Question: Please help me code the following in: JAVA! Please read the task THOROUGHLY and use a lot of COMMENTS. Full points will be awarded, thanks
Please help me code the following in: JAVA!
Please read the task THOROUGHLY and use a lot of COMMENTS.
Full points will be awarded, thanks in advance!
Task:
In this assignment, you will update the Money, Date, Bill, and ArrayList classes. Build a driver to test the functionality. Your code should compile with your driver, but note that you will want to test your code more fully.
1. Modify the Money, Date, and Bill class to implement the Comparable interface. Remember that compareTo takes an Object parameter and you should check to make sure that the object class is actually the correct class for the comparison, as appropriate.
2. Modify the Money, Date, and Bill classes to implement the Cloneable interface. Note that Money and Date can simply copy their private instance variables, since they store only primitive and immutable types. However, you will need to override the clone method, to make it public, since it is protected in the Object class. The Bill class will need to do more, since it incorporates the Money and Date classes, which are mutable. Note that it can (and should) use the clone methods of those classes. Be sure to remove any use of the copy constructor for Money, Date, and Bill in the rest of the code (the definition can exist, but dont use it in other classes; use the clone method instead).
3. Build a class ExpenseAccount that extends your ArrayList. You should remove the limit on the number of bills that can be placed in an account by making your ArrayList dynamically resize itself.
4. Modify Money, Bill, and Date to implement the Serializable interface.
5. Have your ArrayList implement the Iterable interface.
6. Correct any errors in classes below:
Money class:
class Money { private int dollars; private int cents; //Define constructor public Money(int dol) {//Constructor which sets the dollar amount, and sets cents to 0 dollars = dol; cents = 0; }
public Money(int dol, int cent) {//Constructor which initialized dollars and cents. dollars = dol; if(cents >99) { dollars +=1; cents = cents - 100; } else cents = cent; }
public Money(Money lOthr) {//Copy constructor this(lOthr.getDollars(), lOthr.getCents()); }
public int getDollars() { return dollars; }
public void setDollars(int dollars) {//Instance variable dollars constructor this.dollars = dollars; }
public int getCents() { return cents; }
public void setCents(int cents) {//Instance variable cents constructor this.cents = cents; }
public double getMoney() {//Returns amount of money return dollars + cents/100; }
public void setMoney(int dol, int cent) {//Sets money setDollars(dol); setCents(cent); }
public void add(int dol) {//Adds dollars dollars += dol; }
public void add(int dol, int cent) {//Adds cents and dollars dollars += dol; cents =+ cent; if(cents > 99) { dollars += 1; cents = cents-100; } }
public void add(Money lOthr) {//Adds the amounts in other to our money object reducing cents appropriately. add(lOthr.getDollars(), lOthr.getCents());
}
public boolean equals(Object o) { Money lOthr = (Money)o; if(this.dollars == lOthr.getDollars() && this.getCents() == lOthr.getCents()) return true; else return false; }
public String toString() { //Returns money in string format return "$" + getMoney(); } }
Date class:
public class Date { //instance variables private int month; private int day; private int year; public Date(int month, int day, int year) {//Sets instance variables setMonth(month); setDay(day); setYear(year); }
public Date(Date other) {//Instance variables constructor this.month = other.month; this.day = other.day; this.year = other.year; }
public int getMonth() { return month; }
public void setMonth(int month) {//Checks if month entered is valid if(month 12) { System.out.println("Invalid month"); System.exit(-1); } this.month = month; }
public int getDay() { return day; }
public void setDay(int day) {//Checks if day entered is valid if(day 31) { System.out.println("Invalid day"); System.exit(-1); } this.day = day; }
public int getYear() { return year; }
public void setYear(int year) {//Checks if year entered is valid if(year 2024) { System.out.println("Invalid year"); System.exit(-1); } this.year = year; }
public boolean isAfter(Date compareTo) {//Return true if the compareTo date is after the date. int cmp = Integer.compare(compareTo.year, year); if(cmp == 0) { cmp = Integer.compare(compareTo.month, month); if(cmp == 0) { cmp = Integer.compare(compareTo.day, day); return cmp
public String toString() {//Formats date in mm/dd/yyyy return day + "/" + month + "/" + year; }
public boolean equals(Object date) { Date other = (Date) date; return year == other.year && month == other.month && day == other.day; } }
Bill class:
class Bill { //Declare variables private Money amount; private Date dueDate; private Date paidDate; private String originator; public Bill(Money amount, Date dueDate, String originator) {//Constructor for instance variables this.amount = amount; this.dueDate = dueDate; this.originator = originator; this.paidDate = null; } //Defines constructor public Bill(Bill toCopy) { this.amount = toCopy.amount; this.dueDate = toCopy.dueDate; this.originator = toCopy.originator; this.paidDate = toCopy.paidDate; } public Date getDueDate() throws Exception {//Gets due date if(paidDate == null) return dueDate; else if(paidDate.isAfter(dueDate)) throw new Exception("The due date is before the paid date."); else return dueDate; }
public String getOriginator() { return originator; } public boolean isPaid() { if(paidDate != null) return true; else return false; } boolean setPaid(Date onDay) throws Exception {//if datePaid is after the dueDate, the call does not update anything and returns false. if(onDay.before(dueDate)) this.paidDate = onDay; else throw new Exception("The paid date is after the due date."); return true; } public void setUnpaid() { this.paidDate = null; } public void setDueDate(Date nextDate) throws Exception { if(nextDate.isAfter(paidDate)) this.dueDate = nextDate; else throw new Exception("The due date is before the paid date."); } public void setAmount(Money amount) { this.amount = amount; }
public Money getAmount() { return new Money(amount); }
public void setOriginator(String originator) { this.originator = originator; } public String toString() {//Builds a string that reports the amount, when due, to whom, if paid, and if date paid String value = "An amount of " + amount + " is due on " + dueDate + " and "; if(paidDate == null) value += "is still not yet paid."; else value += "was paid on " + paidDate; return value; } public boolean equals(Bill toCompare) {//Returns if the two objects are the same if(toCompare.amount == this.amount && toCompare.dueDate == this.dueDate && toCompare.paidDate == this.paidDate && this.originator == toCompare.originator) return true; else return false; } }
Notes:
-Make sure you comment all methods and the class with javadoc comments.
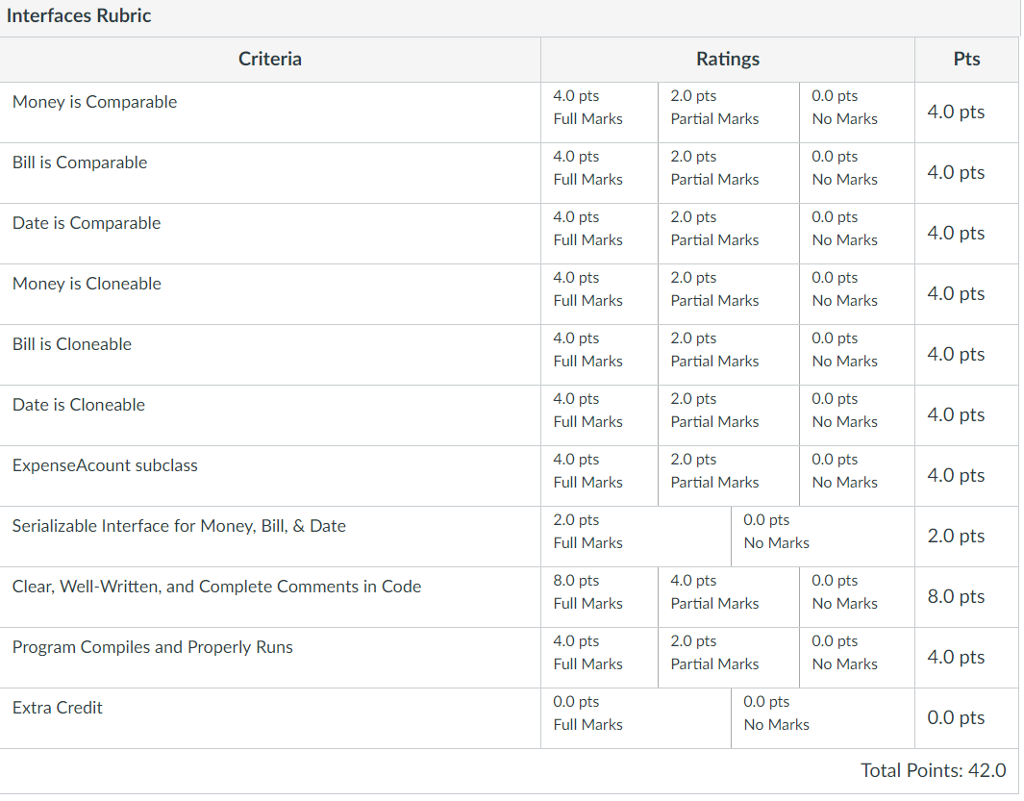
Interfaces Rubric Criteria Ratings 4.0 pts Full Marks 2.0 pts Partial Marks 0.0 pts No Marks Money is Comparable 4.0 pts 4.0 pts Full Marks 2.0 pts 0.0 pts No Marks Bill is Comparable Partial Marks 4.0 pts 4.0 pts Full Marks 2.0 pts Partial Marks 0.0 pts No Marks Date is Comparable 4.0 pts 4.0 pts Full Marks 2.0 pts Partial Marks Money is Cloneable 0.0 pts 4.0 pts No Marks 4.0 pts Full Marks 2.0 pts Partial Marks 0.0 pts No Marks Bill is Cloneable 4.0 pts 4.0 pts Full Marks 2.0 pts Partial Marks 0.0 pts No Marks Date is Cloneable 4.0 pts 4.0 pts Full Marks 2.0 pts 0.0 pts No Marks ExpenseAcount subclass 4.0 pts Partial Marks 2.0 pts Full Marks 0.0 pts No Marks Serializable Interface for Money, Bill, & Date 2.0 pts 8.0 pts Full Marks 4.0 pts Partial Marks 0.0 pts No Marks Clear, Well-Written, and Complete Comments in Code 8.0 pts 4.0 pts Full Marks 2.0 pts Partial Marks 0.0 pts No Marks Program Compiles and Properly Runs 4.0 pts 0.0 pts Full Marks 0.0 pts No Marks Extra Credit 0.0 pts Total Points: 42.0
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


