Question: please help to answer the question within a hour please. please help Question 5 [20 marks] Carbon dioxide gas (A) is absorbed into concentrated aqueous
please help to answer the question within a hour please. please help
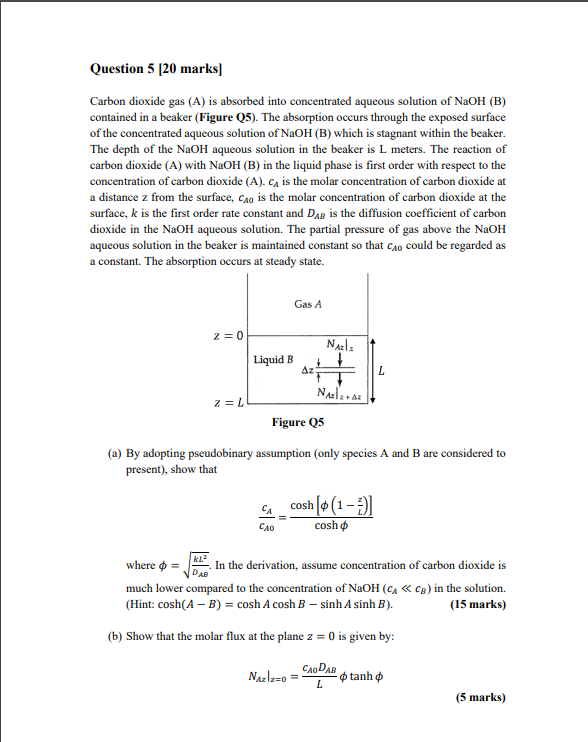
Question 5 [20 marks] Carbon dioxide gas (A) is absorbed into concentrated aqueous solution of NaOH (B) contained in a beaker (Figure Q5). The absorption occurs through the exposed surface of the concentrated aqueous solution of NaOH (B) which is stagnant within the beaker. The depth of the NaOH aqueous solution in the beaker is L meters. The reaction of carbon dioxide (A) with NaOH (B) in the liquid phase is first order with respect to the concentration of carbon dioxide (A). Ci is the molar concentration of carbon dioxide at a distance z from the surface, Cho is the molar concentration of carbon dioxide at the surface, k is the first order rate constant and Das is the diffusion coefficient of carbon dioxide in the NaOH aqueous solution. The partial pressure of gas above the NaOH aqueous solution in the beaker is maintained constant so that Cao could be regarded as a constant. The absorption occurs at steady state. Gas A z = 0 Nal: + Liquid B Az L NAS 2=L Figure 25 (a) By adopting pseudobinary assumption (only species A and B are considered to present), show that cosh [(1-2) cosho CAO ku? where o = In the derivation, assume concentration of carbon dioxide is much lower compared to the concentration of NaOH (CAC) in the solution. (Hint: cosh(A - B) = cosh A cosh B - sinh A sinh B). (15 marks) (b) Show that the molar flux at the plane z = 0 is given by: Nazlz=0 = CAODAB - tanh L
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


