Question: Please halp! Asap!! Question 30 1 pts (TRUE or FALSE?) The expected total return on a share of stock refers to the dividend yield less

Please halp! Asap!!
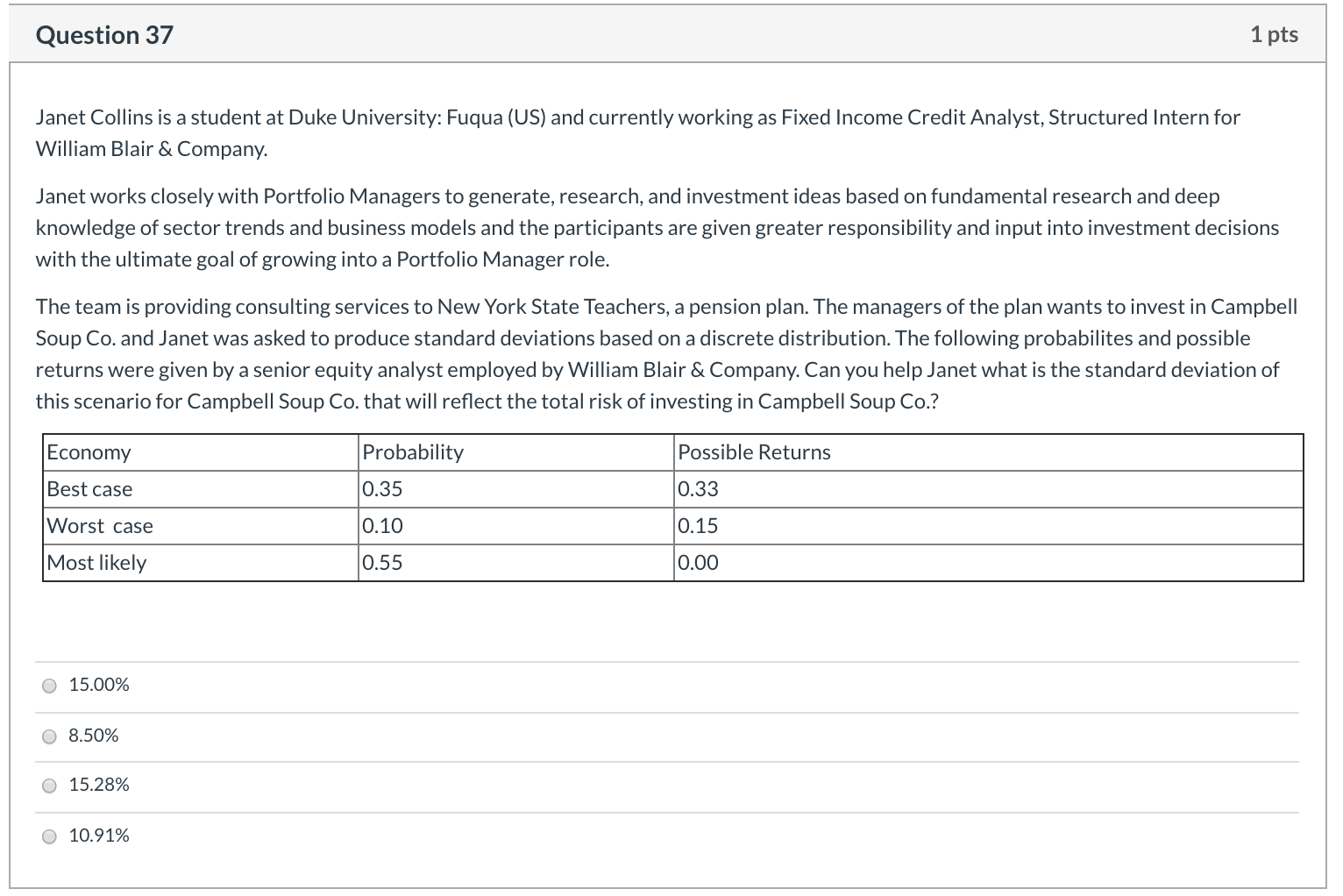
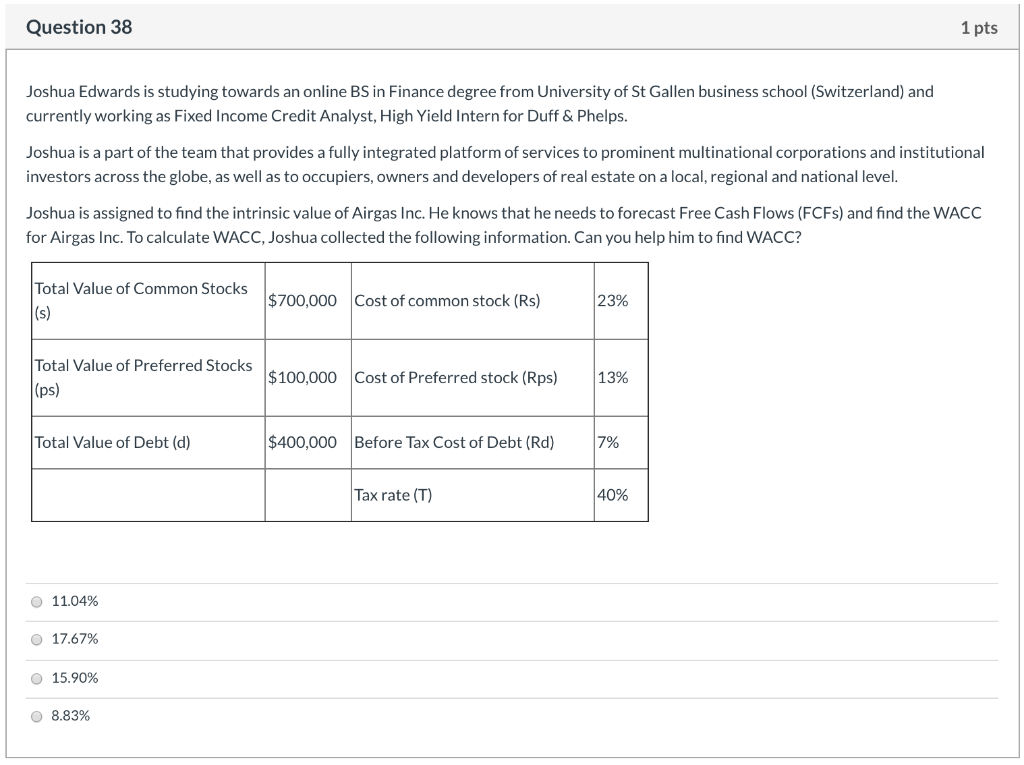
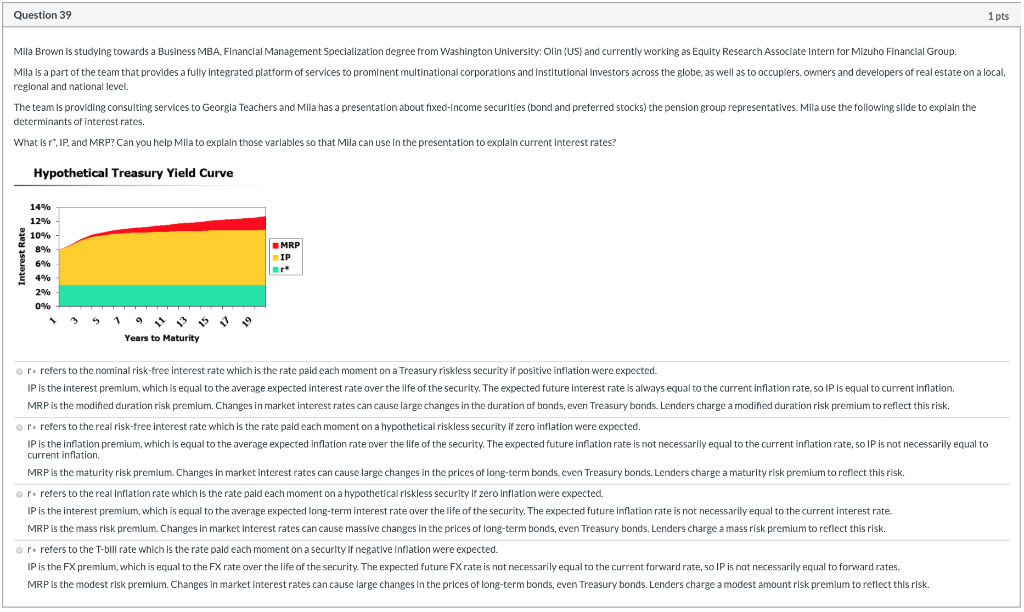
Question 30 1 pts (TRUE or FALSE?) The expected total return on a share of stock refers to the dividend yield less any commissions paid when the stock is purchased and sold. True False Question 31 1 pts (TRUE or FALSE?) When applied to dividends, the horizon value is the intrinsic stock price at the end of the explicit forecast period. True False Question 32 1 pts Akamai Technologies Inc has a beta of 1.33 and the expected market return is 0.2. If the 10-year Treasury bond is currently yielding 0.07 percent, find the cost of capital for Akamai Technologies Inc (round your answers). none of the answers is correct 20% 29% 24% 18% Question 33 1 pts (TRUE or FALSE?) To lower the WACC, since the after-tax cost of debt is lower than the cost of equity, the firm can use more debt and less common equity True False Question 34 1 pts (TRUE or FALSE?) The retention growth equation shows how growth is related to reinvestment as: Growth = ROE(1 - Payout ratio). True False Question 35 1 pts (TRUE or FALSE?) Three inputs are required to use the dividend growth approach: the current bond price, the current coupon, and the average investor's expected coupon rate. True O False Question 36 1 pts $26 per share is the current price for Foster Farms' stock. The dividend is projected to increase at a constant rate of 7.00% per year. The required rate of return on the stock, rs, is 12.00%. What is the stock's expected price 5 years from today? O $36.47 O $40.85 O $37.86 O $38.83 $39.83 Question 37 1 pts Janet Collins is a student at Duke University: Fuqua (US) and currently working as Fixed Income Credit Analyst, Structured Intern for William Blair & Company. Janet works closely with Portfolio Managers to generate, research, and investment ideas based on fundamental research and deep knowledge of sector trends and business models and the participants are given greater responsibility and input into investment decisions with the ultimate goal of growing into a Portfolio Manager role. The team is providing consulting services to New York State Teachers, a pension plan. The managers of the plan wants to invest in Campbell Soup Co. and Janet was asked to produce standard deviations based on a discrete distribution. The following probabilites and possible returns were given by a senior equity analyst employed by William Blair & Company. Can you help Janet what is the standard deviation of this scenario for Campbell Soup Co. that will reflect the total risk of investing in Campbell Soup Co.? Economy Probability Possible Returns 0.33 Best case 0.35 0.10 0.15 Worst case Most likely 0.55 0.00 O 15.00% 8.50% O 15.28% 10.91% Question 38 1 pts Joshua Edwards is studying towards an online BS in Finance degree from University of St Gallen business school (Switzerland) and currently working as Fixed Income Credit Analyst, High Yield Intern for Duff & Phelps. Joshua is a part of the team that provides a fully integrated platform of services to prominent multinational corporations and institutional investors across the globe, as well as to occupiers, owners and developers of real estate on a local, regional and national level. Joshua is assigned to find the intrinsic value of Airgas Inc. He knows that he needs to forecast Free Cash Flows (FCFS) and find the WACC for Airgas Inc. To calculate WACC, Joshua collected the following information. Can you help him to find WACC? Total Value of Common Stocks $700.000 cost of common stock (Rs) (s) 23% Total Value of Preferred Stocks (ps) $100,000 Cost of Preferred stock (Rps) 13% Total Value of Debt (d) $400,000 Before Tax Cost of Debt (Rd) 7% Tax rate (T) 40% 11.04% 17.67% 15.90% 8.83% Question 39 1 pts Mila Brown is studying towards a Business MBA Financial Management Specialization degree from Washington University: Olin (US) and currently working as Equity Research Associate Intern for Mizuho Financial Group. Mila is a part of the team that provides a fully integrated platform of services to prominent multinational corporations and Institutional Investors across the globe, as well as to occuplers, owners and developers of real estate on a local, regional and national level. The team is providing consulting services to Georgia Teachers and Mila has a presentation about fixed-income securities (bond and preferred stocks) the pension group representatives. Mila use the following slide to explain the determinants of interest rates. What is r*, IP, and MRP? Can you help Mila to explain those variables so that Mila can use in the presentation to explain current interest rates? Hypothetical Treasury Yield Curve Interest Rate 14% 12% 10% 8% 6% 2% 0% Years to Maturity or refers to the nominal risk-free interest rate which is the rate paid each moment on a Treasury riskless security if positive inflation were expected. IP is the interest premium, which is equal to the average expected interest rate over the life of the security. The expected future interest rate is always equal to the current inflation rate, so IP is equal to current inflation. MRP is the modified duration risk premium. Changes in market interest rates can cause large changes in the duration of bonds, even Treasury bonds. Lenders charge a modified duration risk premium to reflect this risk. or refers to the real risk-free interest rate which is the rate paid each moment on a hypothetical riskless security if zero inflation were expected. IP is the inflation premium, which is equal to the average expected inflation rate over the life of the security. The expected future inflation rate is not necessarily equal to the current inflation rate, so IP is not necessarily equal to current inflation. MRP is the maturity risk premium. Changes in market interest rates can cause large changes in the prices of long-term bonds, even Treasury bonds. Lenders charge a maturity risk premium to reflect this risk. prefers to the real inflation rate which is the rate paid each moment on a hypothetical riskless security if zero inflation were expected. IP is the interest premium, which is equal to the average expected long-term interest rate over the life of the security. The expected future inflation rate is not necessarily equal to the current interest rate. MRP is the mass risk premium. Changes in market interest rates can cause massive changes in the prices of long-term bonds, even Treasury bonds. Lenders charge a mass risk premium to reflect this risk. Op refers to the T-bill rate which is the rate paid each moment on a security if negative inflation were expected. IP is the FX premium, which is equal to the FX rate over the life of the security. The expected future FX rate is not necessarily equal to the current forward rate, so IP is not necessarily equal to forward rates. MRP is the modest risk premium. Changes in market interest rates can cause large changes in the prices of long-term bonds, even Treasury bonds. Lenders charge a modest amount risk premium to reflect this risk. Question 40 1 pts John Wood is studying towards a Bachelor of Science in Finance online degree from Macquarie Graduate School of Management (Australia) and currently working as Portfolio Management Analyst Intern for United bank of India. John works with a core research team that dissects earnings releases and regulatory filings to assess relevant news events, and model financial statements and industry dynamics, perform detailed valuation work, writing research notes and sector pieces, and speaking tointernal/external clients and management teams about the stocks/sector. The team is providing consulting services to CalSTRS. John is preparing a presentation to the pension plan managers and he is asked about the dual common stock shares. John found the following article from Financial Times to illustrate the pros and cons of dual shares. Which of the following can be better answers to why dual shares limit investor participation and why Hong Kong exchange forbid the practice initially? Can you help John so that he can use in his presentation? Hong Kong exchange moves towards dual share classes: Equities (Usa Region), Dunkley, Emma. Financial Times; London (UK) [London (UK)]16 Dec 2017: 15. The Hong Kong stock exchange has moved a step closer to allowing dual share classes, paving the way for blockbuster listings three years after losing out on technology giant Alibaba's flotation to the US. The exchange announced yesterday that it had concluded a consultation with 360 market stakeholders, including lawyers, accounting firms and investment managers among others, on allowing companies to offer a share class structure that gives more voting rights to certain investors. Following the consultation, HKEX has proposed that, rather than create a new exchange board for such dual share classes, companies using this structure from "emerging and innovative" sectors can list on the main board subject to certain limitations. The proposed limits - aimed at protecting investors - include a ceiling on voting rights of 10 votes per one share. Dual-class shares priovide twice as much dividends and all the investors can participate and purchase the shares. The return from dual shares can be too high and that is the reason initially Hong Kong exchange limited company participation with dual shares. Dual-class shares excludes the founders of the firm from participating in ownership and all the other investors can buy the dual shares and benefit from double dividend distributions. Since the original owners are excluded and it is not fair, initially Hong Kong exchange limited company participation with dual shares. Dual-class shares are convertible to the issuing firm's bonds before its maturity. These brings opportunity to all investors and at times the shares are oversubscribed and that is the reason initially Hong Kong exchange limited company participation with dual shares. O Dual-class shares allows some owners's common shares to count more in voting so those owners, usually the founders of the company, control the company's decision making. Thus, the founders of the company maintain control while the other investors have an opportunity to participate in the company's earnings and growth. That is the reason initially Hong Kong exchange limited company participation with dual shares
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


