girl's bikes, $175. This is the price payable to ABC at this Orlando plant. Objective functions 320- LY The firm's accountant, V.R.Dondeti, has determined that direct labor costs will be 45% of the price that ABC receives for the boys' model and 40% of the price received for the girls' model. Production costs, other than labor but excluding painting and packaging, are $44 per boys' bicycle and $30 per girls' bicycle. Painting and packaging are $20 per bike, regardless of model. The Orlando plant's overall production capacity is 390 bicycles per day. Each boys' bike requires 2.5 labor-hours, each girls' model 2.4 hours. ABC currently employs 120 workers, each of whom puts in a 8-hour day. The firm has no desire to hire or fire to affect labor availability, for it believes its stable workforce is one of its biggest assets. Using a graphing approach, determine the best product mix for ABC. 240- 160- Let X1 = number of boy's bicycles produced per day, X2 = number of girl's bicycles produced per day. 80- Create a set of linear equations to describe the objective function and the constraints. Objective function: Maximize z = [X1 + x2. 0- 0 100 200 300 400 Constraints: Overall production capacity: x2 + x2 . Labor: x1 + x2 Nonnegativity: X1, X2 20. Using the line drawing tool, plot the overall production capacity constraint by picking two endpoints for the line







