Question: please answer questions 5, 6, &7 Why do things have to be so complicated? said Mark to Clive, as he sat at his desk shuffling


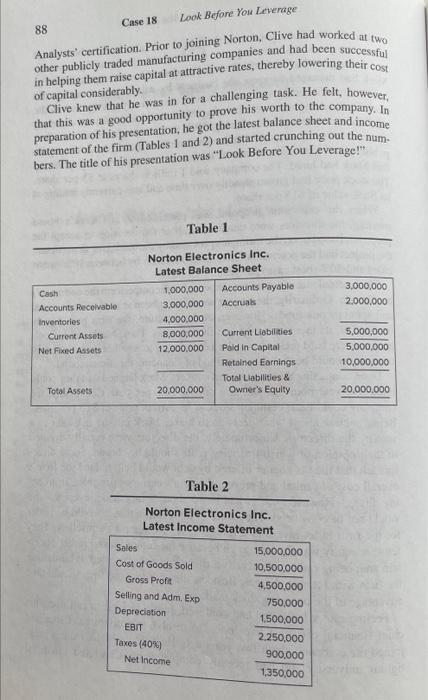

"Why do things have to be so complicated?" said Mark to Clive, as he sat at his desk shuffling papers around. "I need you to come up with a convincing argument." Mark's company, Norton Electronics, had embarked upon an expansion project that had the potential of increasing sales by about 30% per year over the next five years. The additional capital needed to finance the project had been estimated at $5,000,000. What Mark was wondering about was whether he should burden the firm with fixed rate debt or issue common stock to raise the needed funds. Having had no luck with getting the board of directors to vote on a decision, Mark decided to call on Clive Jones, his chief financial officer, to shed some light on the matter. Mark Norton, the chief executive officer of Norton Electronics, established his company about 10 years ago in his hometown of Cleveland, Ohio. After taking early retirement at age 55 , Mark felt that he could really capitalize on his engineering knowledge and contacts within the industry. Mark remembered vividly how easily he had managed to get the company up and running by using $3,000,000 of his own savings and a five-year bank note worth $2,000,000. He recollected how uneasy he had felt about that debt burden and the 14% per year rate of interest that the bank had been charging him. He remembered distinctly how relieved he had been after paying off the loan one year earlier than its five-year term, and the surprised look on the bank manager's face. 86 Case 18 Look Before You Leverage 87 Business had been good over the years, and sales had doubled about every four years. As sales began to escalate with the booming economy and thriving stock market, the firm had needed additional capital. Initially, Mark had managed to grow the business by using internal equity and spontaneous financing sources. However, about five years ago, when the need for financing was overwhelming, Mark decided to take the company public via an initial public offering (IPO) in the over-the-counter market. The issue was very successful and oversubscribed, mainly due to the superb publicity and marketing efforts of the investment underwriting company that Mark had hired. The company sold 1 million shares at $5 per share. The stock price had grown steadily over time and was currently trading at its book value of $15 per share. When the expansion proposal was presented at last week's board meeting, the directors were unanimous about the decision to accept the proposal. Based upon the estimates provided by the marketing department, the project had the potential of increasing revenues by between 10% (worst case) and 50% (best case) per year. The internal rate of return was expected to far outperform the company's hurdle rate. Ordinarily, the projeet would have been started using internal and spontaneous funds. However, at this juncture, the firm had already invested all its internal equity into the business. Thus, Mark and his colleagues were hard pressed to make a decision as to whether long-term debt or equity should be the chosen method of financing this time around. Upon contacting their investment bankers, Mark learned that they could issue five-year notes, at par, at a rate of 10% per year. Conversely, the company could issue common stock at its current price of $15 per share. Being unclear about what decision to make, Mark put the question to a vote by the directors. Unfortunately, the directors were equally divided in their opinion of which financing route should be chosen. Some directors felt that the tax shelter offered by debt would help reduce the firm's overall cost of capital and prevent the firm's earnings per share from being diluted. However, others had heard about "homemade leverage" and would not be convinced. They were of the opinion that it would be better for the firm to let investors leverage their investments themselves. They felt that equity was the way to go because the future looked rather uncertain and, being rather conservative, they were not interested in burdening the firm with interest charges. Besides, they felt that the firm should take advantage of the booming stock market. Feeling rather frustrated and confused, Mark decided to call upon his chief financial officer, Clive Jones, to resolve this dilemma. Clive had joined the company about two years ago. He held an MBA from a prestigious university and had recently completed his Chartered Financial 88 Case 18 Look Before You Leverage Analysts' certification. Prior to joining Norton, Clive had worked at two other publicly traded manufacturing companies and had been successful in helping them raise capital at attractive rates, thereby lowering their cost Clive knew that he was in for a challenging task. He felt, however. of capital considerably. that this was a good opportunity to prove his worth to the company. In preparation of his presentation, he got the latest balance sheet and income statement of the firm (Tables 1 and 2) and started crunching out the numbers. The title of his presentation was "Look Before You Leverage!" Case 18 Look Before You Lrverage 89 uestions: 1. If Norton Electronics Inc, were to raise all of the required capital by issuing debt, what would the impact be on the firm's shareholders? 2. What does "homemade leverage" mean? Using the data in the case, explain how a shareholder might be able to use homemade leverage to create the same payoffs as achieved by the firm. 3. What is the current weighted average cost of capital of the firm? What effect would a change in the debt-to-equity ratio have on the weighted average cost of capital and the cost of equity capital of the firm? 4. The firm's beta was estimated at 1.1. Treasury bills were yielding 4%, and the expected rate of return on the market index was estimated to be 12%. Using various combinations of debt and equity, under the assumption that the costs of each component stay constant, show the effect of increasing leverage on the weighted average cost of capital of the firm. Is there a particular capital structure that maximizes the value of the firm? Explain. 5. How would the key profitability ratios of the firm be affected if the firm were to raise all of the capital by issuing five-year notes? 6. If you were Clive Jones, what would you recommend to the board, and why? 7. What are some issues to be concerned about when increasing leverage? 8. Is it fair to assume that if profitability were positively affected in the short run, due to the higher debt ratio, the stock price would increase? Explain. 9. Using suitable diagrams and the data in the case, explain how Clive could enlighten the board members about Modigliani and Miller's Propositions I and II (with corporate taxes). "Why do things have to be so complicated?" said Mark to Clive, as he sat at his desk shuffling papers around. "I need you to come up with a convincing argument." Mark's company, Norton Electronics, had embarked upon an expansion project that had the potential of increasing sales by about 30% per year over the next five years. The additional capital needed to finance the project had been estimated at $5,000,000. What Mark was wondering about was whether he should burden the firm with fixed rate debt or issue common stock to raise the needed funds. Having had no luck with getting the board of directors to vote on a decision, Mark decided to call on Clive Jones, his chief financial officer, to shed some light on the matter. Mark Norton, the chief executive officer of Norton Electronics, established his company about 10 years ago in his hometown of Cleveland, Ohio. After taking early retirement at age 55 , Mark felt that he could really capitalize on his engineering knowledge and contacts within the industry. Mark remembered vividly how easily he had managed to get the company up and running by using $3,000,000 of his own savings and a five-year bank note worth $2,000,000. He recollected how uneasy he had felt about that debt burden and the 14% per year rate of interest that the bank had been charging him. He remembered distinctly how relieved he had been after paying off the loan one year earlier than its five-year term, and the surprised look on the bank manager's face. 86 Case 18 Look Before You Leverage 87 Business had been good over the years, and sales had doubled about every four years. As sales began to escalate with the booming economy and thriving stock market, the firm had needed additional capital. Initially, Mark had managed to grow the business by using internal equity and spontaneous financing sources. However, about five years ago, when the need for financing was overwhelming, Mark decided to take the company public via an initial public offering (IPO) in the over-the-counter market. The issue was very successful and oversubscribed, mainly due to the superb publicity and marketing efforts of the investment underwriting company that Mark had hired. The company sold 1 million shares at $5 per share. The stock price had grown steadily over time and was currently trading at its book value of $15 per share. When the expansion proposal was presented at last week's board meeting, the directors were unanimous about the decision to accept the proposal. Based upon the estimates provided by the marketing department, the project had the potential of increasing revenues by between 10% (worst case) and 50% (best case) per year. The internal rate of return was expected to far outperform the company's hurdle rate. Ordinarily, the projeet would have been started using internal and spontaneous funds. However, at this juncture, the firm had already invested all its internal equity into the business. Thus, Mark and his colleagues were hard pressed to make a decision as to whether long-term debt or equity should be the chosen method of financing this time around. Upon contacting their investment bankers, Mark learned that they could issue five-year notes, at par, at a rate of 10% per year. Conversely, the company could issue common stock at its current price of $15 per share. Being unclear about what decision to make, Mark put the question to a vote by the directors. Unfortunately, the directors were equally divided in their opinion of which financing route should be chosen. Some directors felt that the tax shelter offered by debt would help reduce the firm's overall cost of capital and prevent the firm's earnings per share from being diluted. However, others had heard about "homemade leverage" and would not be convinced. They were of the opinion that it would be better for the firm to let investors leverage their investments themselves. They felt that equity was the way to go because the future looked rather uncertain and, being rather conservative, they were not interested in burdening the firm with interest charges. Besides, they felt that the firm should take advantage of the booming stock market. Feeling rather frustrated and confused, Mark decided to call upon his chief financial officer, Clive Jones, to resolve this dilemma. Clive had joined the company about two years ago. He held an MBA from a prestigious university and had recently completed his Chartered Financial 88 Case 18 Look Before You Leverage Analysts' certification. Prior to joining Norton, Clive had worked at two other publicly traded manufacturing companies and had been successful in helping them raise capital at attractive rates, thereby lowering their cost Clive knew that he was in for a challenging task. He felt, however. of capital considerably. that this was a good opportunity to prove his worth to the company. In preparation of his presentation, he got the latest balance sheet and income statement of the firm (Tables 1 and 2) and started crunching out the numbers. The title of his presentation was "Look Before You Leverage!" Case 18 Look Before You Lrverage 89 uestions: 1. If Norton Electronics Inc, were to raise all of the required capital by issuing debt, what would the impact be on the firm's shareholders? 2. What does "homemade leverage" mean? Using the data in the case, explain how a shareholder might be able to use homemade leverage to create the same payoffs as achieved by the firm. 3. What is the current weighted average cost of capital of the firm? What effect would a change in the debt-to-equity ratio have on the weighted average cost of capital and the cost of equity capital of the firm? 4. The firm's beta was estimated at 1.1. Treasury bills were yielding 4%, and the expected rate of return on the market index was estimated to be 12%. Using various combinations of debt and equity, under the assumption that the costs of each component stay constant, show the effect of increasing leverage on the weighted average cost of capital of the firm. Is there a particular capital structure that maximizes the value of the firm? Explain. 5. How would the key profitability ratios of the firm be affected if the firm were to raise all of the capital by issuing five-year notes? 6. If you were Clive Jones, what would you recommend to the board, and why? 7. What are some issues to be concerned about when increasing leverage? 8. Is it fair to assume that if profitability were positively affected in the short run, due to the higher debt ratio, the stock price would increase? Explain. 9. Using suitable diagrams and the data in the case, explain how Clive could enlighten the board members about Modigliani and Miller's Propositions I and II (with corporate taxes)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


