Question: Please help me to solve these case. For the point (a): should we consider straightline depreciation in cash flow or only use salvage value as
Please help me to solve these case.
For the point (a): should we consider straightline depreciation in cash flow or only use salvage value as additional income during the 5th year?
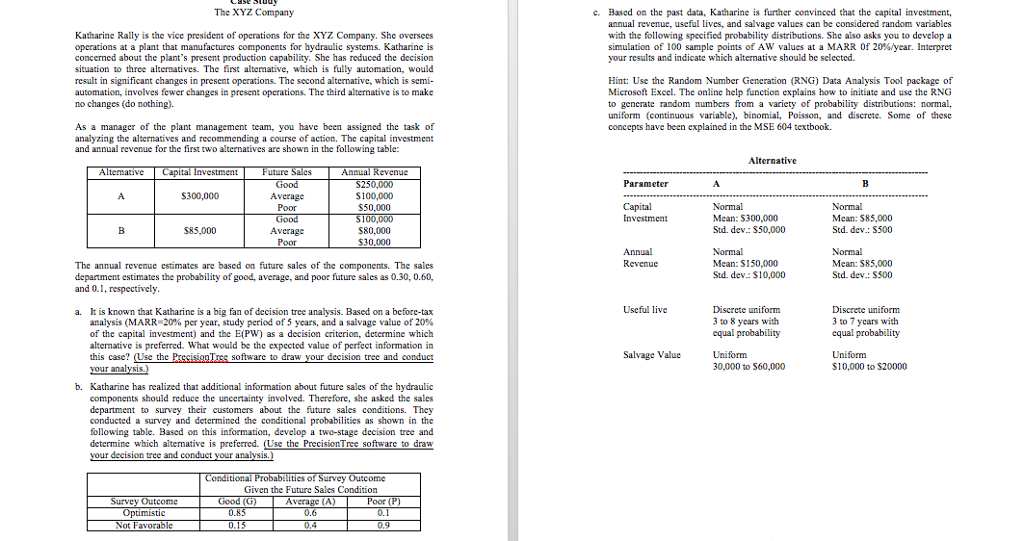
The XYZ Company c. Based on the past data, Katharine is further convinced that the capital investment, annual revenue, useful lives, and salvage values can be considered random variables Katharine Rally is the vice president of operations for the XYZ. Company. She oversees with the following specified probability distributions. She also asks you to develop a operations at a plant that manufactures components for hydraulic systems. Katharine is simulation of 100 sample points of AW values at a MARR Of 20%%/year. Interpret concerned about the plant's present production capability. She has reduced the decision your results and indicate which alternative should be selected. situation to three alternatives. The first alternative, which is fully automation, would result in significant changes in present operations. The second alternative, which is semi- Hint: Use the Random Number Generation (RNG) Data Analysis Tool package of automation, involves fewer changes in present operations. The third alternative is to make Microsoft Excel. The online help function explains how to initiate and use the RNG no changes (do nothing)- to generate random numbers from a variety of probability distributions: normal, As a manager of the plant management team, you have been assigned the task of uniform (continuous variable), binomial, Poisson, and discrete. Some of these concepts have been explained in the MSE 604 textbook. analyzing the alternatives and recommending a course of action. The capital investment and annual revenue for the first two alternatives are shown in the following table: Alternative Alternative Capital Investment Future Sales Annual Revenue Good $250,000 Parameter B $300,000 Average $100,000 Poor $50.000 Capital Normal Normal Good $100,000 Investment Mean: $300,000 Mean: $85,000 $85,000 Average $80.000 Std. dev: $50,000 Std. dev.: $500 Poor $30,000 Annual Normal Normal The annual revenue estimates are based on future sales of the components. The sales Revenue Mean: $150,000 Mean: $85,000 department estimates the probability of good, average, and poor future sales as 0.30, 0.60, Sid. dev: $10,000 Std. dev.: $500 and 0.1, respectively. a. It is known that Katharine is a big fan of decision tree analysis. Based on a before-tax Useful live Discrete uniform Discrete uniform analysis (MARR-20% per year, study period of 5 years, and a salvage value of 20% 3 to 8 years with 3 to 7 years with of the capital investment) and the E(PW) as a decision criterion, determine which equal probability equal probability alternative is preferred. What would be the expected value of perfect information in this case? (Use the Precision Tree software to draw your decision tree and conduct Salvage Value Uniform Uniform your analysis. 30.000 to 560.000 $10.000 to $20000 b. Katharine has realized that additional information about future sales of the hydraulic components should reduce the uncertainty involved. Therefore, she asked the sales department to survey their customers about the future sales conditions. They conducted a survey and determined the conditional probabilities as shown in the following table. Based on this information, develop a two-stage decision tree and determine which alternative is preferred. (Use the PrecisionTree software to draw your decision tree and conduct your analysis.) Conditional Probabilities of Survey Outcome Given the Future Sales Condition Survey Outcome Good (G) Average (A) Poor (P) Optimistic 0.85 0.6 0.1 Not Favorable 0.15 0,4
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


