Question: please answer the questions 1-4 Financial Planning & Control (PMBA 5373) Capital Budgeting Analysis Homework 23 (10 points) due 5:30 p.m., Monday, 12/6/21 Shown below

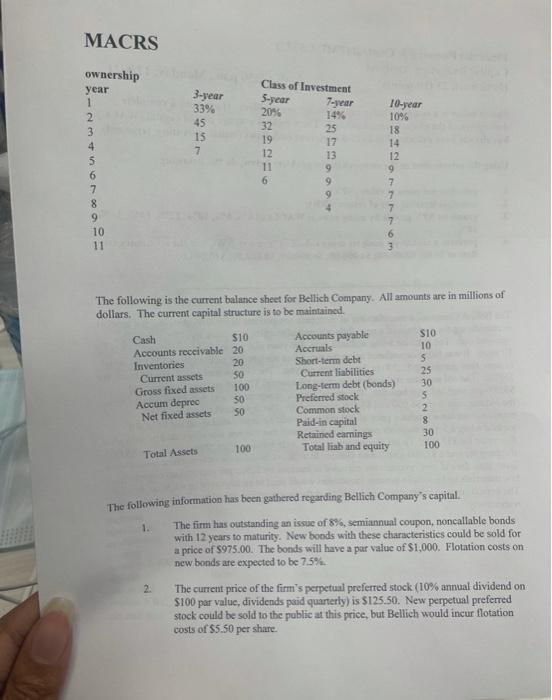

Financial Planning & Control (PMBA 5373) Capital Budgeting Analysis Homework 23 (10 points) due 5:30 p.m., Monday, 12/6/21 Shown below is a comprehensive capital budgeting problem. It contains a complete description of the project being analyzed. The weighted average cost of capital (WACC) has already been calculated as have the relevant cash flows (initial, operating, terminal). Using the information in the comprehensive problem below, do the following: 1. calculate net present value (NPV); 2 calculate internal rate of return (IRR); 3. graph an NPV profile by using annual WACCs of 6%, 8%, 10%, 12%, 14%, 16%, 18%; perform a sensitivity analysis using values of "recover NWC" in the terminal cash flow of $0.00; S2000.00; $4,000.00; $6,000.00; 8,000.00; 10,000.00. inimi 4. The Bellich Company, a manufacturer of electronic components in the 40% marginal tax bracket, is considering the purchase of a new, fully-automated machine to replace an older, manually- operated one. The machine being replaced, now five years old, originally had an expected life of 10 years. It was being depreciated using the simplified straight-line method from $25.000 down to zero, thus generating $2,500 in depreciation per year. The old machine could be sold today for $5,000. The old machine required one operator who earned $25,000 per year in salary and $5,000 per year in fringe benefits. The annual costs of maintenance and defects associated with the old machine were $6,000 and $3,500, respectively. The replacement machine under consideration has a purchase price of $95,000 and would be depreciated using the MACRS method using a 5-year recovery period. It is anticipated that the new machine could be sold after five years for $12,000. To get the automated machine in running order, there would be a $3,000 shipping fee and a $2,000 installation charge. In addition, because the new machine would work faster than the old one, revenues are expected to increase by $2500 per year and investment in raw materials and goods-in-process inventories would need to be increased by a total of $8,000. The annual costs of maintenance and defects on the new machine would be $1,500 and $4.000, respectively MACRS 3-year 339 45 15 7 2 ownership year 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Class of Investment 5-year 7-year 20% 14% 32 25 19 17 12 13 11 9 6 9 9 10-year 10% 18 14 12 9 7 7 The following is the current balance sheet for Bellich Company. All amounts are in millions of dollars. The current capital structure is to be maintained Cash S10 Accounts receivable 20 Inventories 20 Current assets 50 Gross fixed assets 100 Accum deprec 50 Net fixed assets 50 Accounts payable Accruals Short-term debt Current liabilities Long-term debt (bonds) Preferred stock Common stock Paid-in capital Retained earnings Total liaband equity SIO 10 S 25 30 5 2 8 30 100 100 Total Assets The following information has been gathered regarding Bellich Company's capital. The firm has outstanding an issue of 8%, semiannual coupon, noncallable bonds with 12 years to maturity. New bonds with these characteristics could be sold for a price of $975.00. The bonds will have a par value of $1,000. Flotation costs on new bonds are expected to be 7.5%. 2 The current price of the firm's perpetual preferred stock (10% annual dividend on $100 par value, dividends paid quarterly) is $125.50. New perpetual preferred stock could be sold to the public at this price, but Bellich would incur flotation costs of $5.50 per share 3 . . The firm's common stock is currently selling at $96 per share. The last dividend paid was Do = $4.00. Dividends are paid semiannually and investors expect the dividend to grow at a constant 7% annual rate into the foreseeable future. Any new common stock issued would involve flotation costs of 12%. Financial Planning & Control (PMBA 5373) Capital Budgeting Analysis Homework 23 (10 points) due 5:30 p.m., Monday, 12/6/21 Shown below is a comprehensive capital budgeting problem. It contains a complete description of the project being analyzed. The weighted average cost of capital (WACC) has already been calculated as have the relevant cash flows (initial, operating, terminal). Using the information in the comprehensive problem below, do the following: 1. calculate net present value (NPV); 2 calculate internal rate of return (IRR); 3. graph an NPV profile by using annual WACCs of 6%, 8%, 10%, 12%, 14%, 16%, 18%; perform a sensitivity analysis using values of "recover NWC" in the terminal cash flow of $0.00; S2000.00; $4,000.00; $6,000.00; 8,000.00; 10,000.00. inimi 4. The Bellich Company, a manufacturer of electronic components in the 40% marginal tax bracket, is considering the purchase of a new, fully-automated machine to replace an older, manually- operated one. The machine being replaced, now five years old, originally had an expected life of 10 years. It was being depreciated using the simplified straight-line method from $25.000 down to zero, thus generating $2,500 in depreciation per year. The old machine could be sold today for $5,000. The old machine required one operator who earned $25,000 per year in salary and $5,000 per year in fringe benefits. The annual costs of maintenance and defects associated with the old machine were $6,000 and $3,500, respectively. The replacement machine under consideration has a purchase price of $95,000 and would be depreciated using the MACRS method using a 5-year recovery period. It is anticipated that the new machine could be sold after five years for $12,000. To get the automated machine in running order, there would be a $3,000 shipping fee and a $2,000 installation charge. In addition, because the new machine would work faster than the old one, revenues are expected to increase by $2500 per year and investment in raw materials and goods-in-process inventories would need to be increased by a total of $8,000. The annual costs of maintenance and defects on the new machine would be $1,500 and $4.000, respectively MACRS 3-year 339 45 15 7 2 ownership year 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Class of Investment 5-year 7-year 20% 14% 32 25 19 17 12 13 11 9 6 9 9 10-year 10% 18 14 12 9 7 7 The following is the current balance sheet for Bellich Company. All amounts are in millions of dollars. The current capital structure is to be maintained Cash S10 Accounts receivable 20 Inventories 20 Current assets 50 Gross fixed assets 100 Accum deprec 50 Net fixed assets 50 Accounts payable Accruals Short-term debt Current liabilities Long-term debt (bonds) Preferred stock Common stock Paid-in capital Retained earnings Total liaband equity SIO 10 S 25 30 5 2 8 30 100 100 Total Assets The following information has been gathered regarding Bellich Company's capital. The firm has outstanding an issue of 8%, semiannual coupon, noncallable bonds with 12 years to maturity. New bonds with these characteristics could be sold for a price of $975.00. The bonds will have a par value of $1,000. Flotation costs on new bonds are expected to be 7.5%. 2 The current price of the firm's perpetual preferred stock (10% annual dividend on $100 par value, dividends paid quarterly) is $125.50. New perpetual preferred stock could be sold to the public at this price, but Bellich would incur flotation costs of $5.50 per share 3 . . The firm's common stock is currently selling at $96 per share. The last dividend paid was Do = $4.00. Dividends are paid semiannually and investors expect the dividend to grow at a constant 7% annual rate into the foreseeable future. Any new common stock issued would involve flotation costs of 12%
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


