Question: Please do not use the same answer from other posted questions. Thank you for your help. BFS def bfs(map, office): return DFS
Please do not use the same answer from other posted questions. Thank you for your help.

""" BFS """ def bfs(map, office): return
""" DFS """ def dfs(map, office): return
""" Dijkstra's """ def dijkstra(map, office): return
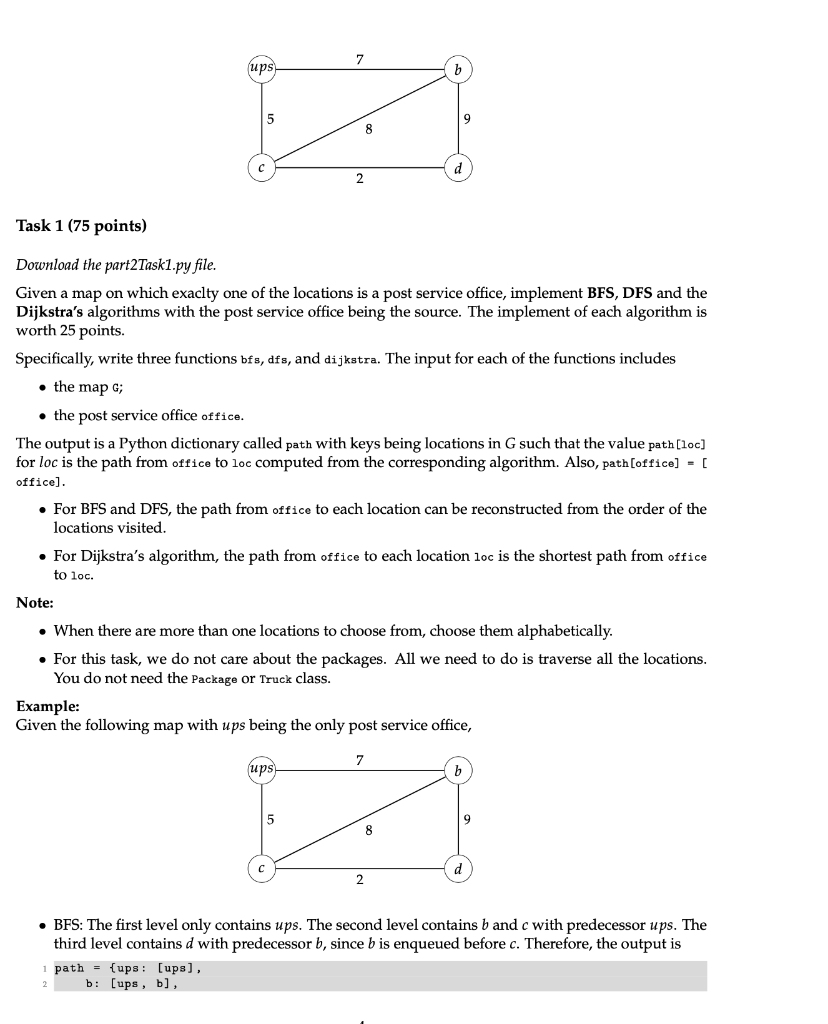
Part 2 Part 2 has two tasks. The first task is to implement some standard graph algorithms with some modifica- tions. The second part is more complicated and the winners get extra credits. Each group must submit only one version and list their members in the submission. Gradescope lets you add your members. In both tasks, we say a map is an undirected and weighted graph G, represented as a Python list of tuples for the edges and their weights in the graph. Each tuple (u,v,w) in G means there is an edge from vertex u to vertex v such that the weight of the edge is w. Since the graph is undirected, you also need to consider the edge from v to u with weight w. Given a path (01, 02, ..., Vn] from location vi to location Un, we say the weight of the path or the distance from vi to vn taking the path is the sum of the weight of all the edges on the path. (Note that this is not the standard representation of a weighted graph. You might find converting the input graph into a adjacency list of adjacency matrix helpful.) Assumptions: The map is connected, i.e., there is at least one path between any two locations. The weigth for every edge is non-negative. Example: The following graph is represented as [(ups, b,7), (ups,c,5), (6,6,8), (6,0,9), (0,2,2)]. The path from ups to b then to d is (ups, b, d). 7 ups N 5 9 8 d 2 Task 1 (75 points) Download the part2Task1.py file. Given a map on which exaclty one of the locations is a post service office, implement BFS, DFS and the Dijkstra's algorithms with the post service office being the source. The implement of each algorithm is worth 25 points. Specifically, write three functions bfs, dfs, and dijkstra. The input for each of the functions includes the map G; the post service office office. The output is a Python dictionary called path with keys being locations in G such that the value path [loc] for loc is the path from office to loc computed from the corresponding algorithm. Also, path [office] = [ office) For BFS and DFS, the path from office to each location can be reconstructed from the order of the locations visited. For Dijkstra's algorithm, the path from office to each location loc is the shortest path from office to loc. Note: When there are more than one locations to choose from, choose them alphabetically. . For this task, we do not care about the packages. All we need to do is traverse all the locations. You do not need the Package or Truck class. Example: Given the following map with ups being the only post service office, 7 ups b 5 9 8 2 BFS: The first level only contains ups. The second level contains b and c with predecessor ups. The third level contains d with predecessor b, since bis enqueued before c. Therefore, the output is 1 path = {ups: [ups), b: [ups, b), 2 3 c: [ups, c], d: [ups, b, d]} 4 DFS: The output is 1 path {ups: [ups], b: [ups, c, d, b], c: [ups, c], d: [ups, c, d]} 2 3 4 Dijkstra's: Starting from ups, the shortest path we take from ups to each of the other locations is computed as: 1 path {ups: [ups], b: [ups, b] , c: [ups, c), d: [ups, c, d]} 2 3 4 Part 2 Part 2 has two tasks. The first task is to implement some standard graph algorithms with some modifica- tions. The second part is more complicated and the winners get extra credits. Each group must submit only one version and list their members in the submission. Gradescope lets you add your members. In both tasks, we say a map is an undirected and weighted graph G, represented as a Python list of tuples for the edges and their weights in the graph. Each tuple (u,v,w) in G means there is an edge from vertex u to vertex v such that the weight of the edge is w. Since the graph is undirected, you also need to consider the edge from v to u with weight w. Given a path (01, 02, ..., Vn] from location vi to location Un, we say the weight of the path or the distance from vi to vn taking the path is the sum of the weight of all the edges on the path. (Note that this is not the standard representation of a weighted graph. You might find converting the input graph into a adjacency list of adjacency matrix helpful.) Assumptions: The map is connected, i.e., there is at least one path between any two locations. The weigth for every edge is non-negative. Example: The following graph is represented as [(ups, b,7), (ups,c,5), (6,6,8), (6,0,9), (0,2,2)]. The path from ups to b then to d is (ups, b, d). 7 ups N 5 9 8 d 2 Task 1 (75 points) Download the part2Task1.py file. Given a map on which exaclty one of the locations is a post service office, implement BFS, DFS and the Dijkstra's algorithms with the post service office being the source. The implement of each algorithm is worth 25 points. Specifically, write three functions bfs, dfs, and dijkstra. The input for each of the functions includes the map G; the post service office office. The output is a Python dictionary called path with keys being locations in G such that the value path [loc] for loc is the path from office to loc computed from the corresponding algorithm. Also, path [office] = [ office) For BFS and DFS, the path from office to each location can be reconstructed from the order of the locations visited. For Dijkstra's algorithm, the path from office to each location loc is the shortest path from office to loc. Note: When there are more than one locations to choose from, choose them alphabetically. . For this task, we do not care about the packages. All we need to do is traverse all the locations. You do not need the Package or Truck class. Example: Given the following map with ups being the only post service office, 7 ups b 5 9 8 2 BFS: The first level only contains ups. The second level contains b and c with predecessor ups. The third level contains d with predecessor b, since bis enqueued before c. Therefore, the output is 1 path = {ups: [ups), b: [ups, b), 2 3 c: [ups, c], d: [ups, b, d]} 4 DFS: The output is 1 path {ups: [ups], b: [ups, c, d, b], c: [ups, c], d: [ups, c, d]} 2 3 4 Dijkstra's: Starting from ups, the shortest path we take from ups to each of the other locations is computed as: 1 path {ups: [ups], b: [ups, b] , c: [ups, c), d: [ups, c, d]} 2 3 4
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


