Question: please help solve these and show working out for each box 5) In order to answer the next question, you need to fill in the
please help solve these and show working out for each box
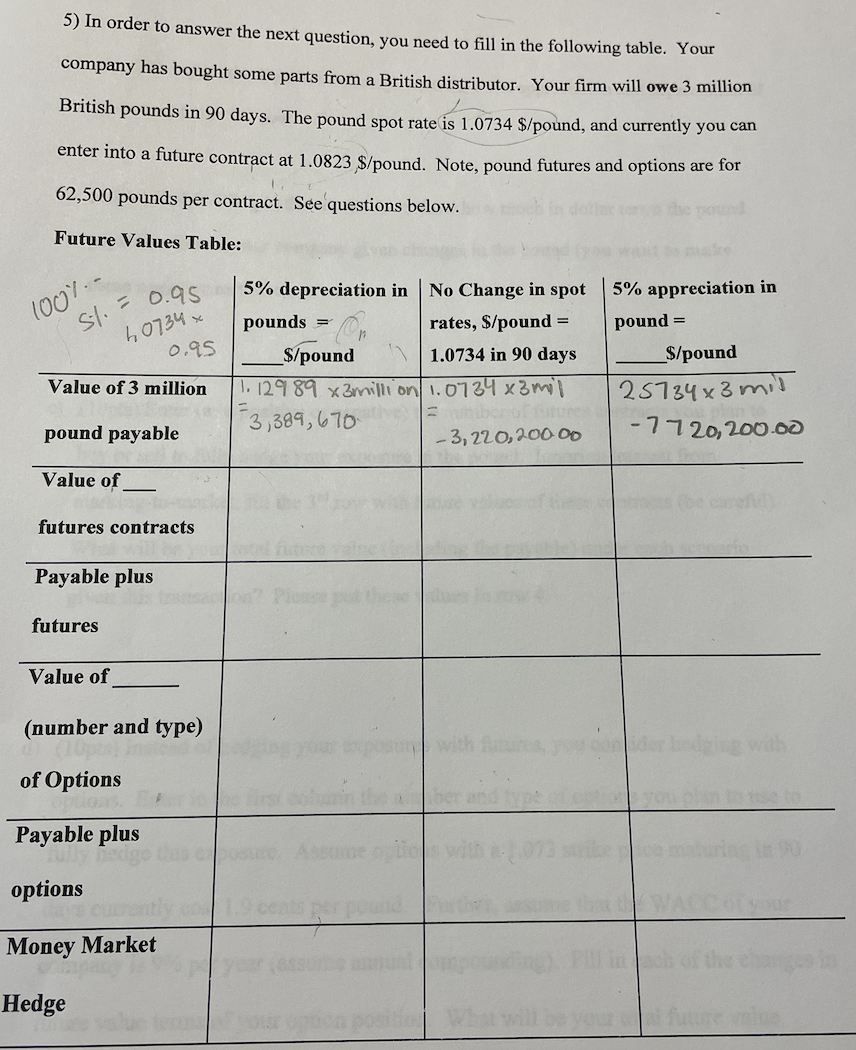


5) In order to answer the next question, you need to fill in the following table. Your company has bought some parts from a British distributor. Your firm will owe 3 million British pounds in 90 days. The pound spot rate is 1.0734$/ pound, and currently you can enter into a future contract at 1.0823$/ pound. Note, pound futures and options are for 62,500 pounds per contract. See questions below. Future Values Table: a) (5pts) Calculate the $/ pound exchange rates for a 5% appreciation and depreciation of the pound in the top row. b) (10pts) Finish filling in the second row; show how much in dollar terms the pound payable will cost your company given changes in the pound (you want to make these negative as these are costs). c) (10pts) Enter (as a positive or negative) the number of futures contracts you plan to buy or sell to fully hedge your exposure in the pound. Ignoring interest from marking-to-market, fill the 3rd row with future values of these contracts (be careful). What will be your total future value (including the payable) under each scenario given this transaction? Please put these values in row 4. d) (10pts) Instead of hedging your exposures with futures, you consider hedging with options. Enter in the first column the number and type of options you plan to use to fully hedge this exposure. Assume options with a 1.073 strike price maturing in 90 days currently cost 1.9 cents per pound. Further, assume that the WACC of your company is 9% per year (assume annual compounding). Fill in each of the changes in future value terms of your option position. What will be your total future value (including the payable) under each scenario given this transaction? Does your company do better with an appreciation or depreciation if you use this hedge? e) (10pts) Now construct a money-market hedge for this exposure. Your firm can borrow pounds at 3.0%, or invest in pounds at 2.8% annual rates. You can borrow US\$ at 3.5% or invest in US\$ at 3.3%. Again these are annually compounded annual rates. Describe exactly how you would construct a money-market hedge. Compare the money market hedge with the futures hedge you constructed above by putting in future values to the table. 5) In order to answer the next question, you need to fill in the following table. Your company has bought some parts from a British distributor. Your firm will owe 3 million British pounds in 90 days. The pound spot rate is 1.0734$/ pound, and currently you can enter into a future contract at 1.0823$/ pound. Note, pound futures and options are for 62,500 pounds per contract. See questions below. Future Values Table: a) (5pts) Calculate the $/ pound exchange rates for a 5% appreciation and depreciation of the pound in the top row. b) (10pts) Finish filling in the second row; show how much in dollar terms the pound payable will cost your company given changes in the pound (you want to make these negative as these are costs). c) (10pts) Enter (as a positive or negative) the number of futures contracts you plan to buy or sell to fully hedge your exposure in the pound. Ignoring interest from marking-to-market, fill the 3rd row with future values of these contracts (be careful). What will be your total future value (including the payable) under each scenario given this transaction? Please put these values in row 4. d) (10pts) Instead of hedging your exposures with futures, you consider hedging with options. Enter in the first column the number and type of options you plan to use to fully hedge this exposure. Assume options with a 1.073 strike price maturing in 90 days currently cost 1.9 cents per pound. Further, assume that the WACC of your company is 9% per year (assume annual compounding). Fill in each of the changes in future value terms of your option position. What will be your total future value (including the payable) under each scenario given this transaction? Does your company do better with an appreciation or depreciation if you use this hedge? e) (10pts) Now construct a money-market hedge for this exposure. Your firm can borrow pounds at 3.0%, or invest in pounds at 2.8% annual rates. You can borrow US\$ at 3.5% or invest in US\$ at 3.3%. Again these are annually compounded annual rates. Describe exactly how you would construct a money-market hedge. Compare the money market hedge with the futures hedge you constructed above by putting in future values to the table
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


