Question: please answer. second picture js the FourierDerivativeMatrix 3. Here we approximate f'Gr) for a periodic function f(x) defined on (0,2) using a nodal Fourier method

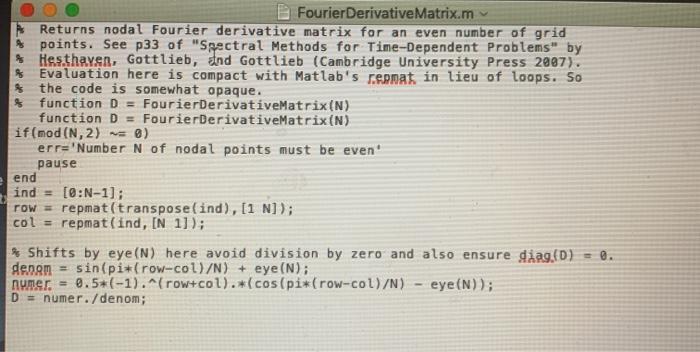
3. Here we approximate f'Gr) for a periodic function f(x) defined on (0,2) using a nodal Fourier method (please don't worry if you have never heard of such). Define a grid of r values via Id = 29 (k-1)/N for k=1,2,....N. Assume throughout that N is an even integer. Define a column vector f with components fx = f(), and a derivative matrix DERNXN with entries djk = { (-1))+k2 cot ( 1 (1 - )/N) ifj #k 0 if j = k. The kth component gk of g = Df then approximates the derivative value f(). A MATLAB function Fourier DerivativeMatrix which returns D (for N even) is posted on UNM Learn For f(x) = exp(sin :) nise FourierDerivativeMatrix to approximate f'(x) as the component g(1+N/2) = 9+N/20 That is, approximate f'(*) as the (I+N/2)st component of Df For N = 4.8. 12. 16,20,24, 28, 32, 36 compute the error (in absolute value) between the approximation and the exact answer (still -1). Plot the set of errors versus N. What do yon observe? A Fourier DerivativeMatrix.m Returns nodal Fourier derivative matrix for an even number of grid points. See p33 of "Spectral Methods for Time-Dependent Problems" by % Hesthaven, Gottlieb, and Gottlieb (Cambridge University Press 2007). Evaluation here is compact with Matlab's cermat in lieu of loops. So % the code is somewhat opaque. $ function D = FourierDerivativeMatrix(N) function D = FourierDerivativeMatrix(N) if(mod (N,2) ) err='Number N of nodal points must be even pause end ind = [@:N-1]; repmat(transpose(ind), [1 N]); col = repmat(ind, IN 1]); * Shifts by eye (N) here avoid division by zero and also ensure diagfD) = 0. denen sin(pi*(row-col)/N) + eye(N); numer. = 0.5*(-1). (row+col).*(cos(pi*(row-col)/N) eye(N)); D = numer./denom; row 3. Here we approximate f'Gr) for a periodic function f(x) defined on (0,2) using a nodal Fourier method (please don't worry if you have never heard of such). Define a grid of r values via Id = 29 (k-1)/N for k=1,2,....N. Assume throughout that N is an even integer. Define a column vector f with components fx = f(), and a derivative matrix DERNXN with entries djk = { (-1))+k2 cot ( 1 (1 - )/N) ifj #k 0 if j = k. The kth component gk of g = Df then approximates the derivative value f(). A MATLAB function Fourier DerivativeMatrix which returns D (for N even) is posted on UNM Learn For f(x) = exp(sin :) nise FourierDerivativeMatrix to approximate f'(x) as the component g(1+N/2) = 9+N/20 That is, approximate f'(*) as the (I+N/2)st component of Df For N = 4.8. 12. 16,20,24, 28, 32, 36 compute the error (in absolute value) between the approximation and the exact answer (still -1). Plot the set of errors versus N. What do yon observe? A Fourier DerivativeMatrix.m Returns nodal Fourier derivative matrix for an even number of grid points. See p33 of "Spectral Methods for Time-Dependent Problems" by % Hesthaven, Gottlieb, and Gottlieb (Cambridge University Press 2007). Evaluation here is compact with Matlab's cermat in lieu of loops. So % the code is somewhat opaque. $ function D = FourierDerivativeMatrix(N) function D = FourierDerivativeMatrix(N) if(mod (N,2) ) err='Number N of nodal points must be even pause end ind = [@:N-1]; repmat(transpose(ind), [1 N]); col = repmat(ind, IN 1]); * Shifts by eye (N) here avoid division by zero and also ensure diagfD) = 0. denen sin(pi*(row-col)/N) + eye(N); numer. = 0.5*(-1). (row+col).*(cos(pi*(row-col)/N) eye(N)); D = numer./denom; row
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


