Question: Please answer the questions below in relation to the case study; Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of Carlsberg in 2018, having regard to the global

Please answer the questions below in relation to the case study;
- Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of Carlsberg in 2018, having regard to the global beer industry and the major players.
- a) Discuss Carlsbergs business-level strategy in 2018. (25% of question 2)
b) Identify, discuss and rank three strategic options to take Carlsberg to the next level. (75% of question 2)
- Select two areas or topics of Strategy theory not covered in your answers to questions 1 and 2. Discuss how these two areas or topics could be applied to and could benefit Carlsberg in 2018.
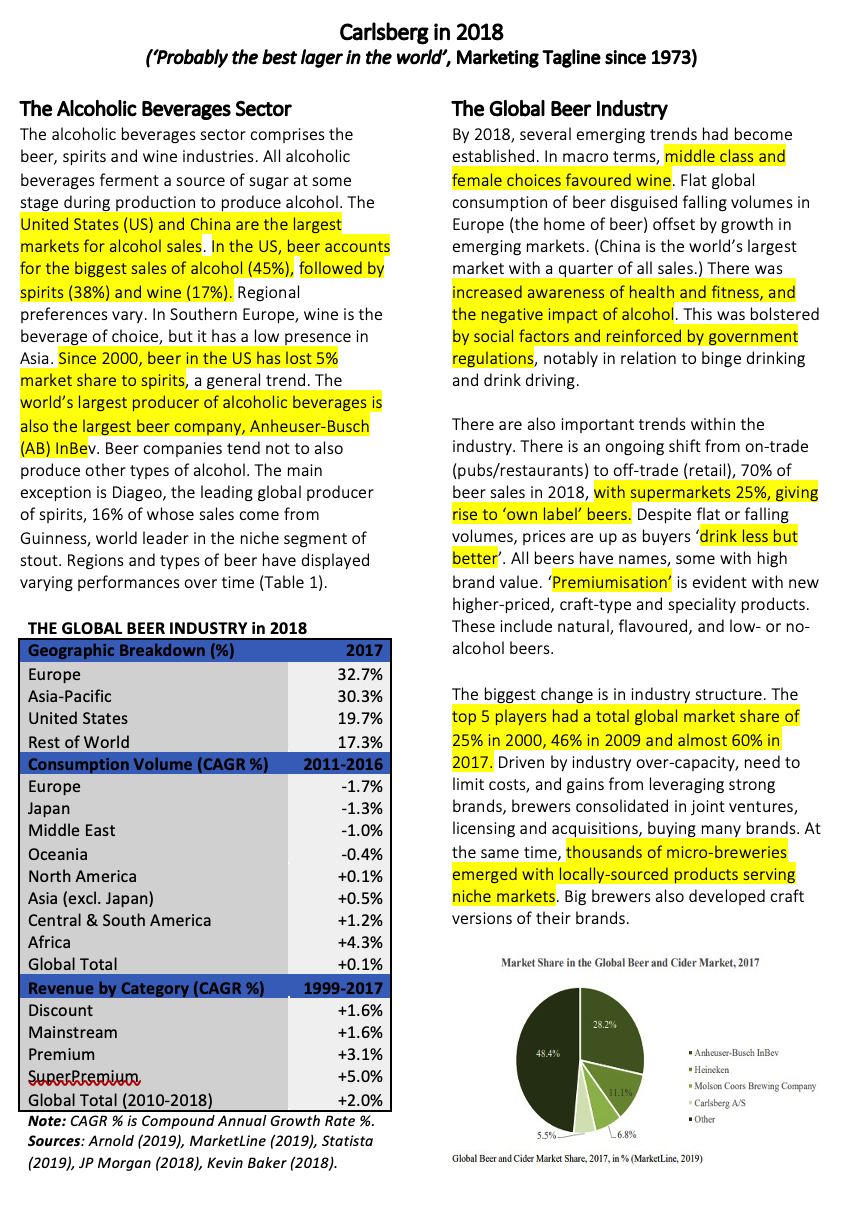
Carlsberg in 2018 ('Probably the best lager in the world', Marketing Tagline since 1973) The Alcoholic Beverages Sector The alcoholic beverages sector comprises the beer, spirits and wine industries. All alcoholic beverages ferment a source of sugar at some stage during production to produce alcohol. The United States (US) and China are the largest markets for alcohol sales. In the US, beer accounts for the biggest sales of alcohol (45%), followed by spirits (38%) and wine (17%). Regional preferences vary. In Southern Europe, wine is the beverage of choice, but it has a low presence in Asia. Since 2000, beer in the US has lost 5% market share to spirits, a general trend. The world's largest producer of alcoholic beverages is also the largest beer company, Anheuser-Busch (AB) InBev. Beer companies tend not to also produce other types of alcohol. The main exception is Diageo, the leading global producer of spirits, 16% of whose sales come from Guinness, world leader in the niche segment of stout. Regions and types of beer have displayed varying performances over time (Table 1). The Global Beer Industry By 2018, several emerging trends had become established. In macro terms, middle class and female choices favoured wine. Flat global consumption of beer disguised falling volumes in Europe (the home of beer) offset by growth in emerging markets. (China is the world's largest market with a quarter of all sales.) There was increased awareness of health and fitness, and the negative impact of alcohol. This was bolstered by social factors and reinforced by government regulations, notably in relation to binge drinking and drink driving. There are also important trends within the industry. There is an ongoing shift from on-trade (pubs/restaurants) to off-trade (retail), 70% of beer sales in 2018, with supermarkets 25%, giving rise to 'own label beers. Despite flat or falling volumes, prices are up as buyers 'drink less but better'. All beers have names, some with high brand value. 'Premiumisation' is evident with new higher-priced, craft-type and speciality products. These include natural, flavoured, and low- or no- alcohol beers. THE GLOBAL BEER INDUSTRY in 2018 Geographic Breakdown (%) 2017 Europe 32.7% Asia-Pacific 30.3% United States 19.7% Rest of World 17.3% Consumption Volume (CAGR %) 2011-2016 Europe -1.7% Japan -1.3% Middle East -1.0% Oceania -0.4% North America +0.1% Asia (excl. Japan) +0.5% Central & South America +1.2% Africa +4.3% Global Total +0.1% Revenue by Category (CAGR %) 1999-2017 Discount +1.6% Mainstream +1.6% Premium +3.1% Super Premium +5.0% Global Total (2010-2018) +2.0% Note: CAGR % is Compound Annual Growth Rate %. Sources: Arnold (2019), MarketLine (2019), Statista (2019), JP Morgan (2018), Kevin Baker (2018). The biggest change is in industry structure. The top 5 players had a total global market share of 25% in 2000, 46% in 2009 and almost 60% in 2017. Driven by industry over-capacity, need to limit costs, and gains from leveraging strong brands, brewers consolidated in joint ventures, licensing and acquisitions, buying many brands. At the same time, thousands of micro-breweries emerged with locally-sourced products serving niche markets. Big brewers also developed craft versions of their brands. Market Share in the Global Beer and Cider Market, 2017 28.2% 48.4% Anheuser-Busch InBev Heineken Molson Coors Brewing Company Carlsberg AS Other 5.5% L6.8% Global Beer and Cider Market Share, 2017, in % (MarketLine, 2019) Coors (both with various forms) Blue Moon and Staropramen; it also has regional brands (e.g. Carling). Molson-Coors licences global brands to sell in North America and Europe from Asahi and Heineken. Major Industry Players Formed from mergers and acquisitions among four leading industry players since 2004, AB-labey is a brewing behemoth. Valued at 111 bn, in 2018 it had revenues of 45.5 bn and EBITDA (earnings before interest, tax, interest and amortisation) of 26.5 bn. Beer volumes of 567 million hectolitres (whl) from 227 breweries are sold in North (111 mbl) and South America (265 whl), with large sales in Asia Pacific (104 mhl and Europe/Middle East/Africa (EMEA) (87 mbl). Performance is driven by two factors. Firstly, via mass-market global brands (Budweiser, Stella Artois and Corona) with International (e.g. Skol, Beck's) and local champion (e.g. Bass, Spaten) brands. Secondly, size and market power yield large benefits in costs, marketing and distribution. Carlsberg in 2018 With a stock market with a value of 13.4 bn, Danish-based Carlsberg is 70% controlled by the founding trust. In 2018, it had revenues of 7.1 bn and beer volumes of 112 ml. 46 mbl is sold in Western Europe, where Carlsberg has market lead shares in Scandinavia, the Baltics, Switzerland and Portugal, with shares in the teens elsewhere. Eastern Europe volumes of 31 mohl in arise in Russia and four former Soviet countries with market shares of 30% +. In Asia (36 mol Carlsberg has strong regional positions in China (especially) and India, with leading shares in eight other markets. It has 76 breweries (25 in China, 8 in Russia). Carlsberg aims to be number 1 or 2 in all its markets. It is a pioneer in environmental sustainability Heineken is the clear number two globally with a stock market value of 42.5 bn and 2018 revenues of 22.5bn. Beer sales total 234 mhl: Americas (83 mhl), Western Europe (80 mbl), EMEA (42 mall and Asia-Packfis 29 (whl). The global brand has instant name recognition. It also has international brands such as Amstel, Sol and Tiger, together with regional and local, and speciality, beers. Its strategy is to be leader in the premium beer segment globally, through advertising and sponsorship of major sports events (Rugby World Cup, Champions League). But its volumes lag AB- laber's in every region and it has much lower margins. Dating from 2016, Carlsberg's 'Sail 22' strategy priorities are: Strengthen the Core; Position of Growth; Create a Winning Culture. Growth is focused on premiumising in Asia and via line extension into craft, speciality and alcohol-free brews from local brands, all funded by a focus on efficiencies, costs and cash generation. Key to the strategy is leveraging company brands. At 93% of volumes, core brands comprise international (Carlsberg, Tuborg, Kronenbourg Grimbergen and Holsten) and local (eg Baltika. Dali and Wusu). Growing category brands (7% of mobl) are craft/speciality and alcohol-free. There are three major brewers with similar valuations and global market shares of 5.5% to 7%. Valued at 15.7 bn, Asahi is the leader in the large but mature Japanese beer market with a 37% share. It has expanded through acquisitions into Western and Eastern Europe, buying the Peroni, Grolsch, Pilsner Urquell and other brands. Asahi is the market leader in Poland (32%), Romania (36%) and the Czech Republic (44%), with positions in Western markets, e.g. Italy (18%). With beer revenues of 12.6 bn in 2018 and cash from the core Japanese business, its strategy is to establish a growth platform in Europe, cross-selling from Asahi's food and soft drinks businesses. In 2018, Carlsberg recorded good results after several difficult years (including a loss in 2015) as 'Sail 22' bore fruit. Going forward, Carlsberg management pondered what strategy options to pursue to take the group to the next level. Formed from the merger of leading Canadian and US brewers, Molson-Coors was valued at 10.3 bn and had revenues of 9 bn and beer sales of 96.6 mbl in 2018. Three-quarters of sales are in North America with 24% in Europe. Molson-Coors has global ambitions. Its global brands are Miller and





