Question: please do not post conputer program , Please write the actual calculation on the image. 1. For the mean and variance of a linear function
please do not post conputer program , Please write the actual calculation on the image.
1. For the mean and variance of a linear function of a random variable Y = aX + b, where a, b are constants, derive
2. Let X be a real-valued random variable. If E(X) = 1 and var(X) = 5, find
3. *Consider the following data sets:
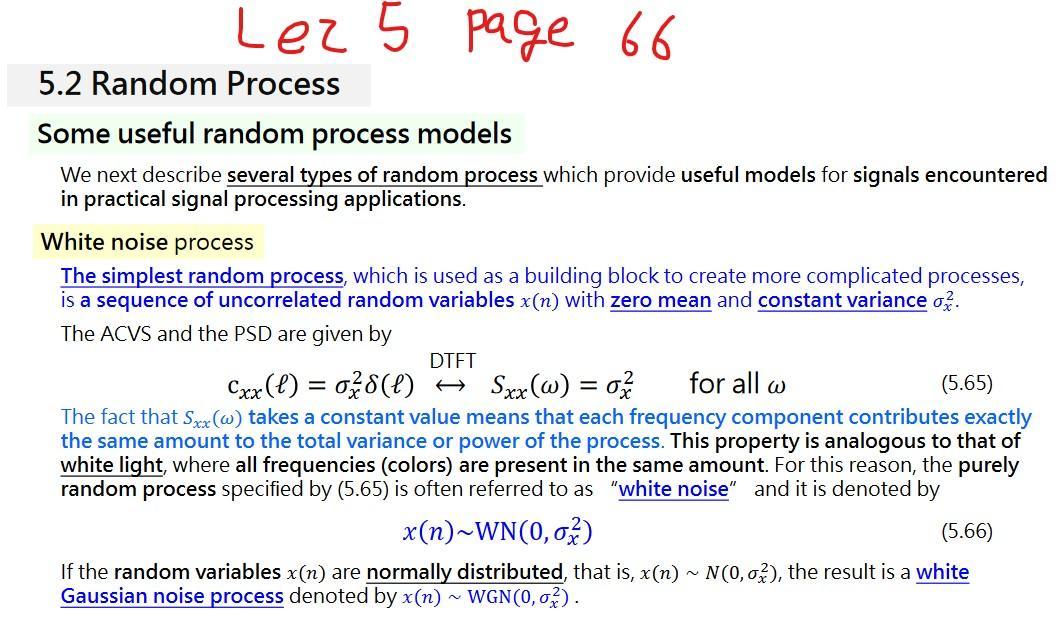
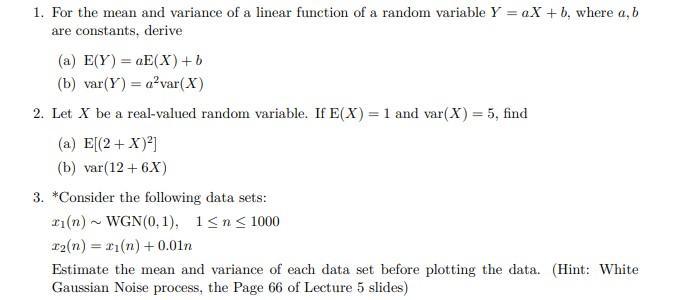
Lez5 page 66 5.2 Random Process Some useful random process models We next describe several types of random process which provide useful models for signals encountered in practical signal processing applications. White noise process The simplest random process, which is used as a building block to create more complicated processes, is a sequence of uncorrelated random variables x(n) with zero mean and constant variance o The ACVS and the PSD are given by DTFT Cxx(1) = o(l) Sxx(W) = o for all w (5.65) The fact that Sxx(w) takes a constant value means that each frequency component contributes exactly the same amount to the total variance or power of the process. This property is analogous to that of white light, where all frequencies (colors) are present in the same amount. For this reason, the purely random process specified by (5.65) is often referred to as "white noise" and it is denoted by x(n)~WN(0,02) (5.66) If the random variables x(n) are normally distributed, that is, x(n) ~ N(0,02), the result is a white Gaussian noise process denoted by x(n) ~ WGN(0,0). = - 1. For the mean and variance of a linear function of a random variable Y =aX+b, where a,b are constants, derive (a) E(Y) =qE(X) + (b) var(Y) = a var( X) 2. Let X be a real-valued random variable. If E(X)= 1 and var(X) = 5, find (a) E[(2 + x)) (b) var(12+6X) 3. *Consider the following data sets: r(n) ~ WGN(0.1), 1
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


