Question: PLEASE ANSWER THE LAST 4 BLANK QUESTIONS. PLEASE ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS IN ORDER. I WILL BE SURE TO LEAVE A THUMBS UP. QUESTION 3 Monsanto
PLEASE ANSWER THE LAST 4 BLANK QUESTIONS. PLEASE ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS IN ORDER. I WILL BE SURE TO LEAVE A THUMBS UP.
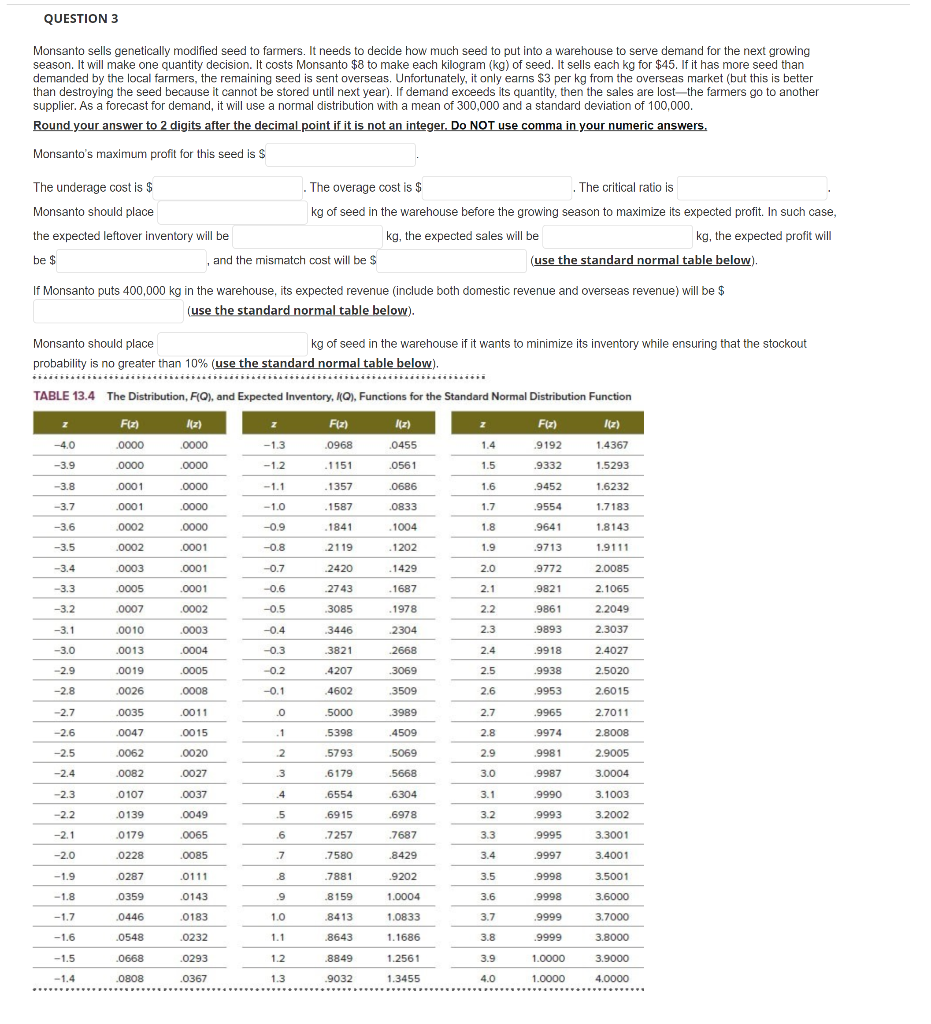
QUESTION 3 Monsanto sells genetically modified seed to farmers. It needs to decide how much seed to put into a warehouse to serve demand for the next growing season. It will make one quantity decision. It costs Monsanto $8 to make each kilogram (kg) of seed. It sells each kg for $45. If it has more seed than demanded by the local farmers, the remaining seed is sent overseas. Unfortunately, it only earns $3 per kg from the overseas market (but this is better than destroying the seed because it cannot be stored until next year). If demand exceeds its quantity, then the sales are lost-the farmers go to another supplier. As a forecast for demand, it will use a normal distribution with a mean of 300,000 and a standard deviation of 100,000. Round your answer to 2 digits after the decimal point if it is not an integer. Do NOT use comma in your numeric answers. Monsanto's maximum profit for this seed is s The underage cost is $ The overage cost is $ The critical ratio is Monsanto should place kg of seed in the warehouse before the growing season to maximize its expected profit. In such case, the expected leftover inventory will be kg, the expected sales will be kg, the expected profit will be $ and the mismatch cost will be $ (use the standard normal table below). If Monsanto puts 400,000 kg in the warehouse, its expected revenue (include both domestic revenue and overseas revenue) will be $ (use the standard normal table below). Monsanto should place kg of seed in the warehouse if it wants to minimize its inventory while ensuring that the stockout probability is no greater than 10% (use the standard normal table below). TABLE 13.4 The Distribution, FQ), and Expected Inventory, (Q), Functions for the Standard Normal Distribution Function ) Fiz) 2 Fiz) A(z) F(z) (7) -4.0 .0000 .0000 -1.3 .0968 .0455 1.4 .9192 1.4367 -3.9 .0000 .0000 -1.2 . 1151 .0561 1.5 .9332 1.5293 -3.8 .0001 .0000 -1.1 .1357 .0686 1.6 .9452 1.6232 -3.7 .0001 .0000 - 1.0 .1587 .0833 1.7 .9554 1.7183 -3.6 .0002 .0000 -0.9 .1841 . 1004 1.8 .9641 1.8143 -3.5 .0002 .0001 -0.8 2119 .1202 1.9 .9713 1.9111 -3.4 .0003 .0001 -0.7 .2420 .1429 2.0 .9772 2.0085 -3.3 .0005 .0001 -0.6 2743 . 1687 2.1 .9821 2. 1065 -3.2 .0007 .0002 -0.5 .3085 .1978 2.2 .9861 2.2049 -3.1 .0010 .0003 -0.4 .3446 .2304 2.3 .9893 2.3037 -3.0 .0013 .0004 -0.3 .3821 .2668 2.4 .9918 2.4027 -2.9 .0019 .0005 -0.2 .4207 3069 2.5 .9938 2.5020 -2.8 .0026 .0008 -0.1 .4602 3509 2.6 .9953 2.6015 -2.7 .0035 .0011 .. .5000 3989 2.7 .9965 2.7011 -2.6 .0047 .0015 .1 .5398 .4509 2.8 .9974 2.8008 -2.5 .0062 .0020 2 .5793 .5069 2.9 .9981 2.9005 -2.4 .0082 .0027 3 .6179 .5668 3.0 .9987 3.0004 -2.3 0107 .0037 4 .6554 .6304 3.1 .9990 3.1003 -2.2 0139 .0049 .5 .6915 .6978 3.2 .9993 3.2002 -2.1 .0179 .0065 .6 .7257 .7687 3.3 .9995 3.3001 -2.0 .0228 .0085 .7 .7580 .8429 3.4 .9997 3.4001 -1.9 .0287 .0111 8 .7881 .9202 3.5 9998 3.5001 -1.8 .0359 .0143 9 .8 159 1.0004 3.6 .9998 3.6000 -1.7 .0446 .0183 1.0 .8413 1.0833 3.7 .9999 3.7000 -1.6 .0548 .0232 1.1 .8643 1.1686 3.8 .9999 3.8000 -1.5 .0668 .0293 1.2 .8849 1.2561 3.9 1.0000 3.9000 -1.4 .0808 .0367 1.3 .9032 1.3455 4.0 1.0000 4.0000Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


