Question: PLEASE HELP: This project is in PYTHON and needs to read a .txt file to get information and then calculate the information of the rectangles
PLEASE HELP: This project is in PYTHON and needs to read a .txt file to get information and then calculate the information of the rectangles
*****INSTRUCTIONS*****
Write a program that reads a text file and computes the area of a polygon from the contents of the text file. This program needs to be written in python, the goal is:
- For each polygon/rectangle (so the code below Polygon.Py, Rectangle.py, and their roots) create the appropriate object, request that each object report its vertices, its perimeter, and its area.
-For the code (that I will paste below), need to modify the Polygon.py code to add a function to compute the area
- modify the constructor in the Polygon.py code to accept a list of vertices as opposed to hard coding the vertices.
-modify the Rectangle code so that length and width are computed, rather than assigned, and so that the area is computed with an improved function for computing the area: 2*(length*width).
Below is what will go inside of the data.txt file. P is a polygon, R is a rectangle.
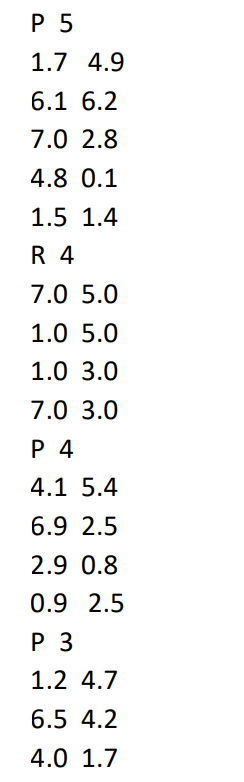
The full code (with syntax and highlighting) can be viewed here: https://pastebin.com/wGSF7KJs
******************************************************************************************
CODE:
******************************************************************************************
#####POINT.PY
######################
######################
Import math
class Point:
def __init__(self,x=0.0,y=0.0):
self.x=x
self.y=y
def __str__(self):
# return(str(self.x) + " " + str(self.y))
return ("{:.2f}".format(self.x) + " " + "{:.2f}".format(self.y))
def translate(self,a=0.0,b=0.0):
self.x=self.x+a
self.y=self.y+b
def scale(self,sx=0.0,sy=0.0):
self.x=self.x*sx
self.y=self.y*sy
def rotate(self, theta_in_degrees=0.0):
theta = (2.0 * 3.14159 / 360.0)*theta_in_degrees
old_x=self.x
old_y=self.y
self.x = (old_x*math.cos(theta)+old_y*math.sin(theta))
self.y = (-old_x*math.sin(theta)+old_y*math.cos(theta))
def distance(self, otherpoint):
a = self.x - otherpoint.x
b = self.y - otherpoint.y
return math.sqrt(a ** 2 + b ** 2)
# return ("{:.2f}".format(math.sqrt(a**2 + b**2)))
######POINTROOT.PY
#####################
#####################
from Point import Point
mypoint=Point(5.0,6.0)
print(mypoint)
print ("Translating MyPoint by (2.0,3.0) ...")
mypoint.translate(2.0,3.0)
print(mypoint)
print ("Translating MyPoint by (-2.0,-3.0) ...")
mypoint.translate(-2.0,-3.0)
print(mypoint)
print ("Scaling MyPoint by (1/2,1/2) ...")
mypoint.scale(0.5,0.5)
print(mypoint)
print ("Scaling MyPoint by (1/2,1/2) ...")
mypoint.scale(2.0,2.0)
print(mypoint)
print ("Rotating MyPoint by 60 degrees ...")
mypoint.rotate(60.0)
print(mypoint)
print ("Rotating MyPoint by -60 degrees ...")
mypoint.rotate(-60.0)
print(mypoint)
print("----")
print("Testing the distance function")
#That is, the following is a test of a distance function
#that computes distance from mypoint to a another point
mysecondpoint=Point(7.0,9.0)
print("mypoint is ",end="")
print(mypoint)
print("mysecondpoint is ",end="")
print(mysecondpoint)
print("Distance from mypoint to mysecondpoint is: ", \
mypoint.distance(mysecondpoint))
####POLYGON.PY
#################
#################
import math
import itertools
from Point import Point
class Polygon(object):
def __init__(self):
self.vertices=[Point(5.0,6.0),Point(5.0,10.0),Point(11.0,10.0),Point(11.0,6.0)]
def translate(self,a=0.0,b=0.0):
for p in self.vertices:
Point.translate(p,a,b)
def scale(self,sx=0.0,sy=0.0):
for p in self.vertices:
Point.scale(p,sx,sy)
def rotate(self,theta_in_degrees=0.0):
for p in self.vertices:
Point.rotate(p,theta_in_degrees)
def __str__(self):
s=""
for p in self.vertices:
# s=s+" "+str(p.x)+" "+str(p.y)+" "
s=s+" "+"{:.2f}".format(p.x)+" "+"{:.2f}".format(p.y)+" "
return(s)
#using itertools.cycle
def perimeter(self):
""" convert a list of points into a list of distances """
print ("Using Polygon's perimeter routine")
distances = []
circular_buffer = itertools.cycle(self.vertices)
previous_point = next(circular_buffer)
for i in range(len(self.vertices)):
point = next(circular_buffer)
d = point.distance(previous_point)
distances.append(d)
previous_point = point
return "{:.2f}".format(sum(distances))
####POLYGONROOT.PY
#####################
#####################
from Polygon import Polygon
mypolygon=Polygon()
print ("the four vertices of the 'hard-coded' mypolygon...")
print(mypolygon)
print ("translating mypolygon by (2.0,3.0)...")
Polygon.translate(mypolygon,2.0,3.0)
print(mypolygon)
print ("translating mypolygon by (-2.0,-3.0)...")
Polygon.translate(mypolygon,-2.0,-3.0)
print(mypolygon)
print ("scaling mypolygon by (0.5,0.5)...")
Polygon.scale(mypolygon,0.5,0.5)
print(mypolygon)
print ("scaling mypolygon by (2.0,2.0)...")
Polygon.scale(mypolygon,2.0,2.0)
print(mypolygon)
print ("rotating mypolygon by 60 degrees...)")
Polygon.rotate(mypolygon,60)
print(mypolygon)
print ("rotating mypolygon by -60 degrees...")
Polygon.rotate(mypolygon,-60)
print(mypolygon)
print("perimeter of mypolygon is ...")
print(mypolygon.perimeter())
###POLYRECROOT.PY
###################
from Polygon import Polygon
from Rectangle import Rectangle
mypolygon=Polygon()
myrectangle=Rectangle()
print ("perimeter of mypolygon is ...")
print (mypolygon.perimeter())
print ("perimeter of myrectangle is ...")
print (myrectangle.perimeter())
mypolygon=myrectangle
print ("perimeter of mypolygon is ...")
print (mypolygon.perimeter())
####RECTANGLE.PY
###################
from Polygon import Polygon
class Rectangle(Polygon):
def __init__(self):
super(Rectangle,self).__init__()
# self.length=6.0 this is the original code
# self.width=4.0 this is the original code
self.length = in_file.readline(0).split() #this is what I modified
slef.width = in_file.readline(0).split() #what i modified
def perimeter(self):
print ("Using Rectangle's perimeter routine")
return 2*self.length+2*self.width
####RECTANGLEROOT.PY
#######################
from Rectangle import Rectangle
######MODIFIED
myrectangle = Rectangle()
in_file = open(project01data.txt)
line = in_file.readline()
###### /MODIFY
print ()
print ("the four vertices of the 'hard-coded' myrectangle are ...")
print(myrectangle)
print ("the manually computed length of myrectangle is ... 6")
print ("the manually computed width of myrectangle is ... 4")
print ()
print ("translating myrectangle by (2.0,3.0)...")
Rectangle.translate(myrectangle,2.0,3.0)
print(myrectangle)
print ("translating myrectangle by (-2.0,-3.0)...")
Rectangle.translate(myrectangle,-2.0,-3.0)
print(myrectangle)
print ("scaling myrectangle by (0.5,0.5)...")
Rectangle.scale(myrectangle,0.5,0.5)
print(myrectangle)
print ("scaling myrectangle by (2.0,2.0)...")
Rectangle.scale(myrectangle,2.0,2.0)
print(myrectangle)
print ("rotating myrectangle by 60 degrees...)")
Rectangle.rotate(myrectangle,60)
print(myrectangle)
print ("rotating myrectangle by -60 degrees...")
Rectangle.rotate(myrectangle,-60)
print(myrectangle)
print ("perimeter of myrectangle is ...")
print (myrectangle.perimeter())
.9 .5 2814 6201 71085 0000 458 5202 1999 727 441 P1674-R7117P4620P-64
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


