Question: Please explain for further understanding Question 4 - Join Implementation This problem will explore different join implementations and the associated IO costs for each model.

Please explain for further understanding
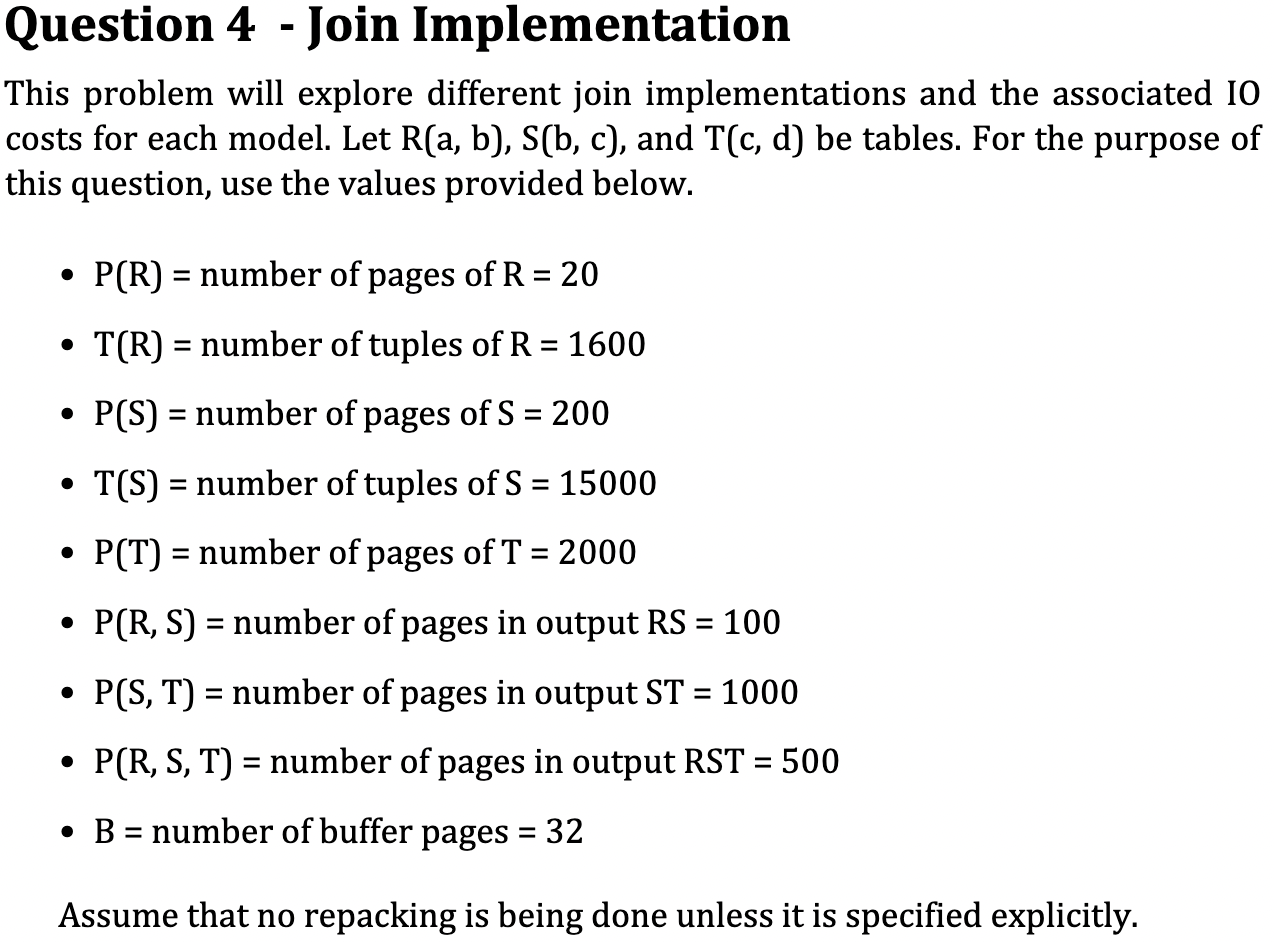
Question 4 - Join Implementation This problem will explore different join implementations and the associated IO costs for each model. Let R(a,b),S(b,c), and T(c,d) be tables. For the purpose of this question, use the values provided below. - P(R)= number of pages of R=20 - T(R)= number of tuples of R=1600 - P(S)= number of pages of S=200 - T(S)= number of tuples of S=15000 - P(T)= number of pages of T=2000 - P(R,S)= number of pages in output RS=100 - P(S,T)= number of pages in output ST=1000 - P(R,S,T)= number of pages in output RST=500 - B= number of buffer pages =32 Assume that no repacking is being done unless it is specified explicitly. Now consider using a block nested loop join. Compute the IO cost for joining R, S and then joining the result with T. Then compute the IO cost for joining S, T and then joining the result with R. Question 4.4 Now consider using a sort-merge join. Compute the IO cost for joining R, S and then joining the result with T. Assume that the tables are not sorted before starting. Also assume that we do not need to do any back up as described in lecture
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


