Question: Please focus on c, d, e, f 2. Despite their ostensible structural similarities, it is found that the side chains of the amino acids tryptophan
Please focus on c, d, e, f
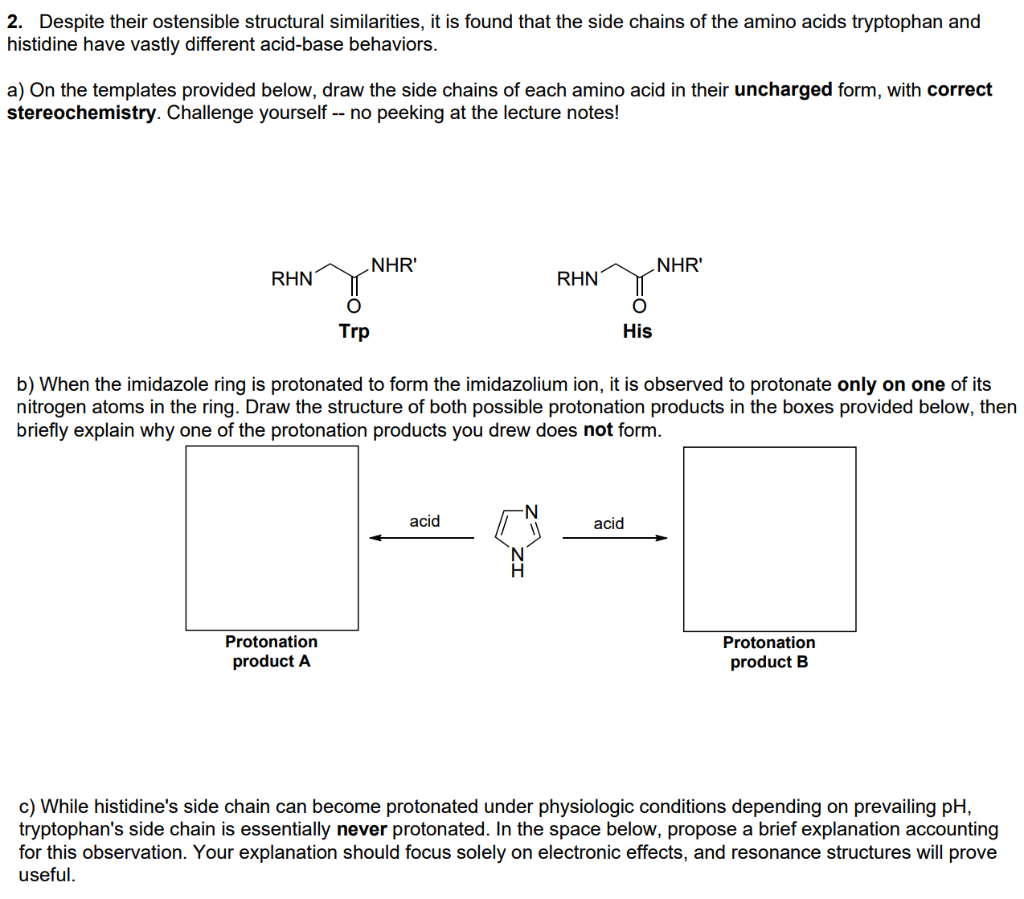
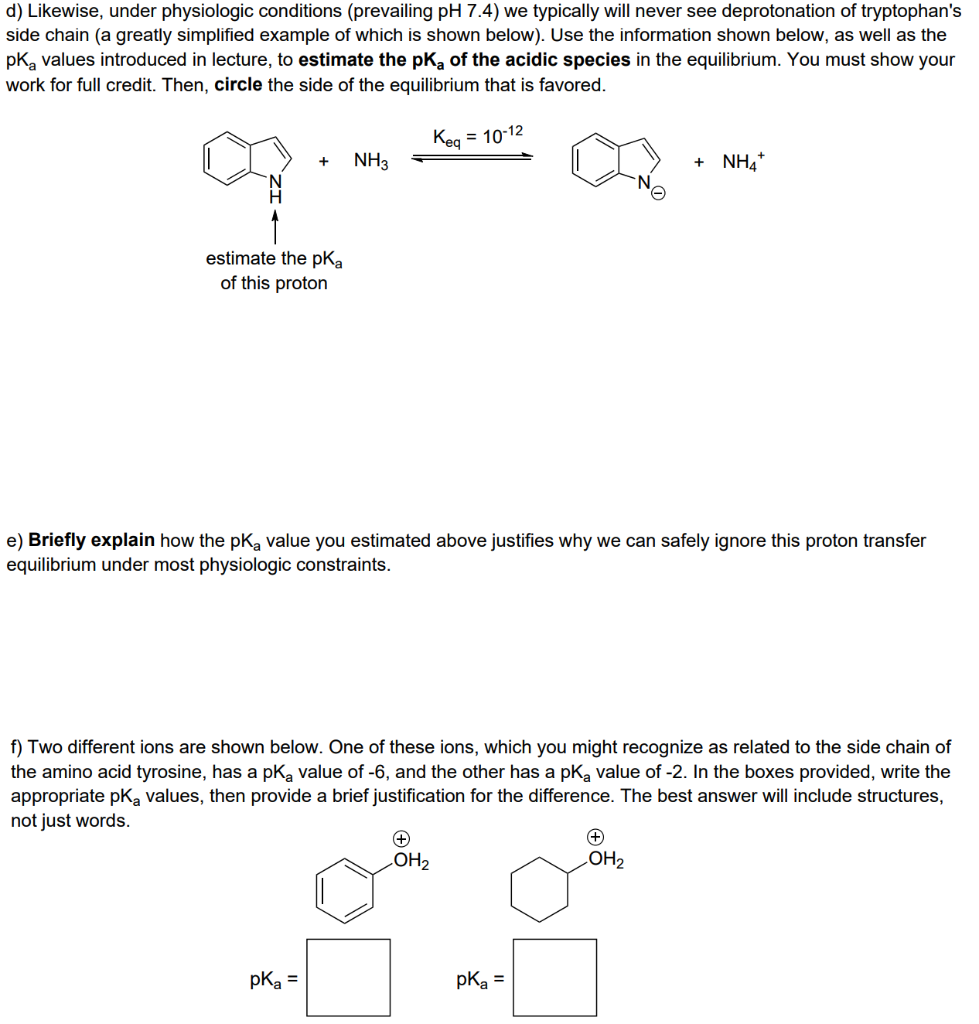
2. Despite their ostensible structural similarities, it is found that the side chains of the amino acids tryptophan and histidine have vastly different acid-base behaviors. a) On the templates provided below, draw the side chains of each amino acid in their uncharged form, with correct stereochemistry. Challenge yourself -- no peeking at the lecture notes! NHR' NHR RHN RHN Trp His b) When the imidazole ring is protonated to form the imidazolium ion, it is observed to protonate only on one of its nitrogen atoms in the ring. Draw the structure of both possible protonation products in the boxes provided below, then briefly explain why one of the protonation products you drew does not form. acid acid Protonation product A Protonation product B c) While histidine's side chain can become protonated under physiologic conditions depending on prevailing pH, tryptophan's side chain is essentially never protonated. In the space below, propose a brief explanation accounting for this observation. Your explanation should focus solely on electronic effects, and resonance structures will prove useful. d) Likewise, under physiologic conditions (prevailing pH 7.4) we typically will never see deprotonation of tryptophan's side chain (a greatly simplified example of which is shown below). Use the information shown below, as well as the pka values introduced in lecture, to estimate the pk, of the acidic species in the equilibrium. You must show your work for full credit. Then, circle the side of the equilibrium that is favored. Keg = 10-12 = + NH3 + NH4+ estimate the pka of this proton e) Briefly explain how the pKa value you estimated above justifies why we can safely ignore this proton transfer equilibrium under most physiologic constraints. f) Two different ions are shown below. One of these ions, which you might recognize as related to the side chain of the amino acid tyrosine, has a pk, value of -6, and the other has a pk, value of -2. In the boxes provided, write the appropriate pk, values, then provide a brief justification for the difference. The best answer will include structures, not just words. + OH2 OH2 pka = pka =
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


