Question: please explain every step with detail 10. Adsorption column design (10 points) An absorption tower is used to absorb ammonia from air using pure water
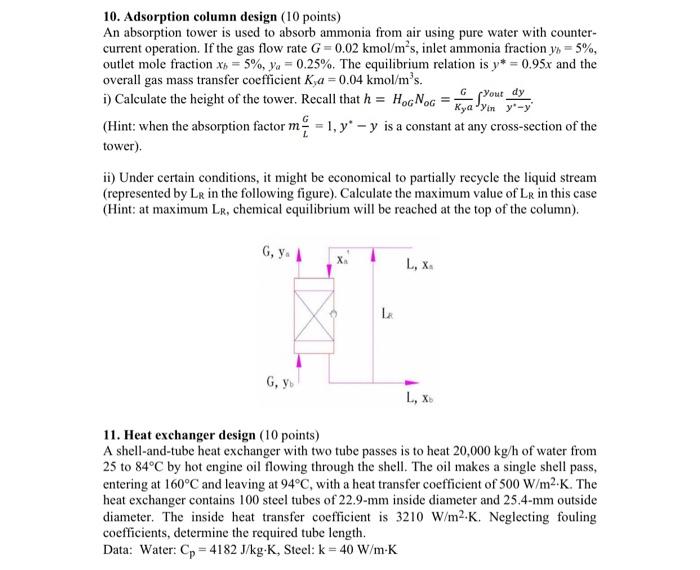
10. Adsorption column design (10 points) An absorption tower is used to absorb ammonia from air using pure water with counter- current operation. If the gas flow rate G=0.02 kmol/m's, inlet ammonia fraction y) = 5%, outlet mole fraction x6 = 5%, ya = 0.25%. The equilibrium relation is y* = 0.95x and the overall gas mass transfer coefficient Kya = 0.04 kmol/m's. 1) Calculate the height of the tower. Recall that h = HOGNOG Your dy Kya-yin y- (Hint: when the absorption factor m = 1, y y is a constant at any cross-section of the tower) ii) Under certain conditions, it might be economical to partially recycle the liquid stream (represented by LR in the following figure). Calculate the maximum value of Lr in this case (Hint: at maximum Lr, chemical equilibrium will be reached at the top of the column). Gy. . L, X H G, y L, X 11. Heat exchanger design (10 points) A shell-and-tube heat exchanger with two tube passes is to heat 20,000 kg/h of water from 25 to 84C by hot engine oil flowing through the shell. The oil makes a single shell pass, entering at 160C and leaving at 94C, with a heat transfer coefficient of 500 W/m2.K. The heat exchanger contains 100 steel tubes of 22.9-mm inside diameter and 25.4-mm outside diameter. The inside heat transfer coefficient is 3210 W/m2.K. Neglecting fouling coefficients, determine the required tube length. Data: Water: Cp=4182 J/kg-K, Steel: k = 40 W/m-K
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


