Question: Please help to figure out Make sure you read and understand the directions before beginning thank you fTheorem 2 (The Principle of Mathematical Induction) For
Please help to figure out
Make sure you read and understand the directions before beginning
thank you
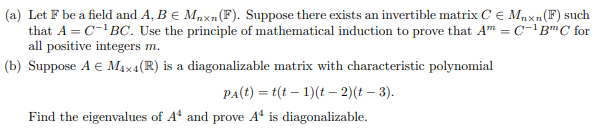

\fTheorem 2 (The Principle of Mathematical Induction) For each positive integer n, let P(n) be a statement. If (1) P (1) is true and (2) the implication If P(k), then P(k + 1). is true for every positive integer k, then P(n) is true for every positive integer n. Proof Assume, to the contrary, that the theorem is false. Then conditions (1) and (2) are satisfied, but there exist some positive integers n for which P(n) is a false statement. Let S = {n EN : P(n) is false). Mathematical Induction Since S is a nonempty subset of N, it follows by the Well-Ordering Principle that S con- tains a least element s. Since P (1) is true, 1 @ S. Thus s 2 2 and s - 1 e N. Therefore, s - 1 @ S and so P(s - 1) is a true statement. By condition (2), P(s) is also true and so s @ S. This, however, contradicts our assumption that s e S. Now how could we conclude that therefore s-1 is not an element of S. I understand that if s=2, then s-1 would not be a element of S since p(1) is true, however what if s is larger then 2 how could I be sure that it s-1 would not be an element of S
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


