Question: Please explain the concept to the output expansion path and also what os the constant returns to scale? does that mean input price ration always
Please explain the concept to the output expansion path and also what os the constant returns to scale? does that mean input price ration always remains constant? please explain it step by step, thanks

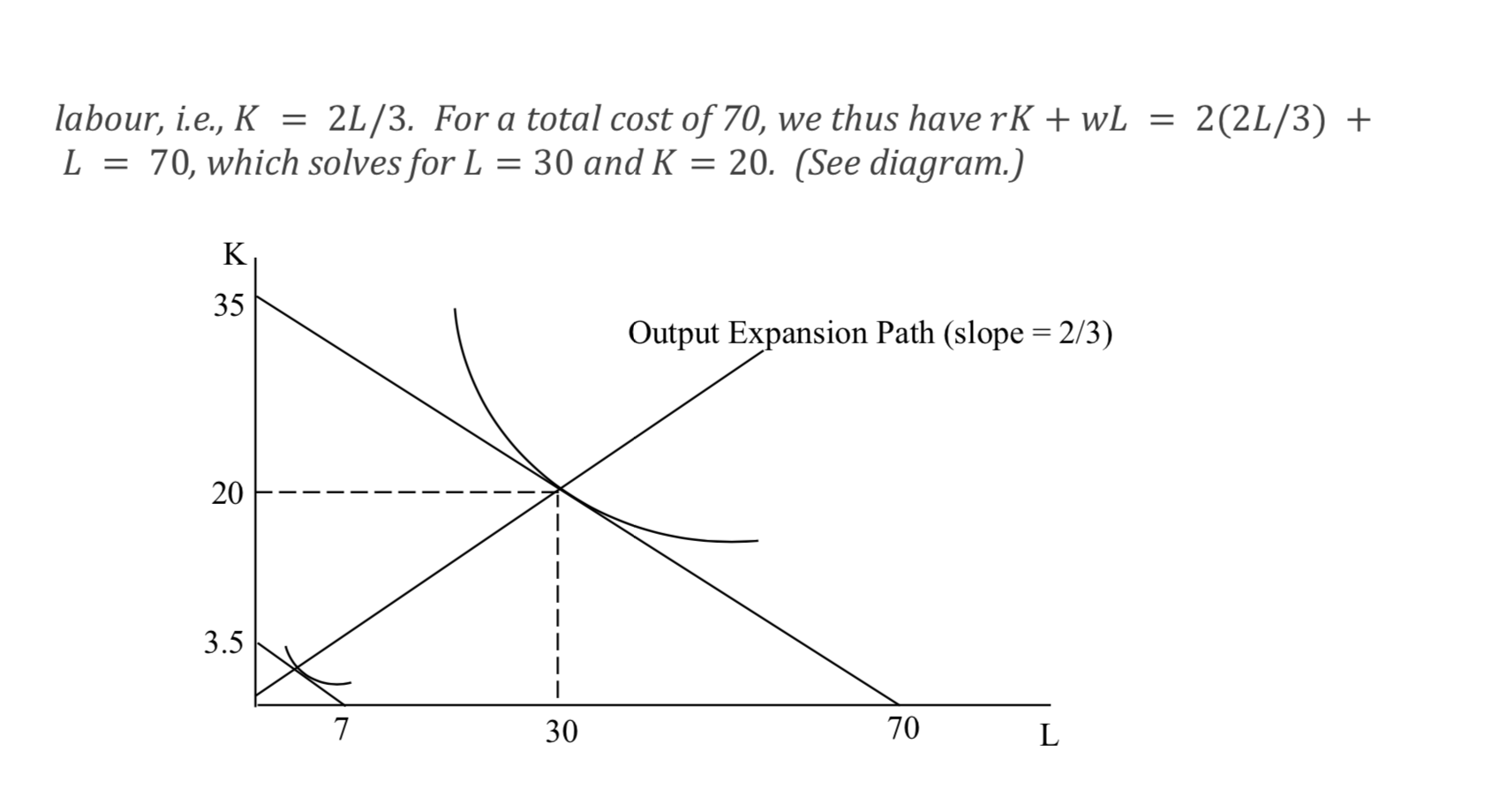
A rm has a production function Q = F (K, L) with constant returns to scale. lnput prices are r = 2 and w = 1. The output-expansion path for this production function at these input prices is a straight line through the origin. When the rm produces 5 units of output, it uses 2 units of K and 3 units of L. How much K and L will it use when its long-run total cost is equal to 70? ANSWER For this production junction, as long as the input price ratio (r/w) remains 2:1, the optimal input bundle will always have 2 units ofcapitalfor every 3 units of labour, i.e., K = 2L/3. For a total cost of 70, we thus have rk + wL = 2(2L/3) + L = 70, which solves for L = 30 and K = 20. (See diagram.) K 35 Output Expansion Path (slope = 2/3) 20 -- - --- 3.5 - 7 30 70 L
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


