Question: Please answer yourself and not using textbook solutions on Chegg!! It is wrong. Will give thumbs up once you do correctly, thanks Suppose that independent
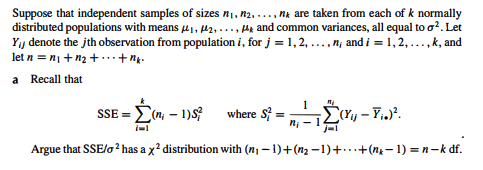
Please answer yourself and not using textbook solutions on Chegg!! It is wrong. Will give thumbs up once you do correctly, thanks
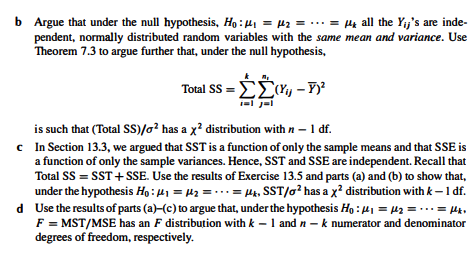
Suppose that independent samples of sizes ni,n2...., nu are taken from each of k normally distributed populations with means H1, M2, ..., Me and common variances, all equal to o?. Let Y, denote the jth observation from population i, for j = 1,2,...,n; and i = 1, 2, ...,k, and let n = n +12+...+nk. a Recall that 1 SSE = (n-1)? where ? (yy-Y..)? n; -1 Argue that SSE/o2 has a y distribution with (n-1)+(12-1)+...+(n-1)=n-kdf. b Argue that under the null hypothesis, H:41 = 42 = ... = My all the Yij's are inde- pendent, normally distributed random variables with the same mean and variance. Use Theorem 7.3 to argue further that, under the null hypothesis, Total SS = EKY , 752 is such that (Total SS)/0? has a x? distribution with n - 1 df. c In Section 13.3, we argued that SST is a function of only the sample means and that SSE is a function of only the sample variances. Hence, SST and SSE are independent. Recall that Total SS = SST + SSE. Use the results of Exercise 13.5 and parts (a) and (b) to show that, under the hypothesis Ho: 41 = H2 = ... = Hk, SST/o has a xa distribution with k - 1df. d Use the results of parts (a)(c) to argue that, under the hypothesis Ho: 41 = 42 = ... = Hks F = MST/MSE has an F distribution with k - 1 and n-k numerator and denominator degrees of freedom, respectively. Suppose that independent samples of sizes ni,n2...., nu are taken from each of k normally distributed populations with means H1, M2, ..., Me and common variances, all equal to o?. Let Y, denote the jth observation from population i, for j = 1,2,...,n; and i = 1, 2, ...,k, and let n = n +12+...+nk. a Recall that 1 SSE = (n-1)? where ? (yy-Y..)? n; -1 Argue that SSE/o2 has a y distribution with (n-1)+(12-1)+...+(n-1)=n-kdf. b Argue that under the null hypothesis, H:41 = 42 = ... = My all the Yij's are inde- pendent, normally distributed random variables with the same mean and variance. Use Theorem 7.3 to argue further that, under the null hypothesis, Total SS = EKY , 752 is such that (Total SS)/0? has a x? distribution with n - 1 df. c In Section 13.3, we argued that SST is a function of only the sample means and that SSE is a function of only the sample variances. Hence, SST and SSE are independent. Recall that Total SS = SST + SSE. Use the results of Exercise 13.5 and parts (a) and (b) to show that, under the hypothesis Ho: 41 = H2 = ... = Hk, SST/o has a xa distribution with k - 1df. d Use the results of parts (a)(c) to argue that, under the hypothesis Ho: 41 = 42 = ... = Hks F = MST/MSE has an F distribution with k - 1 and n-k numerator and denominator degrees of freedom, respectivelyStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


