Question: please help me out with these problems!! 2. Units conversion-E. The viscosity 4 of an oil is 10 cP, and its specific gravity s is

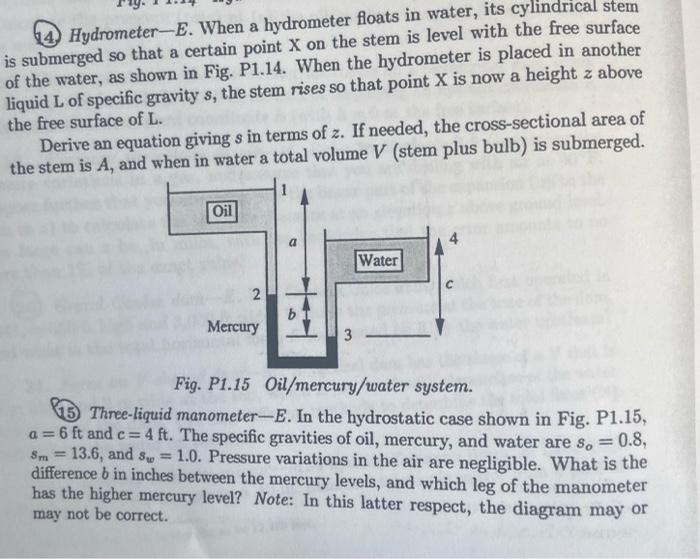
2. Units conversion-E. The viscosity 4 of an oil is 10 cP, and its specific gravity s is 0.8. Reexpress both of these (the latter as density p) in both the Iben, ft, s system and in SI units. Tinite monuercion-F. Use conversion factors to express: (a) the gravita- 2 Meteorite density-E. The Barringer Crater in Arizona was formed 30,000 years ago by a spherical meteorite of diameter 60 m and mass 10 t (tonnes), traveling at 15 km/s when it hit the ground.' (Clearly, all figures are estimates.) What was the mean density of the meteorite? What was the predominant material in the meteorite? Why? If one tonne of the explosive TNT is equivalent to five billion joules, how many tonnes of TNT would have had the same impact as the meteorite? 5. Reynolds number-E. What is the mean velocity Um (ft/s) and the Reynolds number Re = pum/ for 35 gpm (gallons per minute) of water flowing in a 1.05- in. I.D. pipe if its density is p = 62.3 lbm/ft and its viscosity is u = 1.2 cP? What are the units of the Reynolds number? Hydrometer-E. When a hydrometer floats in water, its cylindrical stem is submerged so that a certain point X on the stem is level with the free surface of the water, as shown in Fig. P1.14. When the hydrometer is placed in another liquid L of specific gravity s, the stem rises so that point X is now a height z above the free surface of L. Derive an equation giving s in terms of z. If needed, the cross-sectional area of the stem is A, and when in water a total volume V (stem plus bulb) is submerged. Oil a Water c 2 Mercury 3 Fig. P1.15 Oil/mercury/water system. 1 Three-liquid manometer-E. In the hydrostatic case shown in Fig. P1.15, a=6 ft and c= 4 ft. The specific gravities of oil, mercury, and water are so = 0.8, Sm= 13.6, and sy = 1.0. Pressure variations in the air are negligible. What is the difference b in inches between the mercury levels, and which leg of the manometer has the higher mercury level? Note: In this latter respect, the diagram may or may not be correct. 17. Oil and gas well pressures-M. A pressure gauge at the top of an oil well 18.000 ft deep registers 2,000 psig. The bottom 4,000-ft portion of the well is filled with oil (s = 0.70). The remainder of the well is filled with natural gas (T = 60F, compressibility factor Z = 0.80, and s = 0.65, meaning that the molecular weight is 0.65 times that of air). Calculate the pressure (psig) at (a) the oil/gas interface, and (b) the bottom of the well. (20 Grand Coulee dam-E. The Grand Coulee dam, which first operated in 1941, is 550 ft high and 3,000 ft wide. What is the pressure at the base of the dam, and what is the total horizontal force F lbf exerted on it by the water upstream
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


