Question: Please answer B B I Paste 3 U V 9 D58 XV fox B D E F G H 7 Shrieves Hospital Ltd. is considering

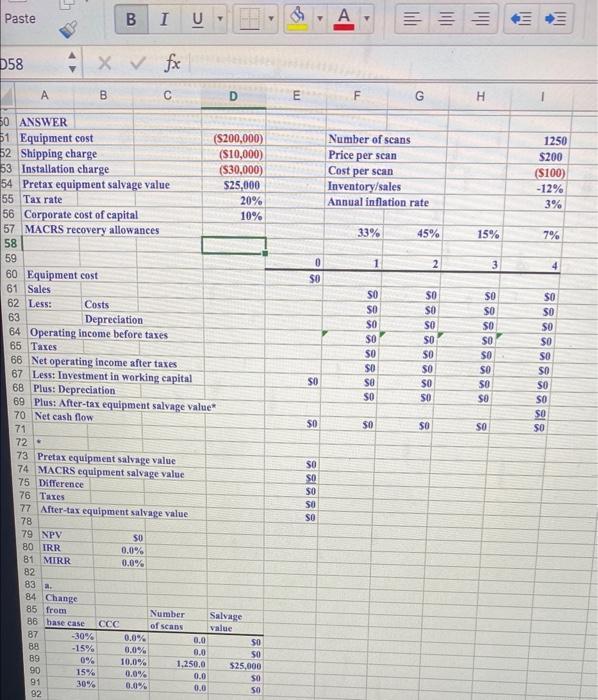
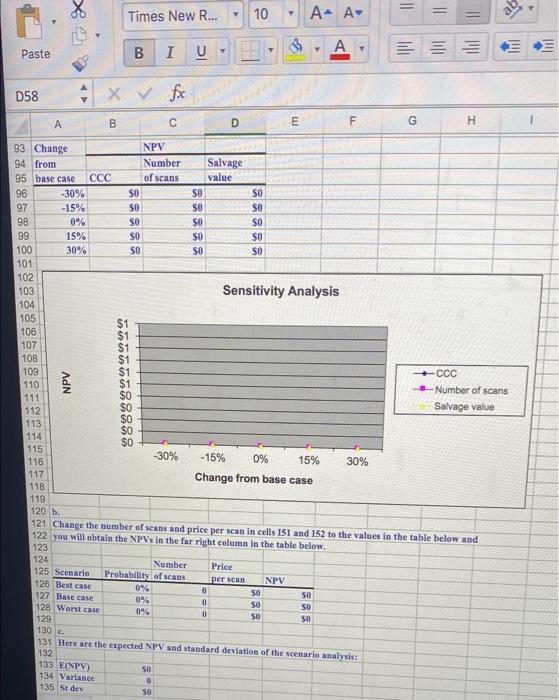
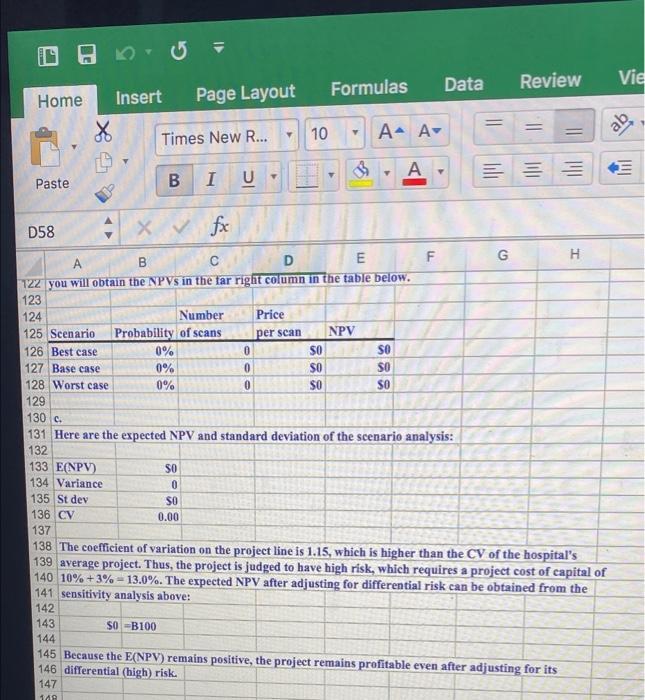
B B I Paste 3 U V 9 D58 XV fox B D E F G H 7 Shrieves Hospital Ltd. is considering adding a new line to its diagnostic product mix, and the capital 8 budgeting analysis is being conducted by Sidney Johnson, a recently graduated MHA. A new bone density scanner would be set up in unused space in Shrieves's main clinic. The machinery's invoice price would be 10 approximately $200,000; another $10,000 in shipping charges would be required; and it would cost an 11 additional S30,000 to install the equipment. The machinery has an economic life of four years, and Shrieves 12 has obtained a special tax ruling which places the equipment in the MACRS three-year class. The machinery 13 is expected to have a salvage value of $25,000 after four years of use. The new line would generate 14 incremental sales of 1,250 scans per year for four years at an incremental cost of $100 per scan in the 15 first year, excluding depreciation. Each scan would generate revenue of $200 in the first year. The price 16 and cost of each scan are expected to increase by 3 percent per year due to inflation. Further, to handle 17 the new line, the hospital's net operating working capital would have to increase by an amount equal to 12 18 percent of sales revenues. The hospital's tax rate is 20 percent, and its corporate cost of capital is 10 19 percent. 20 21 2. Perform a sensitivity analysis on the corporate cost of capital, number of seans, and salvage value. Assume that each of these variables can vary from its base case by plus and minus 15 and 30 percent. 23 Include a sensitivity diagram. 24 b. Perform a scenario analysis using the worst-, most likely, and best-case probabilities in the table below: 25 26 Number of Price Scenario Probability seans 28 Best 25% 1,600 29 Most likely 50% 1,250 $200 30 Worst 25% 900 $160 31 32 c. Assume that Shrieves's average project has a coefficient of variation of NPV in the range of 0.2-0.4. 33 The hospital typically adds or subtracts 3 percentage points to its corporate cost of capital to adjust for 34 risk. Should the new line be accepted? 35 22 27 per scan $240 36 - 37 In the section entitled "Changes in Net Working Capital in Chapter 11, Gapenski states that expansion 38 projects require additional inventories and accounts receivable which must be financed, just as an increase 39 in fixed assets must be financed. In this situation, the hospital's net working capital would have to increase 40 by an amount equal to 12 percent of sales. Sales in Year 1 are estimated at $250,000, so Shrieves must 41 have (.12 $250,000 ) 30,000 in net working capital at Year 0. If sales increase to S257,500 in Year 2, 42 Shrieves must have ( 12 * $257,500 -) 30,900 at Year 1. Because it already has $30,000 of net working 43 capital on hand, its net investment in working capital at Year 1 is just ($30,900 - $30,000) 5900. If sales 44 Increase to $265,225 in Year 3. Its net investment in working capital in Year 2 is (:12 265,225 ) 45 $31, 827-530,900 = 5927. If sales increase to $273.182 in Year 4, its net investment in working capital 46 In Year 3 is (.12 * 273,182) 532,782 - $31,827 5955. Shrleves will have no sales after Year 4, so it will 47 require no working capital at Year 4. Thus, it would have a positive cash flow of 32,782 at Year 4 as 48 working capital is sold but not replaced. 49 Paste B I U Inl D58 x fx V B D E F G H . Number of scans Price per scan Cost per scan Inventory/sales Annual inflation rate 1250 $200 ($100) -12% 3% 33% 45% 15% 7% 1 2 3 4 0 SO SO SO SO $0 SO SO SO SO SO SO SO SO SO 50 SO SO SO SO SO SO 50 se SO SO SO $0 SO SO SO SO SO $0 SO 30 ANSWER 51 Equipment cost (S200,000) 52 Shipping charge ($10,000) 53 Installation charge ($30,000) 54 Pretax equipment salvage value $25,000 55 Tax rate 20% 56 Corporate cost of capital 10% 57 MACRS recovery allowances 58 59 60 Equipment cost 61 Sales 62 Less: Costs 63 Depreciation 64 Operating income before taxes 65 Taxes 66 Net operating income after taxes 67 Less: Investment in working capital 68 Plus: Depreciation 69 Plus: After-tax equipment salvage value* 70 Net cash flow 71 72 73 Pretax equipment salvage value 74 MACRS equipment salvage value 75 Difference 76 Taxes 77 After-tax equipment salvage value 78 79 NPV SO 80 IRR 0.0% 81 MIRR 0.0% 82 83 a. 84 Change 85 from Number Salvage 36 base case of scans value -30% 0.0% 0.0 88 -15% 0.0% SO 89 0% 10.0% 1.250.0 $25,000 90 15% 0.0% SO 91 30% 0.0% SO 92 SO SO SO so 8 SO SO SO 88888 87 SO ee 0.0 0.0 0.0 10 Times New R... . = A- A+ ab I B Paste Inil A U E D58 X fx > B D E E F G G H SSSSS 93 Change NPV 94 from Number Salvage 95 base case CCC of scans value 96 -30% SO SO SO 97 -15% SO SO 98 0% SO so 99 15% SO $0 100 30% SO SO 101 102 103 Sensitivity Analysis 104 105 106 107 10B 109 - 110 Number of scans 111 112 Salvage value 113 114 115 116 -15% 0% 15% 30% 117 Change from base case 118 119 120 b. 121 Change the number of seans and price per scan in cells 151 and 152 to the values in the table below and 122 you will obtain the NPVs in the far right column in the table below. 123 124 Number Price 125 Scenario Probability of scans 126 Best case per scan NPV 0 127 Base case SO $ 0% 0 128 Worst case 50 0% 0 129 SO NPV Tiina8888 -30% 0% 3331 130 C 131 Here are the expected NPV and standard deviation of the scenario analysis: 132 133 ENPV) $0 134 Variance 0 135 Stdev $0 Data Vie Review Formulas Home Insert Page Layout 10 Times New R... ab A A A Paste === I B U D58 X foc m F G H H B D 122 you will obtain the NPVs in the far right column in the table below. 123 124 Number Price 125 Scenario Probability of scans per scan NPV 126 Best case 0% 0 SO so 127 Base case 0% 0 SO SO 128 Worst case 0% 0 SO SO 129 130 c. 131 Here are the expected NPV and standard deviation of the scenario analysis: 132 133 E(NPV) SO 134 Variance 0 135 St dev SO 136 CV 0.00 137 138 The coefficient of variation on the project line is 1.15, which is higher than the CV of the hospital's 139 average project. Thus, the project is judged to have high risk, which requires a project cost of capital of 140 10% +3% - 13.0%. The expected NPV after adjusting for differential risk can be obtained from the 141 sensitivity analysis above: 142 143 SO B100 144 145 Because the E(NPV) remains positive, the project remains profitable even after adjusting for its 146 differential (high) risk. 147 100 B B I Paste 3 U V 9 D58 XV fox B D E F G H 7 Shrieves Hospital Ltd. is considering adding a new line to its diagnostic product mix, and the capital 8 budgeting analysis is being conducted by Sidney Johnson, a recently graduated MHA. A new bone density scanner would be set up in unused space in Shrieves's main clinic. The machinery's invoice price would be 10 approximately $200,000; another $10,000 in shipping charges would be required; and it would cost an 11 additional S30,000 to install the equipment. The machinery has an economic life of four years, and Shrieves 12 has obtained a special tax ruling which places the equipment in the MACRS three-year class. The machinery 13 is expected to have a salvage value of $25,000 after four years of use. The new line would generate 14 incremental sales of 1,250 scans per year for four years at an incremental cost of $100 per scan in the 15 first year, excluding depreciation. Each scan would generate revenue of $200 in the first year. The price 16 and cost of each scan are expected to increase by 3 percent per year due to inflation. Further, to handle 17 the new line, the hospital's net operating working capital would have to increase by an amount equal to 12 18 percent of sales revenues. The hospital's tax rate is 20 percent, and its corporate cost of capital is 10 19 percent. 20 21 2. Perform a sensitivity analysis on the corporate cost of capital, number of seans, and salvage value. Assume that each of these variables can vary from its base case by plus and minus 15 and 30 percent. 23 Include a sensitivity diagram. 24 b. Perform a scenario analysis using the worst-, most likely, and best-case probabilities in the table below: 25 26 Number of Price Scenario Probability seans 28 Best 25% 1,600 29 Most likely 50% 1,250 $200 30 Worst 25% 900 $160 31 32 c. Assume that Shrieves's average project has a coefficient of variation of NPV in the range of 0.2-0.4. 33 The hospital typically adds or subtracts 3 percentage points to its corporate cost of capital to adjust for 34 risk. Should the new line be accepted? 35 22 27 per scan $240 36 - 37 In the section entitled "Changes in Net Working Capital in Chapter 11, Gapenski states that expansion 38 projects require additional inventories and accounts receivable which must be financed, just as an increase 39 in fixed assets must be financed. In this situation, the hospital's net working capital would have to increase 40 by an amount equal to 12 percent of sales. Sales in Year 1 are estimated at $250,000, so Shrieves must 41 have (.12 $250,000 ) 30,000 in net working capital at Year 0. If sales increase to S257,500 in Year 2, 42 Shrieves must have ( 12 * $257,500 -) 30,900 at Year 1. Because it already has $30,000 of net working 43 capital on hand, its net investment in working capital at Year 1 is just ($30,900 - $30,000) 5900. If sales 44 Increase to $265,225 in Year 3. Its net investment in working capital in Year 2 is (:12 265,225 ) 45 $31, 827-530,900 = 5927. If sales increase to $273.182 in Year 4, its net investment in working capital 46 In Year 3 is (.12 * 273,182) 532,782 - $31,827 5955. Shrleves will have no sales after Year 4, so it will 47 require no working capital at Year 4. Thus, it would have a positive cash flow of 32,782 at Year 4 as 48 working capital is sold but not replaced. 49 Paste B I U Inl D58 x fx V B D E F G H . Number of scans Price per scan Cost per scan Inventory/sales Annual inflation rate 1250 $200 ($100) -12% 3% 33% 45% 15% 7% 1 2 3 4 0 SO SO SO SO $0 SO SO SO SO SO SO SO SO SO 50 SO SO SO SO SO SO 50 se SO SO SO $0 SO SO SO SO SO $0 SO 30 ANSWER 51 Equipment cost (S200,000) 52 Shipping charge ($10,000) 53 Installation charge ($30,000) 54 Pretax equipment salvage value $25,000 55 Tax rate 20% 56 Corporate cost of capital 10% 57 MACRS recovery allowances 58 59 60 Equipment cost 61 Sales 62 Less: Costs 63 Depreciation 64 Operating income before taxes 65 Taxes 66 Net operating income after taxes 67 Less: Investment in working capital 68 Plus: Depreciation 69 Plus: After-tax equipment salvage value* 70 Net cash flow 71 72 73 Pretax equipment salvage value 74 MACRS equipment salvage value 75 Difference 76 Taxes 77 After-tax equipment salvage value 78 79 NPV SO 80 IRR 0.0% 81 MIRR 0.0% 82 83 a. 84 Change 85 from Number Salvage 36 base case of scans value -30% 0.0% 0.0 88 -15% 0.0% SO 89 0% 10.0% 1.250.0 $25,000 90 15% 0.0% SO 91 30% 0.0% SO 92 SO SO SO so 8 SO SO SO 88888 87 SO ee 0.0 0.0 0.0 10 Times New R... . = A- A+ ab I B Paste Inil A U E D58 X fx > B D E E F G G H SSSSS 93 Change NPV 94 from Number Salvage 95 base case CCC of scans value 96 -30% SO SO SO 97 -15% SO SO 98 0% SO so 99 15% SO $0 100 30% SO SO 101 102 103 Sensitivity Analysis 104 105 106 107 10B 109 - 110 Number of scans 111 112 Salvage value 113 114 115 116 -15% 0% 15% 30% 117 Change from base case 118 119 120 b. 121 Change the number of seans and price per scan in cells 151 and 152 to the values in the table below and 122 you will obtain the NPVs in the far right column in the table below. 123 124 Number Price 125 Scenario Probability of scans 126 Best case per scan NPV 0 127 Base case SO $ 0% 0 128 Worst case 50 0% 0 129 SO NPV Tiina8888 -30% 0% 3331 130 C 131 Here are the expected NPV and standard deviation of the scenario analysis: 132 133 ENPV) $0 134 Variance 0 135 Stdev $0 Data Vie Review Formulas Home Insert Page Layout 10 Times New R... ab A A A Paste === I B U D58 X foc m F G H H B D 122 you will obtain the NPVs in the far right column in the table below. 123 124 Number Price 125 Scenario Probability of scans per scan NPV 126 Best case 0% 0 SO so 127 Base case 0% 0 SO SO 128 Worst case 0% 0 SO SO 129 130 c. 131 Here are the expected NPV and standard deviation of the scenario analysis: 132 133 E(NPV) SO 134 Variance 0 135 St dev SO 136 CV 0.00 137 138 The coefficient of variation on the project line is 1.15, which is higher than the CV of the hospital's 139 average project. Thus, the project is judged to have high risk, which requires a project cost of capital of 140 10% +3% - 13.0%. The expected NPV after adjusting for differential risk can be obtained from the 141 sensitivity analysis above: 142 143 SO B100 144 145 Because the E(NPV) remains positive, the project remains profitable even after adjusting for its 146 differential (high) risk. 147 100
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


