Question: Please answer E, F, G only. Digital Controls, Inc. (DCI) manufactures two models of a radar gun used by police to monitor the speed of


Please answer E, F, G only.
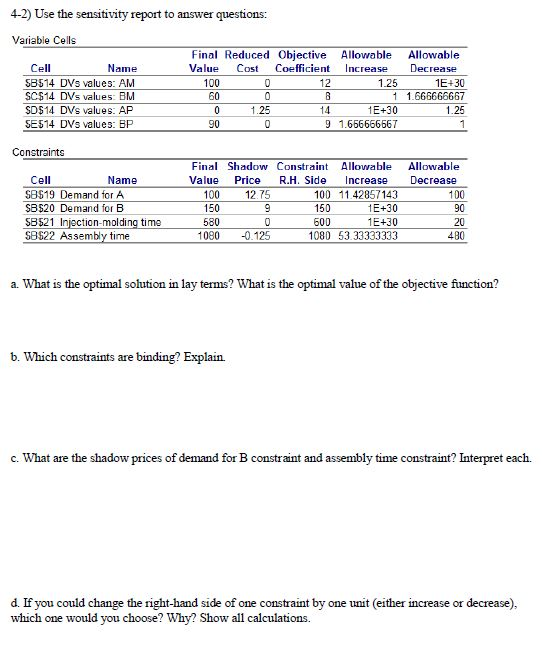
Digital Controls, Inc. (DCI) manufactures two models of a radar gun used by police to monitor the speed of automobiles. Model A has an accuracy of plus or minus 1 mile per hour, whereas the smaller model B has an accuracy of plus or minus 3 miles per hour. For the next week the company has orders for 100 units of model A and 150 units of model B. Although DCI purchases all the electronic components used in both models, the plastic cases for both models are manufactured at a DCI plant in Newark New Jersey. Each manufactured model A case requires 4 minutes of injection-molding time and 6 minutes of assembly time. Each manufactured model B case requires 3 minutes of injection-molding time and 8 minutes of assembly time. For next week the Newark plant has 600 minutes of injection-molding time available and 1080 minutes of assembly time available. The manufacturing cost is $12 per case for model A and $8 per case for model B. Depending upon demand and the time available at the Newark plant, DCI occasionally purchases cases for one or both models from an outside supplier in order to fill customer orders that could not be filled otherwise. The purchase cost is $14 for each model A case and $9 for each model B case. Management wants to develop a minimum cost plan that will determine how many cases of each model should be manufactured at the Newark plant and how many cases of each model should be purchased. The following decision variables were used to formulate a linear programming model for this problem (sensitivity report is provided on the next page): AM= number of cases of model A manufactured by DCI next week BM=number of cases of model B manufactured by DCI next week AP = number of cases of model A purchased by DCI next week BP = number of cases of model B purchased by DCI next week 4-1) Using decision variables defined above, formulate the problem: 4-2) Use the sensitivity report to answer questions: Variable Cells Cell Name SB514 DVS values: AM SC$14 DVs values: BM SC$14 DVs values: BM SD$14 DVS values: AP SE514 DVS values: BP Final Reduced Objective Value Cost Coefficient 100 0 12 6 00 B 0 1 .25 14 90 0 9 Allowable increase 1.25 1 1E+30 1.666666667 Allowable Decrease 1 E+30 1.666666667 1.25 1 Constraints Cell Name $B$19 Demand for A SB$20 Demand for B $B$21 Injection-molding time SB522 Assembly time Final Shadow Constraint Allowable Value Price R.H. Side Increase 100 12.75 100 11.42857143 150 9 1501E+30 580 0 6 00 1E+30 1080 -0.125 1080 53.33333333 Allowable Decrease 100 90 20 480 a. What is the optimal solution in lay terms? What is the optimal value of the objective function? 6. Which constraints are binding? Explain. c. What are the shadow prices of demand for B constraint and assembly time constraint? Interpret each. d. If you could change the right-hand side of one constraint by one unit (either increase or decrease), which one would you choose? Why? Show all calculations. e. State and interpret the ranges of optimality for any one of the objective function coefficients. f. Suppose that the mamfacturing cost decreases to $10.25 per case for model A. Would the optimal solution change? Would the optimal objective function value change? Show all calculations. g. Explain the meaning of reduced cost 1.25 in the sensitivity report. How can you use it? Digital Controls, Inc. (DCI) manufactures two models of a radar gun used by police to monitor the speed of automobiles. Model A has an accuracy of plus or minus 1 mile per hour, whereas the smaller model B has an accuracy of plus or minus 3 miles per hour. For the next week the company has orders for 100 units of model A and 150 units of model B. Although DCI purchases all the electronic components used in both models, the plastic cases for both models are manufactured at a DCI plant in Newark New Jersey. Each manufactured model A case requires 4 minutes of injection-molding time and 6 minutes of assembly time. Each manufactured model B case requires 3 minutes of injection-molding time and 8 minutes of assembly time. For next week the Newark plant has 600 minutes of injection-molding time available and 1080 minutes of assembly time available. The manufacturing cost is $12 per case for model A and $8 per case for model B. Depending upon demand and the time available at the Newark plant, DCI occasionally purchases cases for one or both models from an outside supplier in order to fill customer orders that could not be filled otherwise. The purchase cost is $14 for each model A case and $9 for each model B case. Management wants to develop a minimum cost plan that will determine how many cases of each model should be manufactured at the Newark plant and how many cases of each model should be purchased. The following decision variables were used to formulate a linear programming model for this problem (sensitivity report is provided on the next page): AM= number of cases of model A manufactured by DCI next week BM=number of cases of model B manufactured by DCI next week AP = number of cases of model A purchased by DCI next week BP = number of cases of model B purchased by DCI next week 4-1) Using decision variables defined above, formulate the problem: 4-2) Use the sensitivity report to answer questions: Variable Cells Cell Name SB514 DVS values: AM SC$14 DVs values: BM SC$14 DVs values: BM SD$14 DVS values: AP SE514 DVS values: BP Final Reduced Objective Value Cost Coefficient 100 0 12 6 00 B 0 1 .25 14 90 0 9 Allowable increase 1.25 1 1E+30 1.666666667 Allowable Decrease 1 E+30 1.666666667 1.25 1 Constraints Cell Name $B$19 Demand for A SB$20 Demand for B $B$21 Injection-molding time SB522 Assembly time Final Shadow Constraint Allowable Value Price R.H. Side Increase 100 12.75 100 11.42857143 150 9 1501E+30 580 0 6 00 1E+30 1080 -0.125 1080 53.33333333 Allowable Decrease 100 90 20 480 a. What is the optimal solution in lay terms? What is the optimal value of the objective function? 6. Which constraints are binding? Explain. c. What are the shadow prices of demand for B constraint and assembly time constraint? Interpret each. d. If you could change the right-hand side of one constraint by one unit (either increase or decrease), which one would you choose? Why? Show all calculations. e. State and interpret the ranges of optimality for any one of the objective function coefficients. f. Suppose that the mamfacturing cost decreases to $10.25 per case for model A. Would the optimal solution change? Would the optimal objective function value change? Show all calculations. g. Explain the meaning of reduced cost 1.25 in the sensitivity report. How can you use itStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


