Question: Please complete Programming Exercise 2, from page 1438 of Chapter 20 from your textbook. Please use the data file from the moodle site. 2. Write
Please complete Programming Exercise 2, from page 1438 of Chapter 20 from your textbook. Please use the data file from the moodle site.
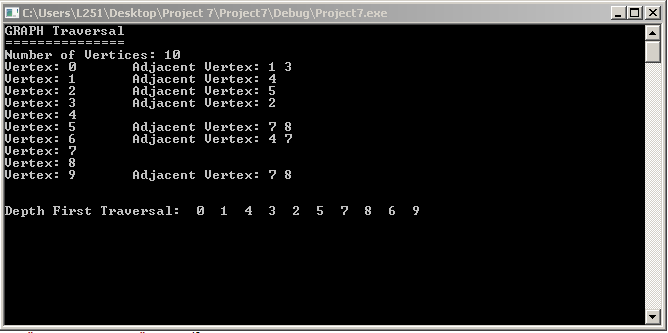
2. Write a program that outputs the nodes of a graph in a breadth first traversal.
Also, please take a look at figure 20-6 on page 1414 and calculate the weights for the following edges:
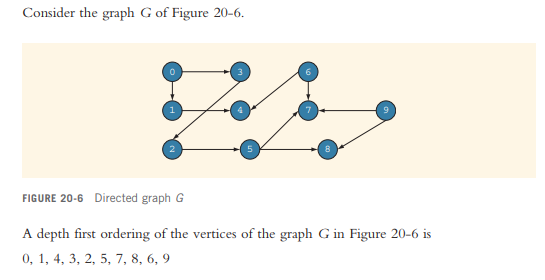
0 -> 1 -> 4
0 -> 3 -> 2 -> 5 -> 7
0 -> 3 -> 2 -> 5 -> 8
6 -> 4
6 -> 7
9 -> 7
9 -> 8
To calculates these weights, please assume the following data:
0 -> 1 = 1
0 -> 3 = 2
1 -> 4 = 3
3 -> 2 = 4
2 -> 5 = 5
5 -> 7 = 6
5 -> 8 = 7
6 -> 4 = 8
6 -> 7 = 9
9 -> 7 = 10
9 -> 8 = 11
Please upload all .cpp file(s) along with the screenshots of all solutions/screens.
Data.txt
10 0 1 3 -999 1 4 -999 2 5 -999 3 2 -999 4 -999 5 7 8 -999 6 4 7 -999 7 -999 8 -999 9 7 8 -999
The current program displays
PROGRAM
#include#include #include #include using namespace std; //********************struct nodeType******************** template struct nodeType { Type info; nodeType *link; }; //***************** class linkedListIterator **************** template class linkedListIterator { public: linkedListIterator() { current = nullptr; } //Default constructor //Postcondition: current = nullptr; linkedListIterator(nodeType *ptr) { current = ptr; } //Constructor with a parameter. //Postcondition: current = ptr; Type operator*() { return current->info; } //Function to overload the dereferencing operator *. //Postcondition: Returns the info contained in the node. linkedListIterator operator++() { current = current->link; return *this; } //Overload the pre-increment operator. //Postcondition: The iterator is advanced to the next // node. bool operator==(const linkedListIterator & right) const { return (current == right.current); } //Overload the equality operator. //Postcondition: Returns true if this iterator is equal to // the iterator specified by right, // otherwise it returns the value false. bool operator!=(const linkedListIterator & right) const { return (current != right.current); } //Overload the not equal to operator. //Postcondition: Returns true if this iterator is not // equal to the iterator specified by // right; otherwise it returns the value // false. private: nodeType *current; //pointer to point to the current /ode in the linked list }; //***************** class linkedListType **************** template class linkedListType { public: const linkedListType & operator=(const linkedListType &) { if (this != &otherList) //avoid self-copy { copyList(otherList); }//end else return *this; } //Overload the assignment operator. void initializeList() { destroyList(); //if the list has any nodes, delete them } //Initialize the list to an empty state. //Postcondition: first = nullptr, last = nullptr, count = 0; bool isEmptyList() const { return(first == nullptr); } //Function to determine whether the list is empty. //Postcondition: Returns true if the list is empty, // otherwise it returns false. void print() const { nodeType *current; //pointer to traverse the list current = first; //set current so that it points to //the first node while (current != nullptr) //while more data to print { cout info link; } }//end print //Function to output the data contained in each node. //Postcondition: none int length() const { return count; } //end length //Function to return the number of nodes in the list. //Postcondition: The value of count is returned. void destroyList() { nodeType *temp; //pointer to deallocate the memory //occupied by the node while (first != nullptr) //while there are nodes in the list { temp = first; //set temp to the current node first = first->link; //advance first to the next node delete temp; //deallocate the memory occupied by temp } last = nullptr; //initialize last to nullptr; first has already //been set to nullptr by the while loop count = 0; } //Function to delete all the nodes from the list. //Postcondition: first = nullptr, last = nullptr, count = 0; Type front() const { assert(first != nullptr); return first->info; //return the info of the first node }//end front //Function to return the first element of the list. //Precondition: The list must exist and must not be // empty. //Postcondition: If the list is empty, the program // terminates; otherwise, the first // element of the list is returned. Type back() const { assert(last != nullptr); return last->info; //return the info of the last node }//end back //Function to return the last element of the list. //Precondition: The list must exist and must not be // empty. //Postcondition: If the list is empty, the program // terminates; otherwise, the last // element of the list is returned. virtual bool search(const Type& searchItem) const = 0; //Function to determine whether searchItem is in the list. //Postcondition: Returns true if searchItem is in the // list, otherwise the value false is // returned. virtual void insertFirst(const Type& newItem) = 0; //Function to insert newItem at the beginning of the list. //Postcondition: first points to the new list, newItem is // inserted at the beginning of the list, // last points to the last node in the list, // and count is incremented by 1. virtual void insertLast(const Type& newItem) = 0; //Function to insert newItem at the end of the list. //Postcondition: first points to the new list, newItem // is inserted at the end of the list, // last points to the last node in the list, // and count is incremented by 1. virtual void deleteNode(const Type& deleteItem) = 0; //Function to delete deleteItem from the list. //Postcondition: If found, the node containing // deleteItem is deleted from the list. // first points to the first node, last // points to the last node of the updated // list, and count is decremented by 1. linkedListIterator begin() { linkedListIterator temp(first); return temp; } //Function to return an iterator at the begining of the //linked list. //Postcondition: Returns an iterator such that current is // set to first. linkedListIterator end() { linkedListIterator temp(nullptr); return temp; } //Function to return an iterator one element past the //last element of the linked list. //Postcondition: Returns an iterator such that current is // set to nullptr. linkedListType() { first = nullptr; last = nullptr; count = 0; } //default constructor //Initializes the list to an empty state. //Postcondition: first = nullptr, last = nullptr, count = 0; linkedListType(const linkedListType & otherList) { first = nullptr; copyList(otherList); }//end copy constructor //copy constructor ~linkedListType() { destroyList(); }//end destructor //destructor //Deletes all the nodes from the list. //Postcondition: The list object is destroyed. protected: int count; //variable to store the number of //elements in the list nodeType *first; //pointer to the first node of the list nodeType *last; //pointer to the last node of the list private: void copyList(const linkedListType & otherList) { nodeType *newNode; //pointer to create a node nodeType *current; //pointer to traverse the list if (first != nullptr) //if the list is nonempty, make it empty destroyList(); if (otherList.first == nullptr) //otherList is empty { first = nullptr; last = nullptr; count = 0; } else { current = otherList.first; //current points to the //list to be copied count = otherList.count; //copy the first node first = new nodeType ; //create the node first->info = current->info; //copy the info first->link = nullptr; //set the link field of //the node to nullptr last = first; //make last point to the //first node current = current->link; //make current point to //the next node //copy the remaining list while (current != nullptr) { newNode = new nodeType ; //create a node newNode->info = current->info; //copy the info newNode->link = nullptr; //set the link of /ewNode to nullptr last->link = newNode; //attach newNode after last last = newNode; //make last point to //the actual last node current = current->link; //make current point //to the next node }//end while }//end else }//end copyList //Function to make a copy of otherList. //Postcondition: A copy of otherList is created and // assigned to this list. }; //********************class unorderedLinkedList******************** template class unorderedLinkedList : public linkedListType { public: bool search(const Type& searchItem) const { nodeType *current; //pointer to traverse the list bool found = false; current = first; //set current to point to the first /ode in the list while (current != nullptr && !found) //search the list if (current->info == searchItem) //searchItem is found found = true; else current = current->link; //make current point to //the next node return found; }//end search //Function to determine whether searchItem is in the list. //Postcondition: Returns true if searchItem is in the // list, otherwise the value false is // returned. void insertFirst(const Type& newItem) { nodeType *newNode; //pointer to create the new node newNode = new nodeType ; //create the new node newNode->info = newItem; //store the new item in the node newNode->link = first; //insert newNode before first first = newNode; //make first point to the //actual first node count++; //increment count if (last == nullptr) //if the list was empty, newNode is also //the last node in the list last = newNode; }//end insertFirst //Function to insert newItem at the beginning of the list. //Postcondition: first points to the new list, newItem is // inserted at the beginning of the list, // last points to the last node in the // list, and count is incremented by 1. void insertLast(const Type& newItem) { nodeType *newNode; //pointer to create the new node newNode = new nodeType ; //create the new node newNode->info = newItem; //store the new item in the node newNode->link = nullptr; //set the link field of newNode //to nullptr if (first == nullptr) //if the list is empty, newNode is //both the first and last node { first = newNode; last = newNode; count++; //increment count } else //the list is not empty, insert newNode after last { last->link = newNode; //insert newNode after last last = newNode; //make last point to the actual //last node in the list count++; //increment count } }//end insertLast //Function to insert newItem at the end of the list. //Postcondition: first points to the new list, newItem // is inserted at the end of the list, // last points to the last node in the // list, and count is incremented by 1. void deleteNode(const Type& deleteItem) { nodeType *current; //pointer to traverse the list nodeType *trailCurrent; //pointer just before current bool found; if (first == nullptr) //Case 1; the list is empty. cout info == deleteItem) //Case 2 { current = first; first = first->link; count--; if (first == nullptr) //the list has only one node last = nullptr; delete current; } else //search the list for the node with the given info { found = false; trailCurrent = first; //set trailCurrent to point //to the first node current = first->link; //set current to point to //the second node while (current != nullptr && !found) { if (current->info != deleteItem) { trailCurrent = current; current = current->link; } else found = true; }//end while if (found) //Case 3; if found, delete the node { trailCurrent->link = current->link; count--; if (last == current) /ode to be deleted //was the last node last = trailCurrent; //update the value //of last delete current; //delete the node from the list } else cout *graph; //array to create adjacency lists public: bool isEmpty() const { return (gSize == 0); } //Function to determine whether the graph is empty. //Postcondition: Returns true if the graph is empty; otherwise, returns false. void createGraph() { ifstream infile; infile.open("data.txt"); int index; int vertex; int adjacentVertex; if (gSize != 0) //if the graph is not empty, make it empty clearGraph(); if (!infile) { cout > gSize; //get the number of vertices cout > vertex; infile >> adjacentVertex; cout > adjacentVertex; if (adjacentVertex != -999) cout [size]; } //Constructor //Postcondition: gSize = 0; maxSize = size; // graph is an array of pointers to linked // lists. ~graphType() { clearGraph(); } //Destructor //The storage occupied by the vertices is deallocated. private: void dft(int v, bool visited[]) { visited[v] = true; cout graphIt; //for each vertex adjacent to v for (graphIt = graph[v].begin(); graphIt != graph[v].end(); ++graphIt) { int w = *graphIt; if (!visited[w]) dft(w, visited); } //end loop } //end dft //Function to perform the depth first traversal of //the graph at a node specified by the parameter vertex. //This function is used by the public member functions //depthFirstTraversal and dftAtVertex. //Postcondition: Starting at vertex, the vertices are // printed using depth first traversal // algorithm. }; //********************main function******************** int main() { cout Consider the graph G of Figure 20-6 FIGURE 20-6 Directed graph G A depth first ordering of the vertices of the graph G in Figure 0, 1, 4, 3, 2, 5, 7, 8, 6,9 20-6 is Consider the graph G of Figure 20-6 FIGURE 20-6 Directed graph G A depth first ordering of the vertices of the graph G in Figure 0, 1, 4, 3, 2, 5, 7, 8, 6,9 20-6 is
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


