Question: Please code in OCaml. For this question, just code the pre_order, compose, depth, and trim functions using the tree_fold function listed in the 3 bottom
Please code in OCaml.
For this question, just code the pre_order, compose, depth, and trim functions using the tree_fold function listed in the 3 bottom images. You are not allowed to use recursion for implementing these functions. Assume that all the other functions listed above (including tree_fold) are already implemented, and you may use them (implement them yourself if needed) to program the 4 functions.
Please only use library functions found in the Stdlib module and the List module libraries, and please check to see if your code works using examples. Thank you.
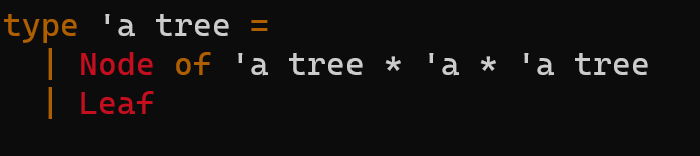
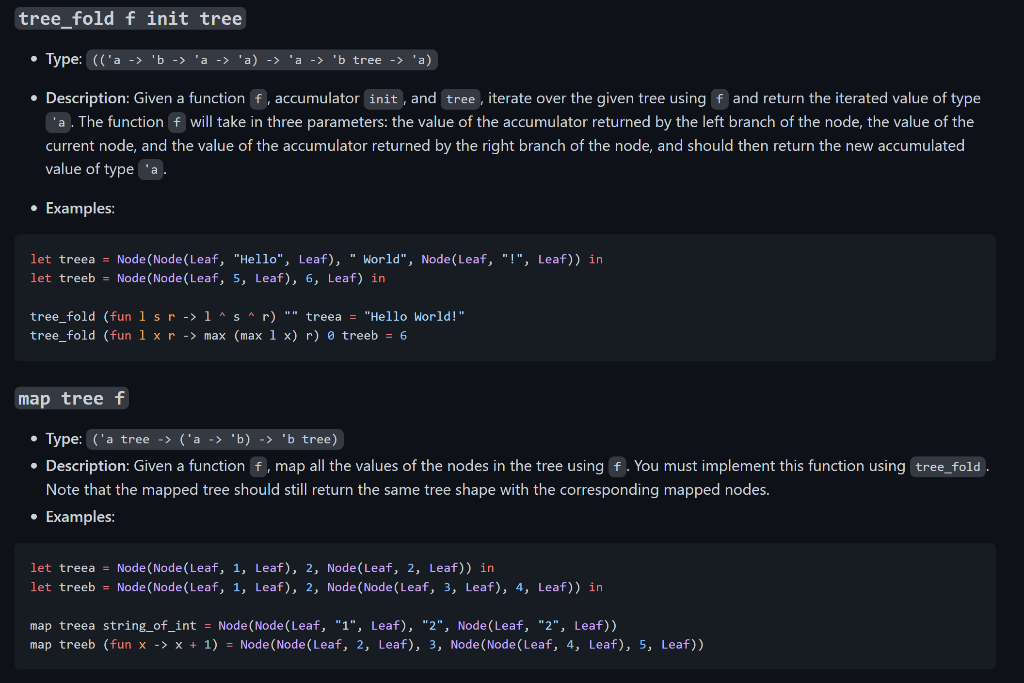
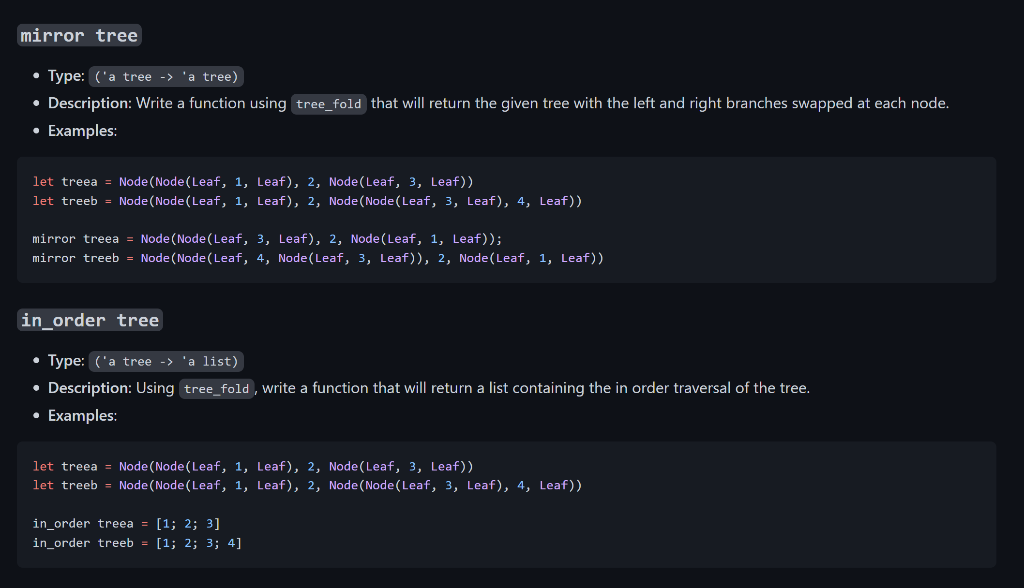
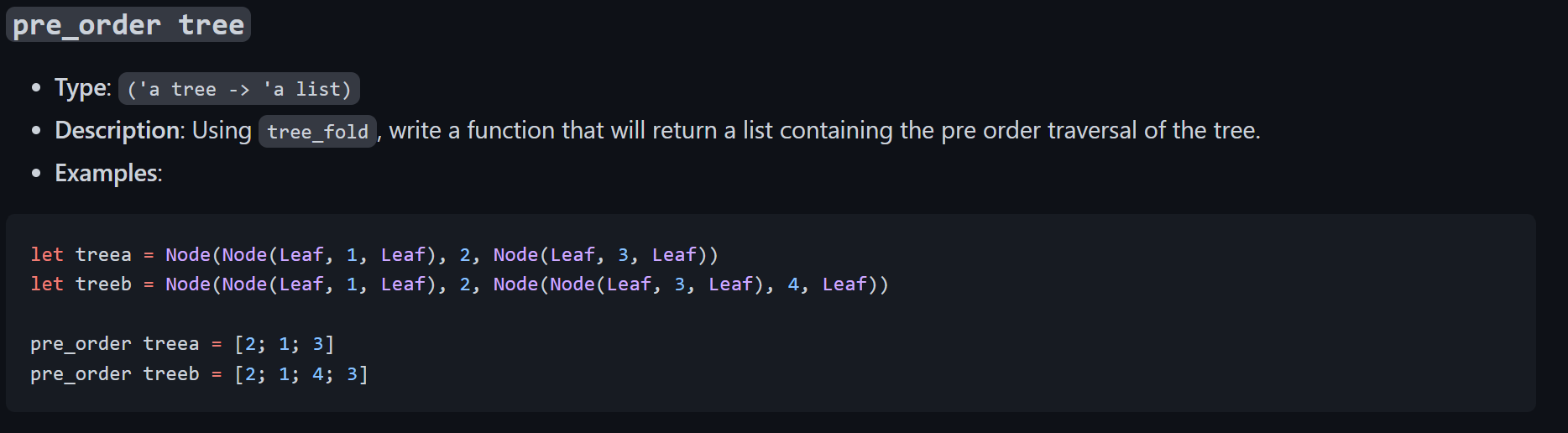
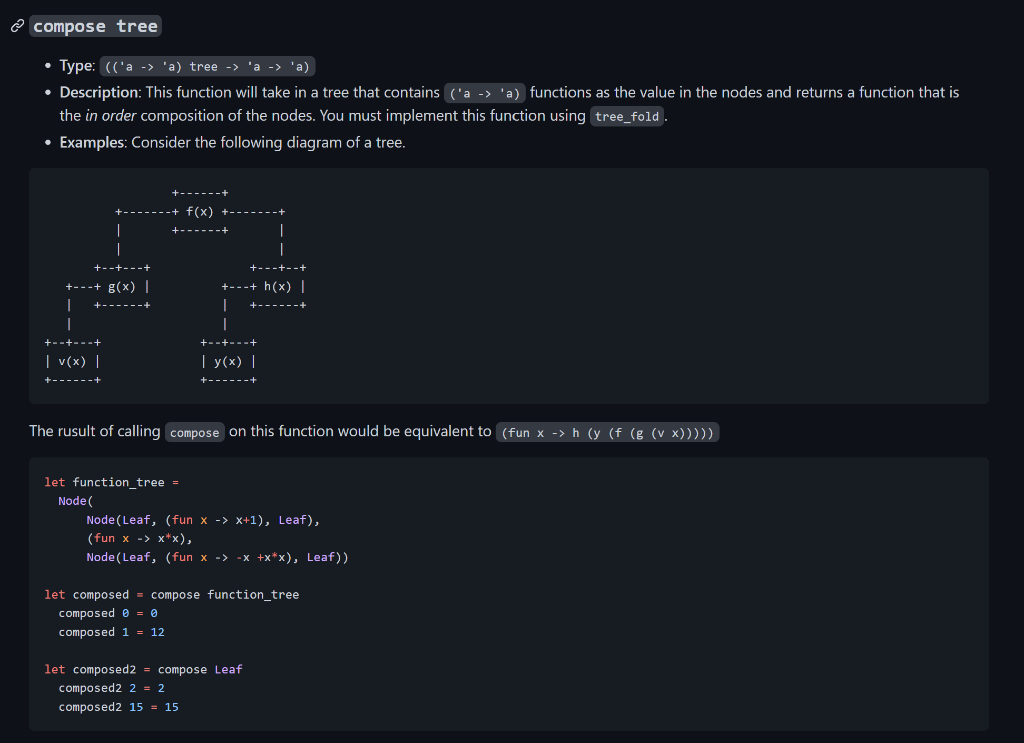
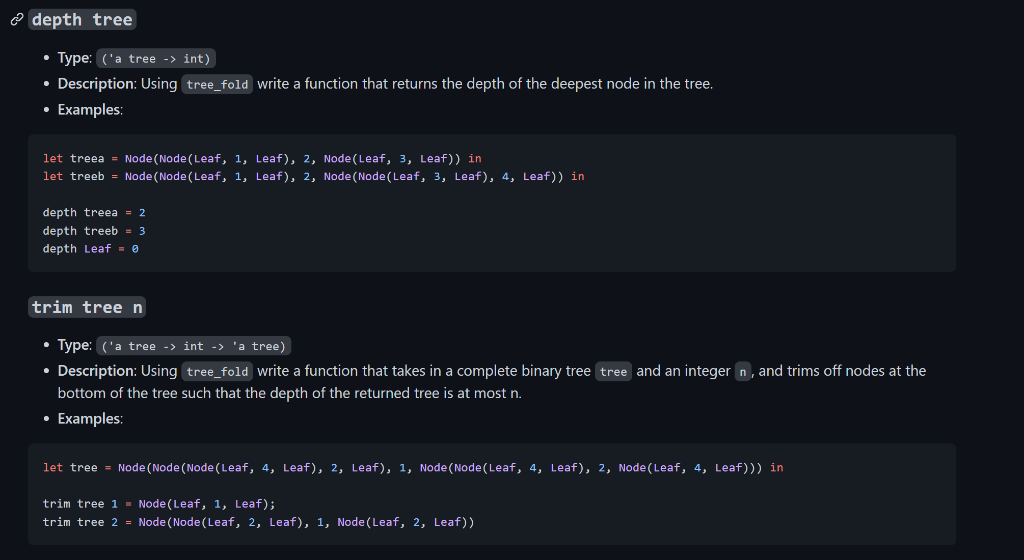
type 'a tree = | Node of 'a tree *'a 'a 'a tree Leaf tree_fold f init tree - Type: (( ' abaa)a ' tree ' a ) - Description: Given a function f, accumulator init, and tree, iterate over the given tree using f and return the iterated value of type 'a. The function f will take in three parameters: the value of the accumulator returned by the left branch of the node, the value of the current node, and the value of the accumulator returned by the right branch of the node, and should then return the new accumulated value of type . - Examples: let treea = Node(Node(Leaf, "Hello", Leaf), " World", Node(Leaf, "!", Leaf)) in let treeb = Node(Node(Leaf, 5 , Leaf), 6, Leaf) in tree_fold (fun 1ssr1sr)" treea = "Hello World!" tree_fold (fun 1rmax(max1x)r treeb =6 map tree f - Type: ('a tree ( ('a 'b) 'b tree) - Description: Given a function f, map all the values of the nodes in the tree using f. You must implement this function using tree_fold . Note that the mapped tree should still return the same tree shape with the corresponding mapped nodes. - Examples: let treea = Node(Node(Leaf, 1, Leaf), 2, Node(Leaf, 2, Leaf)) in let treeb = Node(Node(Leaf, 1, Leaf), 2, Node(Node(Leaf, 3, Leaf), 4, Leaf)) in map treea string_of_int = Node(Node(Leaf, "1", Leaf), "2", Node(Leaf, "2", Leaf)) map treeb (fun xx+1)= Node(Node(Leaf, 2, Leaf), 3, Node(Node(Leaf, 4, Leaf), 5, Leaf)) mirror tree - Type: ('a tree 'a tree) - Description: Write a function using tree_fold that will return the given tree with the left and right branches swapped at each node. - Examples: let treea =Node(Node( Leaf, 1, Leaf), 2, Node(Leaf, 3, Leaf)) let treeb =Node(Node( Leaf, 1, Leaf), 2, Node(Node(Leaf, 3, Leaf), 4, Leaf)) mirror treea =Node(Node(Leaf,3,Leaf),2,Node(Leaf,1,Leaf)); mirror treeb =Node(Node(Leaf,4,Node(Leaf,3,Leaf)),2,Node(Leaf,1,Leaf)) in_order tree - Type: ('a tree ' a list) - Description: Using tree_fold, write a function that will return a list containing the in order traversal of the tree. - Examples: let treea = Node(Node(Leaf, 1, Leaf), 2, Node(Leaf, 3, Leaf) ) let treeb = Node(Node(Leaf, 1, Leaf), 2, Node(Node(Leaf, 3, Leaf), 4, Leaf)) in_order treea =[1;2;3] in_order treeb =[1;2;3;4] pre_order tree - Type: ('a tree 'a list) - Description: Using tree_fold, write a function that will return a list containing the pre order traversal of the tree. - Examples: let treea = Node(Node(Leaf, 1, Leaf), 2, Node(Leaf, 3, Leaf)) let treeb = Node(Node(Leaf, 1, Leaf), 2, Node(Node(Leaf, 3, Leaf), 4, Leaf)) \( \begin{array}{l}\text { pre_order treea }=[2 ; 1 ; 3] \\ \text { pre_order treeb }=[2 ; 1 ; 4 ; 3]\end{array} \) compose tree - Type: (('a ' a ) tree 'a 'a) the in order composition of the nodes. You must implement this function using tree_fold. - Examples: Consider the following diagram of a tree. The rusult of calling compose on this function would be equivalent to ( fun xh(y(f(g(vx))))) let function_tree = Node ( Node(Leaf,(funx>x+1),Leaf))Node(Leaf,(funx>x+xx),Leaf))) \( \begin{aligned} \text { let composed } & =\text { compose function_tree } \\ \text { composed } 0 & =0 \\ \text { composed } 1 & =12 \\ \text { let composed2 } & =\text { compose Leaf } \\ \text { composed2 } 2 & =2 \\ \text { composed2 } 15 & =15\end{aligned} \) depth tree - Type: ('a tree int) - Description: Using tree_fold write a function that returns the depth of the deepest node in the tree. - Examples: let treea = Node(Node(Leaf, 1, Leaf), 2, Node(Leaf, 3, Leaf)) in let treeb = Node(Node(Leaf, 1, Leaf), 2, Node(Node(Leaf, 3, Leaf), 4, Leaf)) in depthtreea=2depthtreeb=3depthLeaf=0 trim tree n - Type: ('a tree int ' a tree) - Description: Using tree_fold write a function that takes in a complete binary tree tree and an integer n, and trims off nodes at the bottom of the tree such that the depth of the returned tree is at most n. - Examples: let tree = Node(Node(Node(Leaf, 4, Leaf), 2, Leaf), 1, Node(Node(Leaf, 4, Leaf), 2, Node(Leaf, 4, Leaf))) in trim tree 1= Node(Leaf, 1, Leaf); trim tree 2= Node(Node(Leaf, 2, Leaf), 1, Node(Leaf, 2, Leaf)) type 'a tree = | Node of 'a tree *'a 'a 'a tree Leaf tree_fold f init tree - Type: (( ' abaa)a ' tree ' a ) - Description: Given a function f, accumulator init, and tree, iterate over the given tree using f and return the iterated value of type 'a. The function f will take in three parameters: the value of the accumulator returned by the left branch of the node, the value of the current node, and the value of the accumulator returned by the right branch of the node, and should then return the new accumulated value of type . - Examples: let treea = Node(Node(Leaf, "Hello", Leaf), " World", Node(Leaf, "!", Leaf)) in let treeb = Node(Node(Leaf, 5 , Leaf), 6, Leaf) in tree_fold (fun 1ssr1sr)" treea = "Hello World!" tree_fold (fun 1rmax(max1x)r treeb =6 map tree f - Type: ('a tree ( ('a 'b) 'b tree) - Description: Given a function f, map all the values of the nodes in the tree using f. You must implement this function using tree_fold . Note that the mapped tree should still return the same tree shape with the corresponding mapped nodes. - Examples: let treea = Node(Node(Leaf, 1, Leaf), 2, Node(Leaf, 2, Leaf)) in let treeb = Node(Node(Leaf, 1, Leaf), 2, Node(Node(Leaf, 3, Leaf), 4, Leaf)) in map treea string_of_int = Node(Node(Leaf, "1", Leaf), "2", Node(Leaf, "2", Leaf)) map treeb (fun xx+1)= Node(Node(Leaf, 2, Leaf), 3, Node(Node(Leaf, 4, Leaf), 5, Leaf)) mirror tree - Type: ('a tree 'a tree) - Description: Write a function using tree_fold that will return the given tree with the left and right branches swapped at each node. - Examples: let treea =Node(Node( Leaf, 1, Leaf), 2, Node(Leaf, 3, Leaf)) let treeb =Node(Node( Leaf, 1, Leaf), 2, Node(Node(Leaf, 3, Leaf), 4, Leaf)) mirror treea =Node(Node(Leaf,3,Leaf),2,Node(Leaf,1,Leaf)); mirror treeb =Node(Node(Leaf,4,Node(Leaf,3,Leaf)),2,Node(Leaf,1,Leaf)) in_order tree - Type: ('a tree ' a list) - Description: Using tree_fold, write a function that will return a list containing the in order traversal of the tree. - Examples: let treea = Node(Node(Leaf, 1, Leaf), 2, Node(Leaf, 3, Leaf) ) let treeb = Node(Node(Leaf, 1, Leaf), 2, Node(Node(Leaf, 3, Leaf), 4, Leaf)) in_order treea =[1;2;3] in_order treeb =[1;2;3;4] pre_order tree - Type: ('a tree 'a list) - Description: Using tree_fold, write a function that will return a list containing the pre order traversal of the tree. - Examples: let treea = Node(Node(Leaf, 1, Leaf), 2, Node(Leaf, 3, Leaf)) let treeb = Node(Node(Leaf, 1, Leaf), 2, Node(Node(Leaf, 3, Leaf), 4, Leaf)) \( \begin{array}{l}\text { pre_order treea }=[2 ; 1 ; 3] \\ \text { pre_order treeb }=[2 ; 1 ; 4 ; 3]\end{array} \) compose tree - Type: (('a ' a ) tree 'a 'a) the in order composition of the nodes. You must implement this function using tree_fold. - Examples: Consider the following diagram of a tree. The rusult of calling compose on this function would be equivalent to ( fun xh(y(f(g(vx))))) let function_tree = Node ( Node(Leaf,(funx>x+1),Leaf))Node(Leaf,(funx>x+xx),Leaf))) \( \begin{aligned} \text { let composed } & =\text { compose function_tree } \\ \text { composed } 0 & =0 \\ \text { composed } 1 & =12 \\ \text { let composed2 } & =\text { compose Leaf } \\ \text { composed2 } 2 & =2 \\ \text { composed2 } 15 & =15\end{aligned} \) depth tree - Type: ('a tree int) - Description: Using tree_fold write a function that returns the depth of the deepest node in the tree. - Examples: let treea = Node(Node(Leaf, 1, Leaf), 2, Node(Leaf, 3, Leaf)) in let treeb = Node(Node(Leaf, 1, Leaf), 2, Node(Node(Leaf, 3, Leaf), 4, Leaf)) in depthtreea=2depthtreeb=3depthLeaf=0 trim tree n - Type: ('a tree int ' a tree) - Description: Using tree_fold write a function that takes in a complete binary tree tree and an integer n, and trims off nodes at the bottom of the tree such that the depth of the returned tree is at most n. - Examples: let tree = Node(Node(Node(Leaf, 4, Leaf), 2, Leaf), 1, Node(Node(Leaf, 4, Leaf), 2, Node(Leaf, 4, Leaf))) in trim tree 1= Node(Leaf, 1, Leaf); trim tree 2= Node(Node(Leaf, 2, Leaf), 1, Node(Leaf, 2, Leaf))
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


