Question: please do in python 3.5 or above also with the successors(file), start with with open(file) as f: contents = f.read() Section 2: Function details rectangle(perimeter,
please do in python 3.5 or above also with the successors(file), start with
with open(file) as f: contents = f.read()
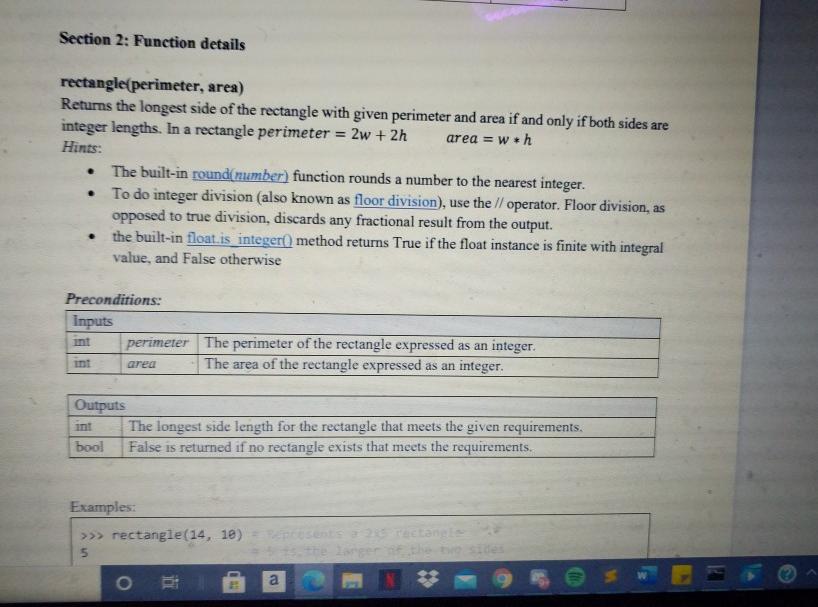
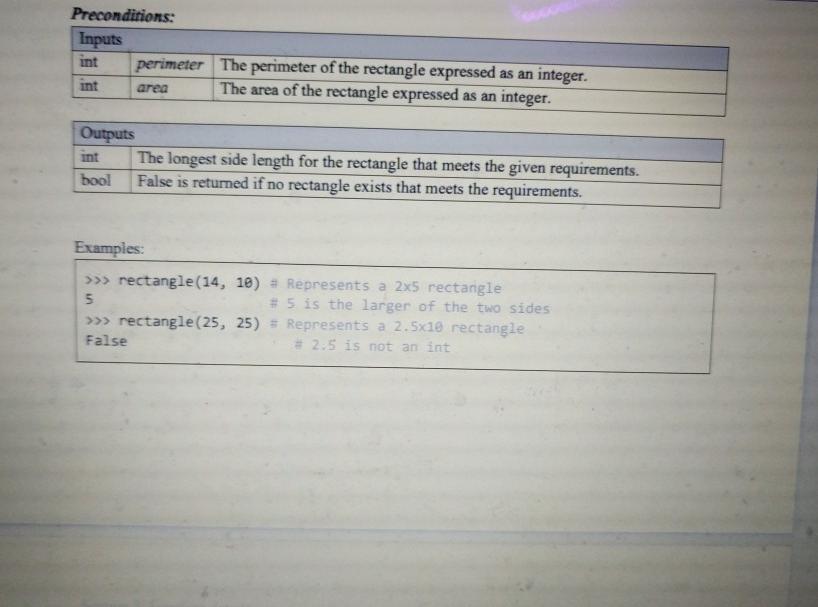
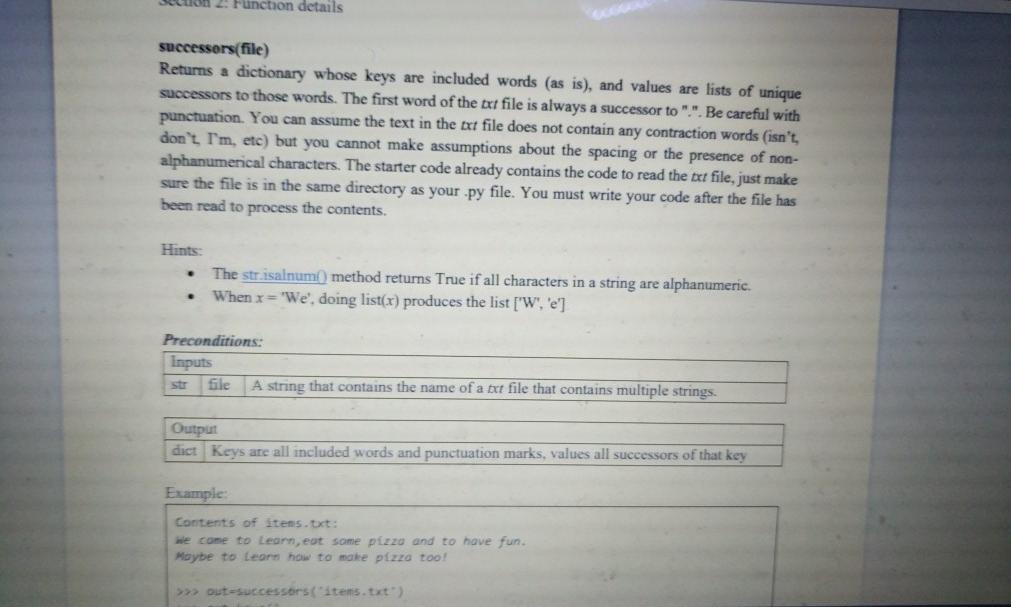
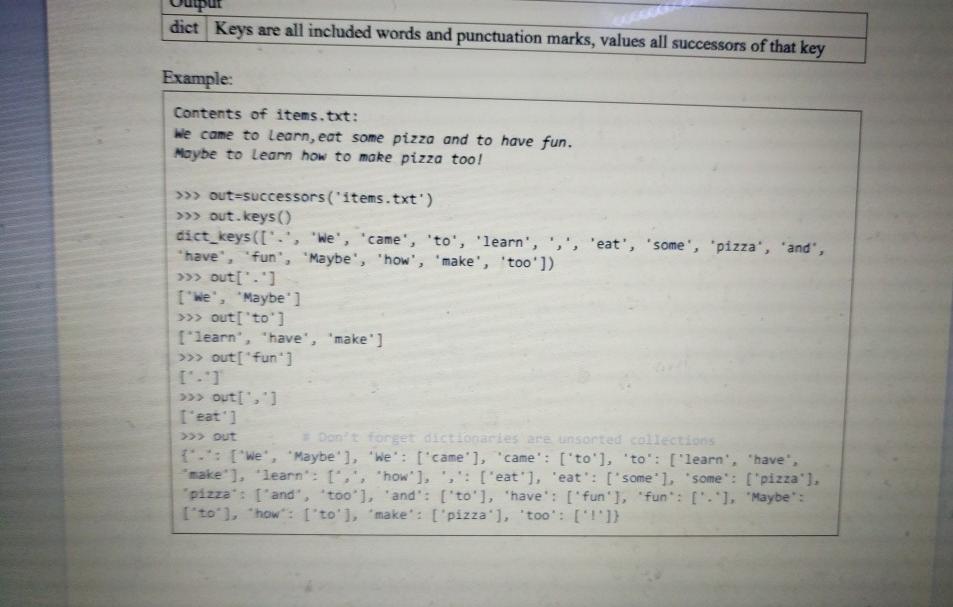
Section 2: Function details rectangle(perimeter, area) Returns the longest side of the rectangle with given perimeter and area if and only if both sides are integer lengths. In a rectangle perimeter 2w + 2h area = wih Hints: The built-in round(number) function rounds a number to the nearest integer. To do integer division (also known as floor division), use the // operator. Floor division, as opposed to true division, discards any fractional result from the output. the built-in float is integer() method returns True if the float instance is finite with integral value, and False otherwise . . . Preconditions: Inputs perimeter The perimeter of the rectangle expressed as an integer. area The area of the rectangle expressed as an integer. Outputs The longest side length for the rectangle that meets the given requirements. bool False is returned if no rectangle exists that meets the requirements Examples: >>> rectangle(14, 18) 5 arger o a Preconditions: Inputs perimeter The perimeter of the rectangle expressed as an integer. int The area of the rectangle expressed as an integer. int area Outputs The longest side length for the rectangle that meets the given requirements. bool False is returned if no rectangle exists that meets the requirements. Examples: >>> rectangle(14, 10) = Represents a 2x5 rectangle 5 # 5 is the larger of the two sides >>> rectangle(25, 25) = Represents a 2.5x18 rectangle False * 2:5 is not an int on 2. Function details successors(file) Returns a dictionary whose keys are included words (as is), and values are lists of unique successors to those words. The first word of the txt file is always a successor to ".". Be careful with punctuation. You can assume the text in the txt file does not contain any contraction words (isn't don't I'm, etc) but you cannot make assumptions about the spacing or the presence of non- alphanumerical characters. The starter code already contains the code to read the txt file, just make sure the file is in the same directory as your .py file. You must write your code after the file has been read to process the contents. Hints: The strisalnum) method returns True if all characters in a string are alphanumeric. When x='We', doing list(x) produces the list ['W', 'e'] Preconditions: Inputs file A string that contains the name of a txt file that contains multiple strings. Output dict Keys are all included words and punctuation marks, values all successors of that key Example Contents of items.txt: we come to Learn, eat some pizzo and to have fun. Maybe to learn how to make pizzo too! >>> out successors("items.txt") dict Keys are all included words and punctuation marks, values all successors of that key Example: Contents of items.txt: We came to learn, eat some pizza and to have fun. Moybe to Learn how to make pizza too! >>>> out=successors("items.txt') >>>> out. keys() dict_keys(['.', 'We', 'came', 'to', 'learn', 's', 'eat', 'some', 'pizza', 'and, "have', 'fun", "Maybe', 'how', 'make', 'too']) >>> out['.') I'We', "Maybe'] >>> out['to'] ["learn", "have', 'make'] >>> out["fun) >>> Out >>>> out(",) I'eat'] Don't forget dictionaries are unsorted collections t.: [we", "Maybe' ], 'We': ['came'], "came': ''to'], 'to': [ 'learn', 'have, make' ], 'learn: 1,, "how'], ',': [ 'eat'), 'eat': [somel, some": ["pizza'). pizza': ['and', 'too'], 'and': ['to'], "have': ['fun'], "fun": ["."), "Maybe ['to'], "how": ['to'], "make": ['pizza'), 'too': ['1'])
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


